Abstract
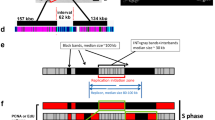
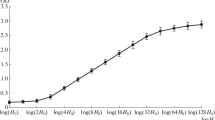
DNA replication in Chironomus larvae that 7 days earlier passed the red-head stage is investigated. When pulse-labelled polytene chromosomes are lysed at 25 ° C there is an enzymatic release of double-stranded DNA replication intermediates from the chromosomes. The released DNA molecules can be divided into two populations by gel electrophoresis in 1.5% agarose gels, one population is centered around slice 18 and the other population is centered around slice 27. Moreover, it is possible to chase with cold thymidine the population of labelled DNA molecules centered around slice 27 into the population centered around slice 18. The intermediates are after a time-lag joined together to produce a high molecular weight DNA which is not released from the chromosomes during cell lysis. Furthermore, in animals treated with 5-fluorodeoxyuridine the intermediates are joined together to produce a double-stranded DNA with the size expected to replicons. In contrast it is known that in late fourth instar larvae there is no subfractionation in 1.5% agarose of the DNA replication intermediates. This indicates that there is a difference in the formation of intermediates in the same tissue at two developmental stages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Darrow, J., Clever, U.: Chromosome activity and cell function in polytenic cells. III. Growth and replication. Develop. Biology 21, 331–348 (1970)
Guy, A., Taylor, J.H.: Actinomycin D inhibits initiation of DNA replication in mammalian cells. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 75, 6088–6092 (1978)
Helling, R., Goodman, H., Boyer, H.: Analysis of endonuclease Eco RI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J. Virol. 14, 1235–1244 (1974)
Lönn, U.: Isolation and partial characterization of replication intermediates in Chironomus polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 77, 29–40 (1980a)
Lönn, U.: Similar size of the replicons in Chironomus polytene chromosomes at two developmental stages. J. Cell Sci. 46, 387–397 (1980b)
Lönn, U.: Double-stranded DNA with the size expected of replicons can be released from Chironomus polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 81, 641–653 (1981)
Lönn, U., Edström, J.-E.: Movements and associations of ribosomal subunits in a secretory cell during growth inhibition by starvation. J. Cell Biol. 73, 696–704 (1977)
Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation, 4. (W. Beermann, ed.). Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Springer 1972
Ringborg, U., Rydlander, L.: Nucleolar-derived ribonucleic acid in chromosomes, nuclear sap and cytoplasm of Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells. J. Cell Biol. 51, 355–368 (1971)
Taylor, J.H.: Replication of DNA in mammalian chromosomes: Isolation of replicating segments. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 70, 1083–1087 (1973)
Thomas, M., Davies, R.: Studies on the cleavage of Bacteriophage lambda DNA with Eco RI restriction endonuclease. J. molec. Biol. 91, 315–328 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lönn, U. The double-stranded DNA replication intermediates formed in Chironomus polytene chromosomes consist of two populations. Chromosoma 84, 221–229 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399133
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00399133