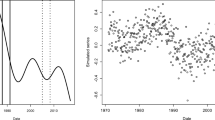
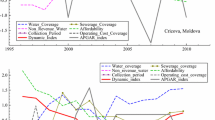
Abstract
Intervention analysis techniques are described for identifying and statistically modelling trends which may be present in water quality time series. At the exploratory data analysis stage, simple graphical and modelling methods can be employed for visually detecting and examining trends in a time series caused by one or more external interventions. For instance, a plot of a robust locally weighted regression smooth through a graph of the observations over time may reveal trends and other interesting statistical properties contained in the time series. In addition, statistical tests, such as different versions of the nonparametric Mann-Kendall test, can be used to detect the presence of trends caused by unknown or known external interventions. To characterize rigorously and estimate trends which may be known in advance or else detected using exploratory data analysis studies, different parametric methods can be utilized at the confirmatory data analysis stage. Specifically, the time series modelling approach to intervention analysis can be employed to estimate the magnitudes of the changes in the mean level of the series due to the interventions. Particular types of regression models can also be used for estimating trends, especially when there are many missing observations. To demonstrate how intervention analysis methods can be effectively used in environmental impact assessment, representative applications to water quality time series are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Box, G. E. P. and Jenkins, G. M.: 1976, ‘Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control’, Holden-Day, San Francisco, 2nd ed., 553 pp.
Box, G. E. P. and Tiao, G. C.: 1975, ‘Intervention Analysis with Applications to Economic and Environmental Problems’, Journal of the American Statistical Association 70 (349), 70–79.
Cleveland, W. S.: 1979, ‘Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots’, Journal of the American Statistical Association 74 (368), 829–836.
D'Astous, F. and Hipel, K. W.: 1979, ‘Analyzing Environmental Time Series’, Journal of the Environmental Engineering Division, American Society of Civil Engineers 105 (EE5), 979–992.
El-Shaarawi, A. H. and Kwiatowski, R. E. (eds.): 1986, Statistical Aspects of Water Quality Monitoring, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Esterby, S. R.: 1985, ‘A Program for Estimating the Point of Change and Degree in Polynomial Regression’, Technical Report, Scientific Series No. 147, National Water Research Institute, Canada Centre for Inland Waters, Burlington, Ontario, Canada.
Esterby, S. R. and El-Shaarawi, A. H.: 1981a, ‘Inference about the Point of Change in a Regression Model’, J. Roy. Stat. Soc. 30 (3), Series C, 277–285.
Esterby, S. R. and El-Shaarawi, A. H.: 1981b, ‘Likelihood Inference about the Point of Change in a Regression Regime’, J. Hydrol. 53, 17–30.
Hipel, K. W. (ed.): 1988, ‘Nonparametric Approaches to Environmental Impact Assessment’, Monograph published by the American Water Resources Association, 5410 Grosvenor Lane, Suite 220, Bethesda, Maryland, U.S.A.
Hipel, K. W., Lennox, W. C., Unny, T. E., and McLeod, A. I.: 1975, ‘Intervention Analysis in Water Resources’, Water Resources Research 11 (6), 855–861.
Hipel, K. W. and McLeod, A. I.: 1989, Time Series Modelling for Water Resources and Environmental Engineers, Elsevier, Amsterdam (in press).
Hipel, K. W., McLeod, A. I., and McBean, E. A.: 1977, ‘Stochastic Modelling of the Effects of Reveroir Operation’, J. Hydrol. 32, 97–113.
Hipel, K. W., McLeod, A. I., and Weiler, R. R.: 1988, ‘Data Analysis of Water Quality Time Series in Lake Erie’, Water Resources Bulletin 24 (3), 533–544.
Hirsch, R. M. and Slack, J. R.: 1984, ‘A Nonparametric Trend Test for Seasonal Data with Serial Dependence’, Water Resources Research 20 (6), 727–732.
Hirsch, R. M., Slack, J. R., and Smith, R. A.: 1982, ‘Techniques for Trend Assessment for Monthly Water Quality Data’, Water Resources Research 18 (1), 107–121.
Jonckheere, A. R.: 1954, ‘A Distribution-Free k-Sample Test Against Ordered Alternatives’, Biometrika 41, 133–145.
Kendall, M. G.: 1975, Rank Correlation Methods, 4th ed., Charles Griffin, London, England.
Lettenmaier, D. P.: 1976, ‘Detection of Trends in Water Quality Data from Records with Dependent Observations’, Water Resources Research 12 (5), 1037–1046.
Lettenmaier, D. P.: 1988, ‘Multivariate Nonparametric Tests for Trend in Water Quality’, Water Resources Bulletin 24 (3), 505–512.
MacNeill, I. B.: 1985, ‘Detecting Unknown Interventions with Application to Forecasting Hydrological Data’, Water Resources Bulletin 21 (4), 785–796.
Mann, H. B.: 1945, ‘Nonparametric Tests against Trend’, Econometrica 13, 245–259.
McLeod, A. I.: 1977, ‘Improved Box-Jenkins Estimators’, Biometrika 64 (3), 531–534.
McLeod, A. I. and Hipel, K. W.: 1989, ‘The McLeod-Hipel Time Series Package’, available from authors at address given with paper title.
McLeod, A. I., Hipel, K. W., and Camacho, F.: 1983, ‘Trend Assessment of Water Quality Time Series’, Water Resources Bulletin 19 (4), 537–547.
McNeil, D. R.: 1987, Interactive Data Analysis, Wiley, New York, 186 pp.
Mosteller, F. and Tukey, J. W.: 1977, Data Analysis and Regression, Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts.
Page, E. B.: 1963, ‘Ordered Hypotheses for Multiple Treatments: A Significance Test for Linear Ranks’, J. Amer. Stat. Assoc. 58, 216–230.
Shaw, D. T. and Maidment, D. R.: 1987, ‘Intervention Analysis of Water Use Restrictions, Austin, Texas’, Water Resources Bulletin 23 (6), 1037–1046.
Tang, S. M. and MacNeill, I. B.: 1988, ‘The Effect of Autocorrelated Errors on Change-Detection Statistics’, Paper presented at the Workshop on Statistical Methods for the Assessment of Point Source Pollution, The Canada Centre for Inland Waters, Burlington, Ontario, Canada.
Tukey, J.: 1977, Exploratory Data Analysis, Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts.
VanBelle, G. and Hughes, J. P.: 1984, Nonparametric Tests for Trend in Water Quality’, Water Resources Research 20 (1), 127–136.
Whitfield, P. H. and Woods, P. F.: 1984, ‘Intervention Analysis of Water Quality Records’, Water Resources Bulletin 20 (5), 657–667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hipel, K.W., McLeod, A.I. Intervention analysis in environmental engineering. Environ Monit Assess 13, 185–201 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394229
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00394229