Abstract
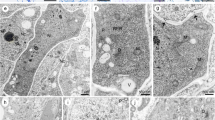
The development of the placenta in the anthocerote Phaeoceros laevis (L.) Prosk. was studied by transmission electron microscopy. By the time the sporophyte emerges from the involucre, a conspicuous placental region is formed by the intrusive growth of sporophyte foot haustorial cells into the adjacent gametophyte vaginula tissue. The separation of gametophyte cells by haustorial cells and their incorporation into the placenta are preceded by the loosening and swelling of their walls and the formation of a periplasmic space. This process causes the disruption of the plasmodesmata, and may eventually result in the complete isolation and consequent degeneration of the cells. Crystals are commonly observed in the vacuoles of gametophyte placental cells. Crystals become more abundant during cytoplasmic degeneration, and are released in the placental lacunae that result from the complete dissolution of gametophyte cells. During the subsequent phase of capsule elongation, the gametophyte placental cells that retain the symplastic connection with the adjoining gametophyte parenchyma develop a wall labyrinth typical of transfer cells. Obliteration of the wall labyrinth by deposition of lightly staining wall material is observed later in sporophyte development, in concomitance with capsule dehiscence. Crystals are negative to the periodic acid/thiocarbohydrazide/silver proteinate test for carbohydrates whilst they are completely digested by pepsin or protease, denoting protein composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PATAg:
-
periodic acid/thiocarbohydrazide/silver proteinate
References
Ben-Arie, R., Kislev, N., Frenkel, C. (1979) Ultrastructural changes in the cell walls of ripening apple and pear fruit. Plant Physiol. 64, 197–202
Bhavannarayana, K., Metha, P.M., Kothari, I.L. (1982) Ultrastructural studies in the pericarp of unripened and ripened tomato fruits. Bull. Soc. Bot. Fr. 129, 13–19
Browning, A.J., Gunning, B.E.S. (1979) Structure and function of transfer cells in the sporophyte haustorium of Funaria hygrometrica. I. The development and ultrastructure of the haustorium. J. Exp. Bot. 30, 1233–1246
Esau, K., Torsch, J. (1984) The sieve plate of Echium (Boraginaceae): Developmental aspects and response of P—protein to protein digestion. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 86, 31–45
Eymé, J., Suire, C. (1967) Au suject de l'infrastructure de la zone placentaire de Mnium cuspidatum Hedw. (mousse bryale acrocarpe). C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Sér. D 265, 1788–1791
Fineran, B.A., Bullock, S. (1979) Ultrastructure of graniferous tracheary elements in the haustorium of Exocarpus bidwillii, a root hemi-parasite of the Santalaceae. Proc. R. Soc. London B 204, 329–343
Gambardella, R. (1987) Ultrastructure and development of the gametophyte vaginula-sporophyte foot complex in the liverwort Targionia hypophylla. Planta 172, 431–438
Gambardella, R., de Lucia Sposito, M.L. (1981–1982) Ultrastructure of the placental region in a liverwort, Mannia androgyna. Delpinoa 23–24, 177–184
Gambardella, R., de Lucia Sposito, M.L. (1983) Placenta ultrastructure in Plagiochasma rupestre (Forst.) Steph. (Marchantiales, Hepaticae). G. Bot. Ital. 177, 166–167
Gambardella, R., Ligrone, R., Castaldo, R. (1981) Ultrastructure of the sporophyte foot in Phaeoceros. Cryptog. Bryol. Lichenol. 2, 23–45
Hébant, C. (1975) Organization of the conducting tissue-system in the sporophytes of Dawsonia and Dendroligotrichum (Polytrichales, Musci). J. Hattori Bot. Lab. 39, 235–254
Kelley, C. (1969) Wall projections in the sporophyte and gametophyte of Sphaerocarpos. J. Cell Biol. 41, 910–914
Lal, M., Chauhan, E. (1981) Transfer cells in the sporophytegametophyte junction of Physcomitrium cyathycarpum. Protoplasma 107, 79–83
Ligrone, R., Gambardella, R., Castaldo, R., Giordano, S., de Lucia Sposito, M.L. (1982a) Gametophyte and sporophyte ultrastructure in Buxbaumia piperi Best (Buxbaumiales, Musci). J. Hattori Bot. Lab. 52, 465–499
Ligrone, R., Gambardella, R., de Lucia Sposito, M.L. (1982b) Ultrastructure of the sporophyte foot-gametophyte vaginula complex in Timmiella barbuloides (Brid.) Moenk. Planta 154, 414–425
Maier, K. (1967) Wandlabyrinthe in Sporophyten von Polytrichum. Planta 77, 108–126
Maier, K., Maier, U. (1972) Localization of beta-glycerophosphatase and Mg++-activated adenosine triphosphatase in a moss haustorium, and the relation of these enzymes to the cell wall labyrinth. Protoplasma 75, 91–112
Marsh, B.H., Doyle, W.T. (1985) Intercellular protein crystals from the gametophyte-sporophyte junction of the hornwort Phaeoceros laevis Prosk. Protoplasma 129, 223–226
Matile, P. (1974) Lysosomes. In: Dynamic aspects of plant ultrastructure, pp. 178–218, Robards, A.W., ed. McGraw Hill, London
O'Brien, T.P. (1970) Further observations on hydrolysis of the cell wall in the xylem. Protoplasma 69, 1–14
Roland, J.C., Sandoz, D. (1969) Détection cytochimique des sites de formation des polysaccharides prémembranaires dans les cellules végétales. J. Microsc. 2, 263–268
Sexton, R., Jameson, G.G.C., Allan, M.H.J.L. (1977) An ultrastructural study of abscission zone cells with special reference to the mechanism of enzyme secretion. Protoplasma 91, 369–387
Spurr, A.R. (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–34
Thomas, R.J., Stanton, D.S., Longendorfer, D.H., Farr, M.E. (1978) Physiological evaluation of the nutritional autonomy of a hornwort sporophyte. Bot. Gaz. 139, 306–311
Wiencke, C., Schulz, D. (1978) The development of transfer cells in the haustorium of the Funaria hygrometrica sporophyte. Bryophyt. Biblioth. 13, 147–167
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gambardella, R., Ligrone, R. The development of the placenta in the anthocerote Phaeoceros laevis (L.) Prosk. Planta 172, 439–447 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393859
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393859