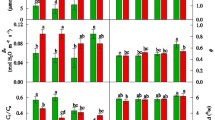
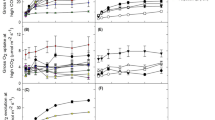
Abstract
The assimilation of 14CO2 into the C4 acids malate and aspartate by leaves of C3, C4 and C3−C4 intermediate Flaveria species was investigated near the CO2 compensation concentration Γ* in order to determine the potential role of phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) carboxylase (EC 4.1.1.31) in reducing photorespiration in the intermediates. Relative to air concentrations of CO2, the proportion of CO2 fixed by PEP carboxylase at Γ* increased in all six C3−C4 intermediate species examined. However, F. floridana J.R. Johnston and F. ramosissima Klatt were shown to be markedly less responsive to reduced external CO2, with only about a 1.6-fold enhancement of CO2 assimilation by PEP carboxylase, as compared to a 3.0- to 3.7-fold increase for the other C3−C4 species examined, namely, F. linearis Lag., F. anomala B.L. Robinson, F. chloraefolia A. Gray and F. pubescens Rydb. The C3 species F. pringlei Gandoger and F. cronquistii A.M. Powell exhibited a 1.5- and 2.9-fold increase in labeled malate and aspartate, respectively, at Γ*. Assimilation of CO2 by PEP carboxylase in the C4 species F. trinervia (Spreng.) C. Mohr, F. australasica Hook., and the C4-like species F. brownii A.M. Powell was relatively insensitive to subatmospheric levels of CO2. The interspecific variation among the intermediate Flaverias may signify that F. floridana and F. ramosissima possess a more C4-like compartmentation of PEP carboxylase and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (EC 4.1.1.39) between the mesophyll and bundle-sheath cells. Chasing recently labeled malate and aspartate with 12CO2 for 5 min at Γ* resulted in an apparent turnover of 25% and 30% of the radiocarbon in these C4 acids for F. ramosissima and F. floridana, respectively. No substantial turnover was detected for F. linearis, F. anomala, F. chloraefolia or F. pubescens. With the exception of F. floridana and F. ramosissima, it is unlikely that enhanced CO2 fixation by PEP carboxylase at the CO2 compensation concentration is a major mechanism for reducing photorespiration in the intermediate Flaveria species. Moreover, these findings support previous related 14CO2-labeling studies at air-levels of CO2 which indicated that F. floridana and F. ramosissima were more C4-like intermediate species. This is further substantiated by the demonstration that F. floridana PEP carboxylase, like the enzyme in C4 plants, undergoes a substantial activation (2.2-fold) upon illuminating dark-adapted green leaves. In contrast, light activation was not observed for the enzyme in F. linearis or F. chloraefolia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PEP:
-
phosphoenolpyruvate
- Rubisco:
-
ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
- Γ:
-
CO2 compensation concentration
- Γ* :
-
a subatmospheric level of CO2 approximating Γ
References
Adams, C.A., Leung, F., Sun, S.S.M. (1986) Molecular properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from C3, C3−C4 intermediate, and C4 Flaveria species. Planta 167, 218–225
Bauwe, H. (1984) Photosynthetic enzyme activities and immunofluorescence studies on the localization of ribulose-1,5-bis-phosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in leaves of C3, C4, and C3−C4 intermediate species of Flaveria (Asteraceae). Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 179, 253–268
Bauwe, H., Chollet, R. (1986) Kinetic properties of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from C3, C4, and C3−C4 intermediate species of Flaveria (Asteraceae). Plant Physiol. 82, 695–699
Bauwe, H., Keerberg, O., Bassüner, R., Pärnik, T., Bassüner, B. (1987) Reassimilation of carbon dioxide by Flaveria (Asteraceae) species representing different types of photosynthesis. Planta 172, 214–218
Bradford, M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254
Brown, R.H., Bassett, C.L., Cameron, R.G., Evans, P.T., Bouton, I.H., Black, C.C., Jr., Sternberg, L.O., DeNiro, M.J. (1986) Photosynthesis of F1 hybrids between C4 and C3−C4 species of Flaveria. Plant Physiol. 82, 211–217
Budde, R.J.A., Chollet, R. (1988) Regulation of enzyme activity in plants by reversible phosphorylation. Physiol. Plant. 72, 435–439
Chastain, C.J., Chollet, R. (1988) Incorporation of 14CO2 into C4 acids by leaves of C3−C4 intermediate and C3 species of Moricandia and Panicum at the CO2 compensation concentration. Planta 173, 411–418
Cheng, S.-H., Franceschi, V.R., Keefe, D., Mets, L.J., Ku, M.S.B. (1987) Photosynthetic characteristics of reciprocal F1 hybrids between C3−C4 intermediate and C4 Flaveria species. In: Progress in photosynthesis research, vol. 3: pp. 637–640, Biggins, J., ed. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Cheng, S.-H., Moore, B.D., Edwards, G.E., Ku, M.S.B. (1988) Photosynthesis in Flaveria brownii, a C4-like species. Leaf anatomy, characteristics of CO2 exchange, compartmentation of photosynthetic enzymes, and metabolism of 14CO2. Plant Physiol. 87, 867–873
Edwards, G.E., Ku, M.S.B. (1987) Biochemistry of C3−C4 intermediates. In: The biochemistry of plants, vol. 10: Photosynthesis, pp. 275–325, Hatch, M.D., Boardman, N.K., eds. Academic Press, San Diego
Edwards, G.E., Walker, D.A. (1983) C3, C4:Mechanisms, and cellular and environmental regulation, of photosynthesis. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford (UK) London
Hatch, M.D. (1972) Synthesis of L-malate-4-14C and determination of label in the C-4 carboxyl of L-malate. Anal. Biochem. 47, 174–183
Holaday, A.S., Chollet, R. (1984) Photosynthetic/photorespiratory characteristics of C3−C4 intermediate species. Photosynth. Res. 5, 307–323
Holaday, A.S., Lee, K.W., Chollet, R. (1984) C3−C4 intermediate species in the genus Flaveria: leaf anatomy, ultrastructure, and the effect of O2 on the CO2 compensation concentration. Planta 160, 25–32
Holoday, A.S., Brown, R.H., Bartlett, J.M., Sandlin, E.A., Jackson, R.C. (1988) Enzymic and photosynthetic characteristics of reciprocal F1 hybrids of Flaveria pringlei (C3) and Flaveria brownii (C4-like species). Plant Physiol. 87, 484–490
Holbrook, G.P., Jordan, D.B., Chollet, R. (1985) Reduced apparent photorespiration by the C3−C4 intermediate species, Moricandia arvensis and Panicum milioides. Plant Physiol. 77, 578–583
Hunt, S., Smith, A.M., Woolhouse, H.W. (1987) Evidence for a light-dependent system for reassimilation of photorespiratory CO2, which does not include a C4 cycle, in the C3−C4 intermediate species Moricandia arvensis. Planta 171, 227–234
Hylton, C.M., Rawsthorne, S., Smith, A.M., Jones, D.A., Woolhouse, H.W. (1988) Glycine decarboxylase is confined to the bundle-sheath cells of leaves of C3−C4 intermediate species. Planta 175, 452–459
Jiao, J.-A., Chollet, R. (1988) Light/dark regulation of maize leaf phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase by in vivo phosphorylation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 261, 409–417
Jiao, J.-A., Chollet, R. (1989) Regulatory seryl-phosphorylation of C4 phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase by a soluble protein kinase from maize leaves. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 269, 526–535
Ku, M.S.B., Monson, R.K., Littlejohn, R.O., Jr., Nakamoto, H., Fisher, D.B., Edwards, G.E. (1983) Photosynthetic characteristics of C3−C4 intermediate Flaveria species. I. Leaf anatomy, photosynthetic responses to O2 and CO2, and activities of key enzymes in the C3 and C4 pathways. Plant Physiol. 71, 944–948
Monson, R.K., Moore, B.d., Ku, M.S.B., Edwards, G.E. (1986) Co-function of C3- and C4-photosynthetic pathways in C3, C4 and C3−C4 intermediate Flaveria species. Planta 168, 493–502
Monson, R.K., Schuster, W.S., Ku, M.S.B. (1987) Photosynthesis in Flaveria brownii A.M. Powell. A C4-like C3−C4 intermediate. Plant Physiol. 85, 1063–1067
Moore, B.d., Ku, M.S.B., Edwards, G.E. (1987) C4 photosynthesis and light-dependent accumulation of inorganic carbon in leaves of C3−C4 and C4 Flaveria species. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 14, 657–668
Moore, B.d., Monson, R.K., Ku, M.S.B., Edwards, G.E. (1988) Activities of principal photosynthetic and photorespiratory enzymes in leaf mesophyll and bundle sheath protoplasts from the C3−C4 intermediate Flaveria ramosissima. Plant Cell Physiol. 29, 999–1006
Peisker, M., Apel, P., Tichá, I., Hák, R. (1988) CO2 compensation concentration in relation to leaf insertion level in three Flaveria species with different photosynthetic pathways. Photosynthetica 22, 1–8
Rawsthorne, S., Hylton, C.M., Smith, A.M., Woolhouse, H.W. (1988) Photorespiratory metabolism and immunogold localization of photorespiratory enzymes in leaves of C3 and C3−C4 intermediate species of Moricandia. Planta 173, 298–308
Reed, J.E., Chollet, R. (1985) Immunofluorescent localization of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and ribulose 1,5-bis-phosphate carboxylase/oxygenase proteins in leaves of C3, C4, and C3−C4 intermediate Flaveria species. Planta 165, 439–445
Rumpho, M.E., Ku, M.S.B., Cheng, S.-H., Edwards, G.E. (1984) Photosynthetic characteristics of C3−C4 intermediate Flaveria species. III. Reduction of photorespiration by a limited C4 pathway of photosynthesis in Flaveria ramosissima. Plant Physiol. 75, 993–996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Published as Paper No. 8832, Journal Series, Nebraska Agricultural Research Division
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chastain, C.J., Chollet, R. Interspecific variation in assimilation of 14CO2 into C4 acids by leaves of C3, C4 and C3−C4 intermediate Flaveria species near the CO2 compensation concentration. Planta 179, 81–88 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395774
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395774