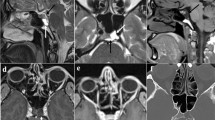
Summary
Wedge-like thickening and enhancement of the septum pellucidum or alveus of hippocampus nearly always signifies direct invasion of the septum (or alveus) by an intraaxial mass. Benign, extraaxial juxtaseptal masses rarely exhibit such change.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schunk H, Bladin P, Davies H (1963) The widened septum pellucidum in hemispheric gliomas. Radiology 80:224–231
Bull J (1967) The corpus callosum. Clin Radiol 18:2–18
Zatz LM, Hanbery JW, Gifford D, Belza J (1967) The diagnosis of tumors of the splenium of the corpus callosum. AJR 101: 130–140
Tönnis W, Brandt P, Walter W (1960) The roentgenological diagnosis of tumors of the corpus callosum. J Neurosurg 17: 183–196
Howieson J, Bull JWD (1966) Radiologic detection of astrocytoma involving the corpus callosum. AJR 98:575–578
Weidner W, Jannetta PJ, Saul R, Hanafee W (1965) The neuroradiology of tumors of the corpus callosum. Neurology 15: 1071–1077
Osborn AG, Poole GJ (1975) Angiographic signs of corpus callosal tumors: a reappraisal. Radiology 115:97–105
Pehov J (1970) Quasi-hydrocephalic arteriovenous dissonance in corpus callosum tumors. Neuroradiology 1:228–232
Lowman RM, Shapiro R, Collins LC (1948) The significance of the widened septum pellucidum. AJR 59:177–196
Wolf A, Bamford TE (1935) Cavum septi pellucidi and cavum vergae. Bull Neurol Inst New York 4:294–309
Thompson IM (1932) On cavum septi pellucidi. J Anat 67:59–77
Naidich TP (1979) Deep and incisural masses. In: Syllabus for the categorical course of neuroradiology, presented at the Annual Meeting of The American Roentgen Ray Society, Toronto, Canada 24–30 March 1979, pp 133–179
El Gammal T, McDaniel FE (1979) The target sign: A CT finding in tumors of the corpus callosum. J Comput Assist Tomogr 3:533–535
Wing SD, Osborn AG (1977) Normal and pathologic anatomy of the corpus callosum by computed tomography. Comput Axial Tomogr 1:183–192
Pendergrass EP, Hodes PJ (1935) Dilatations of the cavum septi pellucidi and cavum vergae. Ann Surg 101:269–295
Farruggia S, Babcock DS (1981) The cavum septi pellucidi: its appearance and incidence with cranial ultrasonography in infancy. Radiology 139:147–150
Shaw CM, Alvord EC (1969) Cava septi pellucidi et vergae: Their normal and pathological state. Brain 92:213–223
Schwidde JT (1952) Incidence of cavum septi pellucidi and cavum vergae in 1032 human brains. Arch Neurol Psychiatr 67: 625–633
Maxwell HP (1946) Incidence of interhemispheric extension of glioblastoma multiforme through the corpus callosum. J Neurosurg 3:54–57
Page LK, Clark R (1981) Gliomas of the septal area in children. Neurosurgery 8:651–655
Altman J (1966) Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis: II. A longitudinal investigation of the kinetics, migration and transformation of cells incorporating tritiated thymidine in infant rats, with special reference to postnatal neurogenesis in some brain regions. J Comp Neurol 128: 431–473
Altman J (1966) Proliferation and migration of undifferentiated precursor cells in the rat during postnatal gliogenesis. Exp Neurol 16:263–278
Clark RG, Milhorat TH (1970) Experimental hydrocephalus: Part 3. Light microscopic findings in acute and subacute obstructive hydrocephalus in the monkey. J Neurosurg 32: 400–413
French JD, Bucy PC (1948) Tumors of the septum pellucidum. J Neurosurg 5:433–449
Globus JH, Kuhlenbeck H (1944) The subependymal cell plate (matrix) and its relationship to brain tumors of the ependymal type. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 3:1–35
Hopewell JW (1975) The subependymal plate and the genesis of gliomas. J Pathol 117:101–103
Lewis PD (1968) Mitotic activity in the primate subependymal layer and the genesis of gliomas. Nature 217:974–975
Privat A (1975) Postnatal gliogenesis in the mammalian brain. Int Rev Cytol 40:281–323
Rydberg E (1932) Cerebral injury in new-born children consequent on birth trauma; With an inquiry into the normal and pathological anatomy of the neuroglia. Chapter II. On the normal microscopical anatomy of the brain of the fetus especially of the glia tissue. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand [Suppl] 10:8–47
Schwarz H, Goolker P, Globus JH (1932) The normal histology of infants' brains. Am J Dis Child 43:889–913
Schunk H (1963) Congenital dilatations of the septum pellucidum. Radiology 81:610–617
Osborn AB, Daines JH, Wing SD (1978) The evaluation of ependymal and subependymal lesions by cranial computed tomography. Radiology 127:397–401
McGeachie RB, Gold HA, Latchaw RE (1977) Periventricular spread of tumor demonstrated by computed tomography. Radiology 125:401–410
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russell, E.J., Naidich, T.P. The enhancing septal/alveal wedge: A septal sign of intraaxial mass. Neuroradiology 23, 33–40 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399703
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399703