Summary
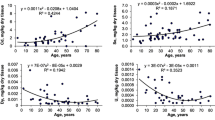
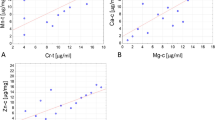
Parallel studies were performed using microfluorimetric DNA determination and X-ray microanalysis on the same thyroid biopsy material to compare the intranuclear DNA and monovalent electrolyte contents (Na+, K+, Cl−). Samples were taken from apparently healthy, adenomatous, and cancerous parts of human thyroid glands removed surgically. The time interval was less than 1 min. The tissues were classified by the pathologist into four main classes: 1) Normal thyroid tissue; 2) benign adenomas; 3) differentiated (follicular and papillary) carcinomas; and 4) anaplastic cancers. The results revealed that the level of aneuploidization showed an increase parallel with the malignancy of the studied tumor. At the same time, a similar tendency was found in the average values of the intranuclear Na+:K+ ratios. The results obtained in this way confirm the possibility that the electric properties of the cell membrane, that is the sustained membrane depolarization, may have a role in the regulation of DNA synthesis and in mitogenesis. These results may offer new diagnostic and/or therapeutic possibilities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y, Ichikawa Y, Homma M, Ito K, Mimura T (1977) TSH receptor and adenylate cyclase in undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma. Lancet 2:506
Abe Y, Ichikawa Y, Muraki T, Ito K, Homma M (1981) Thyrotropin (TSH) receptor and adenylate cyclase activity in human thyroid tumors: absence of high affinity receptor and loss of TSH responsiveness in undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 52:23–28
Böhm N, Sandritter W (1975) DNA in human tumors: A cytophotometric study. Curr Top Pathol 60:151–219
Carayon P, Thomas-Morvan C, Castanas E, Tubiana M (1980) Human thyroid cancer membrane thyrotropin binding and adenylate cyclase activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 51:915–920
Clark OH, Castner BJ (1979) Phyrotropin “receptors” in normal and neoplastic human thyroid tissue. Surgery 85:621–632
Clark OH (1981) TSH supression in the management of thyroid nodules and thyroid cancer. World J Surg 5:39–47
Cone CD Jr (1971) Unified theory on the basic mechanism of normal mitotic control and oncogenesis. J Theor Biol 30:161–181
Crile G (1966) Endocrine dependency of papillary carcinomas of the thyroid. JAMA 195:721–724
Dunhill TP (1937) The surgery of the thyroid gland (The Lettsomian Lectures). Trans Med Soc (Lond) 60:234
Greer MA, Astwood EB (1953) Treatment of simple goiter with thyroid. J Clin Endocrinol 13:1312–1331
Hall TA, Clarke-Anderson M, Appleton T (1973) The use of thin specimens for X-ray microanalysis in biology. J Microsc 99:177–182
Hempelmann LH, Furth J (1978) Etiology of thyroid cancer. In: Greenfield LD (ed) Thyroid cancer. CRC Press, West Palm Beach, Florida, pp. 37–47
Kalderon AE, Sheth V (1978) Secretion and adenylate cyclase in thyroid nodules. Arch Pathol Lab Med 102:381–386
Koch KL, Leffert HL (1979) Increased sodium ion influx is necessary to initiate rat hepatocyte proliferation. Cell 18:153–163
Lukács GL, Balázs Gy, Zs. -Nagy I (1979) Cytofluorimetric measure ments on the DNA contents of tumor cells in human thyroid gland. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 95:265–272
Molenaar WM, Mummery CL, Van der Saag PT, De Laat SW (1982) Modulation of Na+-transport during the cell cycle of neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol 112:27–34
Wynder EL (1952) Some practical aspects of cancer prevention. N Engl J Med 246:573–582
Zs. -Nagy I, Pieri C, Giuli C, Bertoni-Freddari C, Zs.-Nagy V (1977) Energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis of the electrolytes in biological bulk specimen. I. Specimen preparation, beam penetration and quantitative analysis. J Ultrastruct Res 58:22–33
Zs. -Nagy I (1979) The role of membrane structure and function in cellular aging: a review. Mech Ageing Dev 9:237–246
Zs. -Nagy I, Lustyik Gy, Zs.-Nagy V, Zarándi B, Bertoni-Freddari C (1981) Intracellular Na+:K+ ratios in human cancer cells as revealed by energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis. J Cell Biol 90:769–777
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukács, G.L., Zs.-Nagy, I., Lustyik, G. et al. Microfluorimetric and X-ray microanalytic studies on the DNA content and Na+:K+ ratios of the cell nucleic in various types of thyroid tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 105, 280–284 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395759
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00395759