Abstract
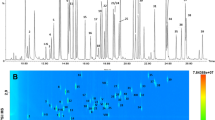
The extensive use of the broad range of pesticides employed to maintain golf courses has prompted serious environmental concerns in Japan since courses tend to be located in mountainous regions, often in close proximity to virgin water sources. Since older empirical methods are not appropriate for substance identification and determination of substance concentrations on the ppb order, gas chromatographyquadrupole mass spectrometry (GC/QPMS) can be employed. A simple extraction of 500 ml of drainage pond water gives a sample which allows identification of pesticides with quantitation on the ppb order using selected ion monitoring (SIM). A sample of drainage pond water from a golf course revealed fenitrothion, funitrothion, chlorothalonil and isoprothiolane in concentrations of 120.1, 20.7, 45.6 and 130.5 ppb, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Mainchi Shinbun, 25th Feb. 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murata, T., Takahashi, S. Identification of residual pesticides in water by GC/QPMS. Environ Monit Assess 19, 55–62 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401297
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401297