Summary
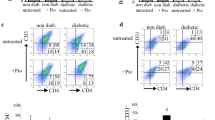
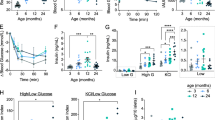
A single dose of cyclophosphamide (250 mg/kg) is known to synchronize and accelerate development of diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. We have reported previously that cyclophosphamide treatment of 10-week-old female non-obese diabetic mice induces a shift from T-helper type 2 to T-helper type 1 activity in islet lesions. We now show that this shift in regulatory T-cell function is preceded by the expression of interleukin-12 in the islets as well as in the spleen. In the spleen macrophages were identified as the interleukin-12 expressing cell type. At the same time there was little induction of tumour necrosis factor alpha gene expression by macrophages. Since interleukin-12 is well known to drive T-helper cell type 1 responses we assume that interleukin-12 released by macrophages mediates the accelerating effect of cyclophosphamide on islet inflammation in non-obese diabetic mice. mRNA expression of the p40 chain of interleukin-12 in response to cyclophosphamide was not seen in macrophages of Balb/c mice and thus represents an immune abnormality of non-obese diabetic mice favouring T-helper type 1 reactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CY:
-
Cyclophosphamide
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- G3PDH:
-
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- IFN-γ:
-
interferon-gamma
- IL-4:
-
interleukin-4
- IL-12:
-
interleukin-12
- NK cells:
-
natural killer cells
- NOD:
-
non-obese diabetic
- PSL:
-
phosphor stimulated luminescence
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
- Th1/2:
-
T-helper cell type 1/2
- TNFα:
-
tumour necrosis factor alpha
References
Rothe H, Faust A, Schade U et al. (1994) Cyclophosphamide treatment of female non-obese diabetic mice causes enhanced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and interferon-gamma, but not interleukin-4. Diabetologia 37: 1154–1158
Trinchieri G (1994) Interleukin-12: a cytokine produced by antigen-presenting cells with immunregulatory functions in the generation of T-helper cells type I and cytotoxic lymphocytes. Blood 48: 4008–4027
Harding FA, McArthur JG, Gross JA, Raulet DH, Allison JP (1992) CD28 mediated signalling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T cell clones. Nature 356: 607–609
Linsey PS, Ledbetter JA (1993) The role of CD28 receptor during T cell responses to antigen. Annu Rev Immunol 11: 191–196
Lee K-U, Amano K, Yoon J-W (1988) Evidence for initial involvement of macrophages in development of insulitis in NOD mice. Diabetes 37: 989–991
Rabinovitch A, Sorensen O, Suarez-Pinzon WL, Power RF, Rajotte RV, Bleackley RC (1994) Analysis of cytokine mRNA expression in syngenic islet grafts of NOD mice: interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma mRNA expression correlate with graft rejection and interleukin 10 with graft survival. Diabetologia 37: 833–845
Bette M, Jin SC, Germann MKH, Weihe E, Rüde E, Fleischer B (1994) Differential expression of mRNA encoding interleukin-12 p35 and p40 subunits in situ. Eur J Immunol 24: 2435–2440
Trembleau S, Penna G, Bosi E, Mortara A, Gately MK, Adorini L (1995) Interleukin 12 administration induces T helper type I cells and accelerates autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. J Exp Med 181: 817–821
Pennline KJ, Roque-Gaffney E, Monahan M (1994) Recombinant human IL-10 prevents the onset of diabetes in the nonobese diabetic mouse. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 71: 169–175
Kolb-Bachofen V, Kolb H (1989) A role for macrophages in the pathogenesis of type I diabetes. Autoimmunity 3: 145–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothe, H., Burkart, V., Faust, A. et al. Interleukin-12 gene expression is associated with rapid development of diabetes mellitus in non-obese diabetic mice. Diabetologia 39, 119–122 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00400422
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00400422