Abstract
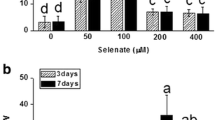
Experiments were conducted in order to specify the reductants responsible for the carbon dioxide fixation of the symbiotic sulfur bacteria in the gutless marine oligochaete Phallodrilus leukodermatus (Annelida) from shallow calcareous sediments in Bermuda. Carbon dioxide-uptake rates were suppressed by S= and stimulated by S2O3 =. Individuals which hosted bacteria containing reserve energy substances maintained a high short-term CO2-uptake activity, while bacteria in worm homogenates and in worms treated with an antibiotic (Baypen) did not show any significant metabolic activity. Absolute uptake rates in P. leukodermatus were usually considerably higher than those reported for other animals harbouring prokaryotic sulfuroxidizing symbionts. Utilization of thiosulfate rather than sulfide is compatible with the preferred occurrence of the worms around the redox discontinuity layer and has been confirmed in other “thiobiotic” animals. Sulfur stored in the symbiotic bacteria appears to be oxidized to sulfate and be excreted when the worms are held under energy-limited conditions. The data emphasize the complexity of the possible metabolic pathways involved in the oxidation of reduced-sulfur compounds by bacterial symbionts in marine invertebrates.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Almgren, T., Hagström, A. (1974). The oxidation rate of sulfide in seawater. Wat. Res. 8: 395–400
Belkin, S., Nelson, D. C., Jannasch, H. W. (1986). Symbiotic assimilation of CO2 in two hydrothermal vent animals, the mussel Bathymodiolus thermophilus and the tube worm Riftia pachyptila. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 170: 110–121
Cavanaugh, C. M. (1983). Symbiotic chemoautotrophic bacteria in marine invertebrates from sulphide-rich habitats. Nature, Lond. 302: 58–61
Cavanaugh, C. M., Levering, P. R., Maki, J. S., Mitchell, R., Lidstrom, M. E. (1987). Symbiosis of methylotrophic bacteria and deep-sea mussels. Nature, Lond. 325: 346–348
Childress, J. J., Fisher, C. R., Brooks, J. M., Kennicutt, II, M. C., Bidigare, R., Anderson, A. E. (1986). A methanotrophic marine mollusean (Bivalvia, Mytilidae) symbiosis: mussels fueled by gas. Science, N.Y. 233: 1306–1308
Childress, J. J., Mickel, T. J. (1982). Oxygen and sulfide consumption rates of the vent clam Calyptogena pacifica. Mar. Biol. Lett. 3: 73–80
Cuhel, R. L., Taylor, C. D., Jannasch, H. W. (1981). Assimilatory sulfur metabolism in marine microorganisms: characteristics and regulations of sulfate transport in Pseudomonas halodurans and Altermonas luteo-violaceus. J. Bact. 147: 340–349
Dando, P. R., Southward, A. J. (1986). Chemoautotrophy in bivalve molluscs of the genus Thyasira. J. mar. biol. Ass. U. K. 66: 915–929
Dando, P. R., Southward, A. J., Southward, E. C., Barrett, R. L. (1986). Possible energy sources for chemoautotrophic prokaryotes symbiotic with invertebrates from a Norwegian fjord. Ophelia 26: 135–150
Dando, P. R., Southward, A. J., Southward, E. C., Terwilliger, N. B., Terwilliger, R. C. (1985). Sulphur-oxidizing bacteria and haemoglobin in gills of the bivalve mollusc Myrtea spinifera. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 23: 85–98
Felbeck, H. (1983). Sulfide oxidation and carbon fixation by the gutless clam Solemya reidi: an animal-bacteria symbiosis. J. comp. Physiol. (Sect. B) 152: 3–11
Felbeck, H., Liebezeit, G., Dawson, R., Giere, O. (1983). CO2 fixation in tissues of marine oligochaetes (Phallodrilus leukodermatus and P. planus) containing symbiotic, chemoautotrophic bacteria. Mar. Biol. 75: 187–191
Fenchel, T. (1969). The ecology of marine microbenthos. IV. Structure and function of the benthic ecosystem, its chemical and physical factors and the microfauna communities with special reference to the ciliate Protozoa. Ophelia 6: 1–182
Fenchel, T. M., Riedl, R. J. (1970). The sulfide system: a new biotic community underneath the oxidized layer of marine sand bottoms. Mar. Biol. 7: 255–268
Giere, O. (1985). The gutless marine tubificid Phallodrilus planus, a flattened oligochaete with symbiotic bacteria. Results from morphological and ecological studies. Zoologica Scr. 14: 279–286
Giere, O., Felbeck, H., Dawson, R., Liebezeit, G. (1984). The gutless oligochaete Phallodrilus leukodermatus Giere, a tubificid of structural, ecological and physiological relevance. Hydrobiologica 115: 83–89
Giere, O., Langheld, C. (1987). Structural organisation, transfer and biological fate of endosymbiotic bacteria in gutless oligochaetes. Mar. Biol. 93: 641–650
Giere, O., Liebezeit, G., Dawson, R. (1982). Habitat conditions and distribution pattern of the gutless oligochaete Phallodrilus leukodermatus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 8: 291–299
Hammen, C. S. (1966). Carbon dioxide fixation in marine invertebrates. V. Rate and pathway in the oyster. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 17: 289–296
Howarth, R. W., Giblin, A., Gale, J., Peterson, B. J., Luther, III, G. W. (1983). Reduced sulfur compounds in the pore waters of a New England salt marsh. Ecol. Bull., Stockholm 35: 135–152
Howarth, R. W., Teal, J. M. (1980). Energy flow in a salt marsh ecosystem: the role of reduced inorganic sulfur compounds. Am. Nat. 116: 862–872
Jannasch, H. W., Wirsen, C. O. (1985). The biochemical versatility of chemosynthetic bacteria at deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Bull. biol. Soc. Wash. 6: 325–334
Jannasch, H. W., Wirsen, C. O., Nelson, D. C., Robertson, L. A. (1985). Thiomicrospira crunogena sp. nov., a colorless, sulfuroxidizing bacterium from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Int. J. system. Bact. 35: 422–424
Jørgensen, B. B. (1982). Ecology of the bacteria of the sulphur cycle with special reference to anoxic-oxic interface environments. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. (Ser. B) 298: 543–561
Jones, M. L. (ed.) (1985). Hydrothermal vents of the eastern Pacific: An overview. Bull. biol. Soc. Wash. 6: 1–545
Kelly, D. P. (1982). Biochemistry of the chemolithotrophic oxidation of inorganic sulfur. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. (Ser. B) 298: 499–528
Morris, B., Barnes, J., Brown, F., Markham, J. (1977). The Bermuda marine environment. A report of the Bermuda inshore waters investigations 1976–1977. Spec. Publs Bermuda biol. Stn Res. 15: 1–120
Powell, M. A., Somero, G. N. (1986). Adaptations to sulfide by hydrothermal vent animals: sites and mechanism of detoxification and metabolism. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 171: 274–290
Schmaljohann, R., Flügel, H. J. (1987). Methane-oxidizing bacteria in Pogonophora. Sarsia 72: 91–98
Slepecky, R. A., Law, J. H. (1961). A rapid spectrophotometric assay of α-, β-unsaturated acid and β-hydroxy acid. Analyt. Chem. 32: 1697–1699
Southward, A. J., Southward, E. C., Dando, P. R., Barrett, R. L., Ling, R. (1986). Chemoautotrophic function of bacterial symbionts in small Pogonophora. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 66: 415–437
Southward, A. J., Southward, E. C., Dando, P. R., Rau, G. H., Felbeck, H., Flügel, H. (1981). Bacterial symbionts and low 13C/12C ratios in tissues of Pogonophora indicate unusual nutrition and metabolism. Nature, Lond. 293: 616–620
Steudel, R. (1985). Neue Entwicklungen in der Chemie des Schwefels und des Selens. Nova Acta Leopoldina 59 (264): 231–246
Steudel, R., Holdt, G., Göbel, T., Hazeu, W. (1987). Chromatographische Trennung höherer Polythionate SnO6 2- (n=3...22) und deren Nachweis in Kulturen von Thiobacillus ferrooxidans; molekulare Zusammensetzung bakterieller Schwefelausscheidungen. Angew. Chem. 99: 143–146
Steudel, R., Holdt, G., Nagorka, R. (1986). On the autoxidation of aqueous sodium polysulfide. Z. Naturf. (Sect. B) 41: 1519–1522
Tabatabai, M. A. (1974). A rapid method for determination of sulfate in water samples. Envir. Lett. 7: 237–243
Tuttle, J. H. (1985). The role of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria at deepsea hydrothermal vents. Bull. biol. Soc. Wash. 6: 335–344
Tuttle, J. H., Jannasch, H. W. (1977). Thiosulfate stimulation of microbial dark assimilation of carbon dioxide in shallow marine environments. Microb. Ecol. 4: 9–25
Tuttle, J. H., Wirsen, C. O., Jannasch, H. W. (1983). Microbial activities in the emitted hydrothermal waters of the Galápagos Rift vents. Mar. Biol. 73: 293–299
Vetter, R. D., Wells, M. E., Kurtsman, A. L., Somero, G. N. (1987). Sulfide detoxification by the hydrothermal vent crab Bythograea thermydron and other decapod crustaceans. Physiol. Zoöl. 60: 121–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giere, O., Wirsen, C.O., Schmidt, C. et al. Contrasting effects of sulfide and thiosulfate on symbiotic CO2-assimilation of Phallodrilus leukodermatus (Annelida). Mar. Biol. 97, 413–419 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397771
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397771