Abstract
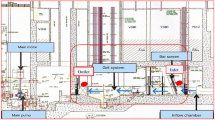
This paper describes a novel technique of measuring ambient hydrogen sulphide (H2S) concentrations simultaneously at several locations around a wastewater treatment plant. A commercially purchased H2S monitor is modified to operate in a ‘static mode’ to enable degree of darkening on pieces of lead acetate tapes to be correlated againts the exposure duration and the ambient H2S concentration of sewage air. The technique can yield mapped contours of time—average H2S concentrations as low as 0.2 ppm. The methodology is exemplified for a wastewater treatment plant in Ipswich, Queensland. Isopleths of H2S concentration obtained at the wastewater site for two different meteorological conditions reveal that high levels of H2S are detected around the plant's inlet structure and primary clarifiers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matthews, P. J. and Boon, A. G.: 1978, ‘Odour Nuisance in Sewerage and Treatment System: Problems and Control’, Water Pollution Control. 77 (2), 248–258.
Reinsch, D. A., Parr-Smith, G. A., and Cornell, M. A.: 1977, ‘Odour Assessment and Control in Sewage Treatment Works’, Proc. of the 7th Fed. Convention, Australian Water and Wastewater Association, Canberra, Australia, September.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koe, L.C.C. Ambient hydrogen sulphide levels at a wastewater treatment plant. Environ Monit Assess 5, 101–108 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396395
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396395