Abstract
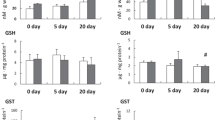
Zinc and copper levels in the gills, kidney and intestine of the dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula L. collected in a 80 to 120 m deep zone close to Barcelona (Spain) during the months of February–March 1981 were measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry after subacute (10 ppm Zn for 3 wk) and acute (80 ppm Zn for 24 h) treatment with ZnSO4. Individuals exposed to 80 ppm Zn accumulated Zn in the gills, whereas no significant increase in Zn content was found in the kidney or intestine. No differences in the Cu content of any of these tissues were found. Dogfish exposed to 10 ppm Zn for 3 wk displayed an increase in Zn content of the gills, kidney and intestine. An increase in the Cu concentration of the gills was also recorded which may suggest that Cu, and hence Zn and other heavy metals, are excreted via the gills when the kidney and intestine are overloaded. A light-microscopic study of the gill epithelium was carried out on dogfish treated with 10 ppm Zn for 3 wk, 80 ppm Zn for 24 h and 175 ppm Zn for 14 h, and chloride cell response was quantified. Chloride cells increased in number after each treatment, even appearing in the secondary lamellae following treatment with 175 ppm Zn. It is suggested that the chloride cell may excrete bivalent ions when dogfish are exposed to an excess of bivalent salts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Ahuja, S. K.: Chloride-cell and mucus cell response to chloride and sulphate enriched media in the gills of Gambusia affinis affinis (Baird and Girard) and Catla catla (Hamilton). J. exp. Zool. 173, 231–250 (1970)
Baker, J. T. P.: Histological and electron microscopical observations on copper poisoning in the winter flounder (Pseudopleuronectes americanus). J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 26, 2785–2793 (1969)
Bouquegneau, J. M.: Evidence for the protective effect of metallothioneins against inorganic mercury injuries to fish. Bull envir. Contam. Toxicol. 23, 218–219 (1979)
Bryan, G. W.: The effects of heavy metals (other than mercury) on marine and estuarine organisms. Proc. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 177, 389–410 (1971)
Bryan, G. W.: Bioaccumulation of marine pollutants. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 286, 483–505 (1979)
Conte, F. P. and D. H. Lin: Kinetics of cellular morphogenesis in gill epithelium during seawater adaptation of Oncorhynchus (Walbaum). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 23, 945–957 (1967)
Coombs, T. L.: Heavy metal pollutants in the aquatic environment. In: Animals and environmental fitness, pp 283–302. Ed. by R. Gilles. Oxford and New York: Pergamon Press 1980
Crespo, S.: Efectes de la contaminació per zinc sobre el sistema branquial del peix gat Scyliorhinus canicula L., 200 pp. PhD thesis, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona 1980
Crespo, S. and J. Balasch: Mortality, accumulation and distribution of zinc in the gill system of the dogfish following zinc treatment. Bull envir. Contam. Toxicol. 24, 940–944 (1980a)
Crespo, S. and J. Balasch: Zinc in the gills of the dogfish: differences due to sex and body weight. Revta esp. Fisiol. 36, 189–192 (1980b)
Crespo, S., R. Flos, J. Balasch and G. Alonso: Zinc in the gills of the dogfish (Scyliorhinus canicula L.) related to experimental aquatic zinc pollution. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 63C 261–266 (1979)
Cuadras, J., A. Gimeno, R. Flos and S. Crespo: Levels of copper and zinc in tissues of the hermit crab Dardanus arrosor (Herbst) from the Barcelona coast (Decapoda, Anomura). Crustaceana 40, 79–87 (1981)
Doyle, W. L. and D. Gorecki: The so-called chloride cell of the fish gill. Physiol. Zoöl. 34, 81–85 (1961)
Dunel, S. and P. Laurent Ultrastructure of marine teleost gill epithelia: SEM and TEM study of the chloride cell apical membrane. J. Morph. 165, 175–186 (1980)
Edwards, R. W. and W. M. Brown: Pollution and fisheries: a progress report. Wat. Pollut. Control 66, 63–78 (1967)
Eisler, R. and G. R. Gardner: Acute toxicology to an estuarine teleost of mixtures of cadmium, copper and zinc salts. J. Fish Biol. 5, 131–142 (1973)
Flos, R., A. Caritat and J. Balasch Zinc content in organs of dog-fish (Scyliorhinus canicula L.) subject to sublethal experimental aquatic zinc pollution. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 64C, 77–81 (1979)
George, S. G., E. Carpene, T. L. Coombs, J. Overnell and A. Youngson: Characterization of cadmium-binding proteins from the common mussel Mytilus edulis (L.). Biochim. biophys. Acta 580, 225–233 (1979)
George, S. G. and B. J. S. Pirie: Metabolism of zinc in the mussel Mytilus edulis: a combined ultrastructural and biochemical study. J. mar. biol. Ass. U. K. 60, 575–591 (1980)
George, S. G., B. J. S. Pirie, A. R. Cheyne, T. L. Coombs and P. T. Grant: Detoxication of metals by marine bivalves: an ultrastructural study of the compartmentation of copper and zinc in the oyster Ostrea edulis. Mar. Biol. 45, 147–156 (1978)
George, S. G., B. J. S. Pirie and T. L. Coombs: The kinetics of accumulation and excretion of ferric hydroxide in Mytilus edulis (L.) and its distribution in the tissues. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 23, 71–81 (1976)
Hossler, F. E.: The gill arch of the mullet Mugil cephalus. III. Rate of response to salinity changes. Am. J. Physiol. 238, 160–165 (1980)
Hossler, F. E., J. R. Ruby and T. D. McIlwain: The gill arch of the mullet Mugil cephalus. II. Modification in surface ultrastructure and Na, K-ATPase content during adaptation to various salinities. J. exp. Zool. 208, 399–405 (1979)
Hughes, G. M. and D. E. Wright: A comparative study of the ultrastructure of the water-blood pathway in the secondary lamellae of teleost and elasmobranch fishes —benthic forms. Z. Zellforsch. 104, 478–493 (1970)
Karnaky, K. J., Jr.: Ion-secreting epithelia: chloride cells in the head-region of Fundulus heteroclitus. Am. J. Physiol. 238, 185–198 (1980)
Karnaky, K. J., Jr., S. A. Ernst and C. W. Philpott: Teleost chloride cell. I. response of pupfish Cyprinidon variegatus gill Na, K-ATPase and chloride cell fine structure to various high salinity environments. J. Cell Biol. 70, 144–156 (1976)
Kessel, R. G. and H. W. Beams: Electron microscope studies on the gill filament of Fundulus heteroclitus from seawater and fresh water with special reference to the ultrastructural organization of the chloride cell. J. Ultrastruct. Res 6, 77–87 (1962)
Kito, H., Y. Ose, T. Sato, T. Ishikawa and T. Tazawa: Formation of metallothionein in fish. J. Pharmacobio-Dynamics (Japan) 3, 23–24 (1980)
Laurent, P. et S. Dunel: Relations anatomiques des ionocytes (céllules à chlorure) avec le compartiment veineux branchial: définition de deux types d'épithélium de la branchie de poissons. C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 286, 1447–1450 (1978)
Laurent, P. and S. Dunel: Morphology of gill epithelia in fish. Am. J. Physiol. 238, 147–159 (1980)
Lowe, D. M. and M. N. Moore: The cytochemical distribution of zinc (ZnII) and iron (FeIII) in the common mussel Mytilus edulis and their relationship with lysosomes. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 59, 851–859 (1979)
Maetz, J.: Fish gills: mechanisms of salt transfer in freshwater and seawater. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. (Ser. B) 262, 209–249 (1971)
Masoni, A. et F. Garcia-Romeu: Accumulation et excrétion de substances organiques par les cellules à chlorure de la branchie d'Anguilla anguilla L. adaptée a l'eau de mer. Z. Zellforsch. 133, 389–398 (1972)
Munshi, D.: Chloride cells in the gills of fresh water teleosts. Q. Jl microsc. Sci. 105, 75–90 (1964)
Nakatani, R. E.: Response of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) ingesting zinc-65. In: Proceedings of a Symposium on Disposal of Radioactive Wastes into Seas, Oceans and Surface Waters, pp 809–823. Vienna: International Atomic Agency 1966
Noël-Lambot, F.: Distribution of cadmium, zinc and copper in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Existence of cadmium-binding proteins similar to metallothioneins. Experientia 32, 324–326 (1976)
Noël-Lambot, F., J. M. Bouquegneau, F. Frankenne et A. Disteche: Le role des metallothionéines dans le stockage des métaux lourds chez les animaux marins. Revue int. Océanogr. méd. 49, 13–20 (1978a)
Noël-Lambot, F., C. Gerday, and A. Disteche: Distribution of Cd, Zn and Cu in the liver and gills of the eel Anguilla anguilla with special reference to metallothioneins. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 61C, 177–187 (1978b)
Overnell, J. and T. L. Coombs: Purification and properties of plaice metallothionein, a cadmium-binding protein from the liver of the plaice Pleuronectes platessa. Biochem. J. 183, 277–283 (1979)
Philpott, C. W.: Tubular system membranes of teleost chloride cells: osmotic response and transport sites. Am. J. Physiol. 238, 171–184 (1980)
Shirai, N. and S. Utida: Development and degeneration of the chloride cell during seawater and freshwater adaptation of the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Z. Zellforsch. 103, 247–264 (1970)
Sutherland, J. and C. W. Majors: Internal heavy metal changes as a consequence of exposure of Mytilus edulis, the blue mussel, to elevated external copper levels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 68C, 63–67 (1981)
Viarengo, A., M. Pertica, G. Mancinelli, G. Zanicchi and M. Orunesu: Rapid induction of copper-binding proteins in the gills of metal exposed mussels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 67C, 215–218 (1980)
Wright, D. E.: The structure of the gills of the elasmobranch S. canicula L. Z. Zellforsch. 144, 489–509 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crespo, S., Soriano, E., Sampera, C. et al. Zinc and copper distribution in excretory organs of the dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula and chloride cell response following treatment with zinc sulphate. Mar. Biol. 65, 117–123 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397075
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397075