Abstract
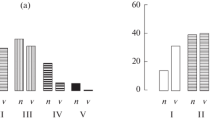
Information about visible symptoms of forest damage was collected during 1984–1987 from 13 reference areas established by the Swedish Environmental Monitoring Programme. The annual occurence of needle loss on Norway spruce and Scots pine was estimated visually and expressed as a percentage of defoliation on the upper parts of the tree-crowns. As the reference areas are situated all over Sweden from Lat. 55° to 69° the climate factors, such as temperature, winds, drought, humidity and snow cover, vary within a wide range. There are also altitudinal differences-sites are situated from 50 to 720 m above sea level. Two of the northernmost sites, which are also the high altitude ones, had the highest defoliation values. In the south, the most severely defoliated trees were growing on sites near the western and the eastern coasts. The estimated defoliation level was mainly lower in 1986 and 1987, compared with the level in 1984. A wide range of environmental factors influence tree health. Trees are subjected to several kinds of stress-factors causing several kinds of damage. Besides the natural stresses, there is also, a long-term effect of air pollutants. Diversity in resistance and susceptibility to air pollutants, as well as the exposition to winds and humidity, are affecting needle loss.
The exposures to chemicals occurring under forest conditions are different at different parts of Sweden. The observed defoliation of conifers does not seem to have a linear relationship with the pollution gradient but are also attributable to natural stress factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alenäs, I. and Skärby, L.: 1988, ‘Deposition of Plant Nutrients in Relation to Crown Thinning in a Swedish Coniferous Forest’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 38, 223–228.
Bartuska, A. et al.: 1985, ‘Assessments of Acid Depostion and its Effects’, NAPAP, Draft Contribution, Washington, D.C., 1985.
Bergkvist, B.: 1987, ‘Soil Solution Chemistry and Metal Budgests of Spruce Forest Ecosystem in S. Sweden’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 33, 131–154.
Bergkvist, B., Folkeson, L., and Olsson, K.: 1986, ‘Fluxes of Protons, Metals and Anions in Spruce, Beech and Birch Forest Ecosystems’, in Direct Effects of Dry and wet Deposition on Forest Ecosystemsin Particular Canopy Interactions, Workshop, COST 612, Kungälv, 19–23 oktober 1986. SLU/CEC.
Bringmark, L.: 1987, ‘Övervakning av markkemi och markbiologi i PMK's referensomr℘den’, National Swedish Envir. Prot. Board Report 3339.
Degermark, C. (ed.): 1985, ‘Climate and Chemistry of Water at Svartberget. Reference Measurements 1984’, Swedish Univ. of Agricultural Sci., Vindeln 1985 (in Swedish).
Garland, J. A. and Branson, J. R.: 1977 ‘Deposition of Sulfur Dioxide to Pine Forest Assessed by a Radioactive Tracer Method’, Tellus 29 (5), 445–454.
Granat, L.: 1987, ‘Luft-och nederbördskemiska statiosnätet inom PMK’, National Swedish Envir. Port. Board Report 3328.
Hasselrot, B. and Grennfelt, P.: 1987, ‘Deposition of Air Pollutants in a Wind-exposed Forest-Edge’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 34, 135–143.
Hinrichsen, D.: 1986, ‘Multiple Pollutants and Forest Decline’, Ambio 15(5), 258–265.
ICP: 1987, Manual on Methodologies and Criteria for harmonized Sampling, Assessment, Monitoring and Analysis of the Effect of Air Pollution on Forests’, Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution, Global Environment Monitoring System.
Innes, J. L.: 1987a, ‘Acid Rain. Its Effects. Its Causes’, European Environment Review 1(1987), 5.
Innes, J. L.: 1987b, ‘The Interpretation of International Forest Health Data’, R. Perry et al. (ed.), in Acid Rain: Scientific and Technical Advances, Ealing, UK 1987. Selper Ltd.
Karhu, M. and Huttunen, S.: 1986, ‘Erosion Effects of Air Pollution on Needle Surfaces’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 31, 417–423.
Matzner, E.: 1985, ‘Effects of Acid Precipitation on Soils-Principles Demonstrated in two Forest Ecosystems of North Germany’, Symposium of the Effects of Air Pollution on Forest and Water Ecosystems, Helsinki, April 23–24, 1985, 47–56.
Miller, H. G.: 1985, ‘Acid Flux and the Influence of Vegetation’, Symposium on the Effects of Air Pollution on Forest and Water Ecosystems. Helsinki April 23–24, 1985, pp. 37–46.
Monitor: 1985: ‘The National Environmental Monitoring Programme’, National Swedish Envir. Prot. Board, Stockholm 1985.
Nihlg‘rd, B.: 1985, ‘The Ammonium Hypothesis.-An Additional Explanation to the Forest Dieback in Europa’, Ambio 14(1), 2–8.
Nilsson, S. and Duinker, P.: 1987, ‘The Extent of Forest Decline in Europe. A Synthesis of Survey Results’, Environment 29, 9.
Prinz, B.: 1987, ‘Causes of Forest Damage in Europe. Major Hypothesis and Factors’, Environment 29(9), 11–15, 32–37.
Rosén, K. and Lundmark-Thelin, A.: 1985, ‘Throughfall Chemistry in a Mixed Coniferous Forest in Central Sweden’, Rep. in Forest Ecology and Forest Soils 51, Swedish Univ. of Agricultural Sci., Uppsala.
Skärby, L. and Selldén, G.: 1984, ‘The Effects of Ozone on Crops and Forests’, Ambio 13:2, 68–72.
Ulrich, B.: 1983, ‘Interaction of Forest Canopies with Atmospheric Constituents: SO2, Alkali and Earth Alkali Cations and Chloride’, in Ulrich, B. and Pankrath, J. (eds.), Effect of Accumulation of Air Pollutants in Forest Ecosystems, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Walsman, J. M. and Hoffman, M. R.: 1988, ‘Nutrient Leaching from Pine Needles Impacted by Acidic Cloudwater’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 37, 193–201.
Wiman, B.: 1984, ‘Deposition av tungmetallhaltinga och försurande aerosoler till skogsekosystem, National Swedish Envir. Prot. Board PM 1908.
Winkler, P.: 1985: ‘Die messtechnische Erfassung der trockenen und nassen Deposition’, in Waldschäden: Einflussfaktoren und ihre Bewertung, VDI Berichte 560, Düsseldorf.
Woodman, J. N. and Cowling, E. B.: 1987, ‘Airborne Chemicals and Forest Health-Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andersson, B. Defoliation of coniferous trees-assessments 1984–87. Environ Monit Assess 14, 23–43 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394355