Summary
This experiment investigated the possibility that chlordiazepoxide (CDP) has unique properties that account for state dependent learning, and prevention of conflict-induced behavior fixations.
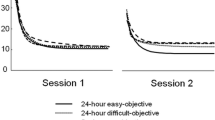
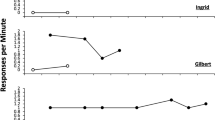
One group of rats were given a discrimination problem on a Lashley jumping stand, but on even days all responses were punished. Another group were treated the same way except than on even days all responses were rewarded. Each of these groups were subdivided, half of the Ss were given CDP on even days, the other half no drug. The results showed that punishment on even days for the response to be learned disrupted learning more than reward for responses that were to be avoided. CDP practically eliminated these disruptive effects and aided learning for the punishment group, but led to a slower rate of learning for the reward group. These findings confirmed the hypothesis that CDP attenuates the effects of negative incentives, and that this property accounts for the drug's cue value in discrimination learning and for its fixation prevention characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bindra, D., and H. Reichert: The nature of dissociation: Effects of transitions between normal and barbiturate induced states on reversal learning and habituation. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 330–344 (1967).
Brown, A., R. S. Feldman, and J. W. Moore: Conditional discrimination learning based on chlordiazepoxide: Dissociation or cue ? J. comp.physiol. Psychol. (in press) (1968).
Cook, L.: Effects of drugs on operant conditioning. In H. Steinberg (Ed.): Animal behavior and drug action, pp. 23–43. London: Churchill 1964.
—, and R. T. Kelleher: Drug effects on the behavior of animals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 96, 315–335 (1962).
Feldman, R. S.: The prevention of fixations with chlordiazepoxide. J. Neuro-psychiat. 3, 254–259 (1962).
—: Further studies on assay and testing on fixation-preventing psychotropic drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 6, 130–142 (1964).
—, and K. F. Green: Effects of chlordiazepoxide on fixated behavior in squirrel monkeys. J. Psychopharmacol. 1, 37–45 (1966).
— —: Antecedents to behavior fixations. Psychol. Rev. 74, 250–271 (1967).
—, and W. T. Liberson: The effect of reserpine on behavior fixation in rats. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 53, 483–487 (1960).
Geller, I.: Use of approach avoidance behavior (conflict) for evaluating depressant drugs. In J. H. Nodine, and J. H. Moyer (Eds.): Psychosomatic Medicine, pp. 267–274. Philadelphia: Lea and Febiger 1962.
—, J. T. Kulak, and J. Seifter: The effects of chlordiazepoxide and chlorpromazine on a punishment discrimination. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 3, 374–385 (1962).
Heise, G. A., and E. Boff: Continuous avoidance as a base-line for measuring behavioral effects of drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 3, 264–282 (1962).
Lewis, E. M., and R. S. Feldman: The depressive effect of chlordiazepoxide on a negative incentive. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 6, 143–150 (1964).
Liberson, W. T., R. S. Feldmam, and P. Ellen: The behavioral analysis of the effects of meprobamate as compared with other tranquillizers and ECS. In: Neuropsychopharmacology, Vol. 1, pp. 351–357. Bradley, P. B., Deniker, P., Radouco-Thomas, C. (Eds.). New York: Elsevier 1959.
Lubar, J. L., and A. A. Perachio: One-way and two-way learning and transfer of an active avoidance response in normal and cingulectomized cats. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 60, 46–52 (1965).
Overton, D. A.: State-dependent or “dissociated” learning produced with pentobarbital. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 57, 3–12 (1964).
—: State dependent learning produced by depressant and atropine-like drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 6–31 (1966).
Sachs, E., M. Weingarten, and N. W. Klein: Effects of chlordiazepoxide on the acquisition of avoidance learning and its transfer to the normal state and other drug conditions. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 9, 17–30 (1966).
Scheckel, C. L., and H. J. McConnell: Response latency as a measure of approach and approach-avoidance behavior in the rat. Paper presented at EPA meeting. New York City 1963.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This experiment was supported by Research Grant MH-01061, United States Public Health Service. Chlordiazepoxide was generously supplied by HoffmannLaRoche Inc., Nutley, New Jersey. The animals were run by Pieper Toyama and Nancy F. Feldman. The statistical analysis was done by Dennison Smith. Nancy F. Feldman also composed and drew the figures.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feldman, R.S. The mechanism of fixation prevention and “Dissociation” learning with chlordiazepoxide. Psychopharmacologia 12, 384–399 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401344
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401344