Abstract
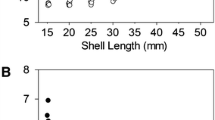
Body zinc concentrations (on a soft parts dry weight basis) in 18 composite collections of mussels (Mytilus edulis) taken from different shore levels within a single mussel bed on the north shore of the Tyne estuary at Tynemouth, on 25 October, 1980, showed highly significant correlations with 4 allometric, size-related factors. A negative correlation was found between body zinc concentration and a flesh condition (FC) index defined as mg dry flesh wt per g dry shell wt. Positive correlations were found between body zinc concentration and width: height ratio, width: length ratio and shell valve inequality index (SVI) defined as the weight of heavier shell valve/weight of lighter shell valve. Unlike earlier observations on a single population taken from a single habitat, this heterogeneous collection showed no significant relationship between body zinc concentration and body size as determined by soft-parts dry weight. Body zinc concentration and allometric ratios were, however, related to position on the shoreline. It is suggested that, where mussels are collected from different habitats, environmental factors probably have a greater influence on body size than age. Therefore, normalization of trace metal concentrations to a standard body weight may not be appropriate where specimens are collected from a variety of habitats. Allometric ratios are related to age, but are independent of absolute size, and may therefore provide a more suitable basis for normalization of trace metal concentration within a monitoring programme.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bayne, B. L.: Mussel watching. Nature, Lond. 275, 87–88 (1978)
Boyden, C. R.: Trace element content and body size in molluscs. Nature, Lond. 251, 311–314 (1974)
Boyden, C. R.: Effect of size upon metal content of shellfish. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57, 675–714 (1977)
Harris, J. E., G. J. Fabris, P. J. Statham and F. Tawfik: Biogeochemistry of selected heavy metals in Western Port, Victoria and use of invertebrates as indicators with emphasis on Mytilus edulis planatus. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 30, 159–178 (1979)
Lobel, P. B.: Bioaccumulation of zinc in Mytilus edulis, 142 pp. Ph. D. thesis, Department of Zoology, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle upon Tyne, England 1981
Lobel, P. B. and D. A. Wright: Relationship between body zinc concentration and allometric growth measurements in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar. Biol. 66, 145–150 (1982)
Lobel, P. B. and D. A. Wright: Frequency distribution of zinc in the common mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Estuaries (Solomons, Md). (In press)
Manly, R. and W. O. George: The occurrence of some heavy metals in populations of the freshwater mussel Anodonta anatina (L.) from the River Thames. Envir. Pollut. 14, 139–154 (1977)
Phillips, D. J. H.: The common mussel Mytilus edulis as an indicator of pollution by zinc, cadmium, lead and copper. I. Effects of environmental variables on uptake of metals. Mar. Biol. 38, 59–69 (1976)
Seed, R.: Ecology. In: Marine mussels; their ecology and physiology. pp 13–65. Ed. by B. L. Bayne. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1976
Simpson, R. D.: Uptake and loss of zinc and lead by mussels (Mytilus edulis) and relationships with body weight and reproductive cycle. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 10, 74–78 (1979)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Contribution No. 1222 of the Center for Estuarine and Environmental Studies of the University of Maryland
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lobel, P.B., Wright, D.A. Total body zinc concentration and allometric growth ratios in Mytilus edulis collected from different shore levels. Mar. Biol. 66, 231–236 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397027
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397027