Summary
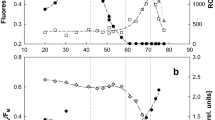
A simplified extraction procedure was used to study the effect of red and far-red light (683 and 712 nm) on the incorporation of 32P and on the distribution pattern of various phosphate fractions in 8 min-experiments under nitrogen. Nitrogen was used to avoid competition for energy-rich phosphate bonds between CO2-fixation and the formation of polyphosphates. The total incorporation of 32P was higher in red than in far-red light, and so was the percentage of the acidsoluble organic phosphate. In the absence of oxygen the incorporation in the dark was rather low and mainly confined to orthophosphate. The ratio between the amount of labelling of polyphosphates and that of acid-soluble organic phosphates was higher in far-red light and in the dark than in red light.
DCMU, even in a nitrogen atmosphere, produced a servre inhibition in red light. This inhibition increased with increasing light intensity. The labelling of organic phosphates was more affected than that of polyphosphates, while orthophosphate incorporation was least inhibited. In far-red light, DCMU exerted little influence except at a rather high light intensity, showing that cyclic photophosphorylation was proceeding alone.
Antimycin A, on the other hand, was almost ineffective in strong red light, but produced a serious inhibition in far-red light. In red light of medium intensity, antimycin effected some inhibition, although much less than DCMU. Under these conditions the effect of the two inhibitors was additive when they were applied together. Labelling of polyphosphates was more sensitive to antimycin A than labelling of acid-soluble organic phosphates.
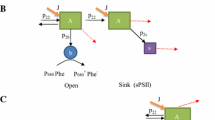
It may be concluded from the data presented that far-red light produces conditions for pure cyclic photophosphorylation, whereas a large proportion of the photophosphorylation taking place in red light in the absence of CO2 and exogenous oxygen might be regarded as “pseudocyclic”. The distribution pattern of the phosphorylated fractions under the different conditions suggests that polyphosphate formation in the light is favoured but not exclusively effected by cyclic photophosphorylation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Baker, A. L., and R. R. Schmidt: Further studies on the intracellular distribution of phosphorus during synchronous growth of Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biochim. biophys. Acta. (Amst.) 82, 336–342 (1964).
French, C. S.: The chlorophylls in vivo and in vitro. In: Handbuch der Planzenphysiologi Bd. 5, 1, S. 252–297. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1960.
Good, N. E.: Inhibitors of the Hill reaction. Plant Physiol. 36, 788–803 (1961).
— and A. H. Brown: The contribution of endogenous oxygen to the respiration of photosynthesizing Chlorella cells. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 50, 544–554 (1961).
Heber, U., K. A. Santarius, W. Urbach u. W. Ullrich: Photosynthese und Phosphathaushalt. Intrazellulärer Transport von 14C- und 32P-markierten Intermediärprodukten zwischen den Chloroplasten und dem Cytoplasma und seine Folgen für die Regulation des Stoffwechsels. Z. Naturforsch. 19b, 576–587 (1964).
Izawa, S., T. N. Connolly, G. D. Winget, and N. E. Good: Inhibition and uncoupling of photophosphorylation in chloroplasts. In: Energy conversion by the photosynthetic apparatus. Brookhaven Symposia in Biol. 19, 169–187 (1966).
Kaden, J.: Der Phosphatstoffwechsel synchronisierter Ankistrodesmuskulturen. Diss. Würzburg 1965.
Kanai, R., S. Miyachi, and S. Miyachi: Light-induced formation and mobilization of polyphosphate „C” in Chlorella cells. Studies on Microalgae and Photosynthetic Bacteria, p. 613–618. Tokyo: The University of Tokyo Press 1963.
—: Einbau von 32P in verschiedene Phosphatfraktionen, besonders Polyphosphate, bei einzelligen Grünalgen (Ankistrodesmus braunii) im Licht und im Dunkeln. Arch. Mikrobiol. 62, 56–71 (1968).
Kuhl, A.: Die Biologie der kondensierten anorganischen Phosphate. Ergebn. Biol. 23, 144–186 (1960).
Lysek, G.: Effect of photophosphorylation and substrate uptake on the metabolism of polyphosphates in Ankistrodesmus braunii. In: Proceedings of the Internat. Congr. of Photosynthesis Research, Freudenstadt (im Druck, 1968).
Miyachi, S., and H. Tamiya: Distribution and turnover of phosphate compounds in growing Chlorella cells. Plant and Cell Physiol. 2, 405–414 (1961).
Nobel, P. S.: A rapid technique for isolating chloroplasts with high rates of endogenous photophosphorylation. Plant Physiol. 42, 1389–1394 (1967).
—: Chloroplast shrinkage and increased photophosrylation in vitro upon illuminating intact plants of Pisum sativum. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 153, 170–182 (1968).
Overbeck, J.: Untersuchungen zum Phosphathaushalt von Grünalgen. VI. Ein Beitrag zum Polyphosphatstoffwechsel des Phytoplanktons. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 76, 276–286 (1963).
Simonis, W., u. W. Urbach: Untersuchungen zur lichtabhängigen Phosphorylierung bei Ankistrodesmus braunii. IX. Beeinflussung durch Phosphatkonzentrationen, Temperatur, Hemmstoffe, Na+-Ionen und Vorbelichtung. In: Studies on Microalgae and Photosynthetic Bacteria, p. 597–611. Tokyo: The University of Tokyo Press 1963.
Tanner, W., and O. Kandler: The lack of relationship between cyclic photophosphorylation and CO2 fixation. In: Proceedings of the Internat. Congr. of Photosynthesis Research, Freudenstadt (im Druck, 1968).
—: Glucose assimilation of Chlorella in monochromatic light of 658 and 711 nm. In: J. B. Thomas, and J. C. Goedheer, Currents in photosynthesis, p. 243–250. Rotterdam: A. D. Donker 1966.
Ullrich, W., W. Urbach, K. A. Santarius, u. U. Heber: Die Verteilung des Orthophosphates auf Plastiden, Cytoplasma und Vakuole in der Blattzelle und ihre Veränderung im Licht-Dunkel-Wechsel. Z. Naturforsch. 20b, 905–910 (1965).
Urbach, W., and W. Simonis: Inhibitor studies on the photophosphorylation in vivo by unicellular algae (Ankistrodesmus) with Antimycin A, HO QNO, Salicylaldoxime and DCMU. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 17, 39–45 (1964).
——: Further evidence for the existence of cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation in vivo by means of desaspidin and DCMU. Z. Naturforsch. 22b, 537–540 (1967).
Vidaver, A.: Separate action spectra for the two photochemical systems of photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 41, 87–89 (1966).
—: Oxygen uptake and evolution following monochromatic flashes in Ulva and action spectrum for system I. Plant Physiol. 40, 7–12 (1965).
Walker, D. A., W. Cockburn, and C. W. Baldry: Photosynthetic oxygen evolution by isolated chloroplasts in the presence of carbon cycle intermediates. Nature (Lond.) 216, 597–599 (1967).
Wintermans, J. F. G. M.: Polyphosphate formation in Chlorella in relation to photosynthesis. Meded. Landbouwhogeschool, Wageningen 55, 69–126 (1955).
Yanagita, T.: Successive determination of the free, acid-labile and residual phosphates in biological systems. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 55, 260–268 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. F. Overbeck zum 70. Geburtstag gewidmet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullrich, W., Simonis, W. Die Bildung von Polyphosphaten bei Ankistrodesmus braunii durch Photophosphorylierung im Rotlicht von 683 und 712 nm unter Stickstoffatmosphäre. Planta 84, 358–367 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396428
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396428