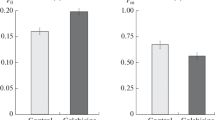
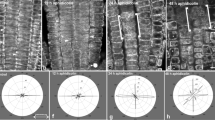
Abstract
When roots of Lepidium sativum L. are immersed in a colchicine solution (10-4 mol l-1), the cortical microtubules of statocytes are affected such that the dense network ofmicrotubules at the distal cell edges, between the endoplasmic reticulum and the plasma membrane, disappears almost completely, whereas the microtubules, lining the anticlinal cell walls are reduced only to a limited extent. Upon inversion of colchicine-pretreated roots, the distal complex of endoplasmic reticulum sinks into the interior of the statocyte. Germination of seeds in the cold (3–4°C) leads to a retardation of statocyte development; the elaborated system of endoplasmic reticulum is lacking, and only a few microtubules are observable, lining the plasma membrane along the anticlinal cell walls. During an additional 4 h at 24°C, groups of microtubules develop near the plasma membrane in the distal one-third of the statocytes, coaligning with newly synthesized cisternae of the endoplasmic reticulum. It is proposed that, particularly at the distal statocyte pole, microtubules in coordination with cross-bridging structures, act in stabilizing the polar arrangement of the distal endoplasmic reticulum and, in turn, facilitate an integrated function of amyloplasts, endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane in graviperception.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
endoplasmic reticulum
- MT:
-
microtubule
References
Brown, D.L., Stearns, M.E., Macrae, T.H. (1982) Microtubule organizing centres. In: The cytoskeleton in plant growth and development, pp. 55–83, Lloyd, C.W., ed. Academic Press, London
Buckhout, T.J. (1983) ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport in endoplasmic reticulum isolated from roots of Lepidium sativum L. Planta 159, 84–90
Burgess, J., Northcote, D.H. (1968) The relationship between the endoplasmic reticulum and microtubular aggregation and disaggregation. Planta 80, 1–14
Busby, C.H., Gunning, B.E.S. (1983) Orientation of microtubules against transverse cell walls in roots of Azolla pinnata R. Br. Protoplasma 116, 78–85
Cox, G., Juniper, B.E. (1983) High-voltage electron microscopy of whole, critical-point dried plant cells—fine cytoskeletal elements in the moss Bryum tenuisetum. Protoplasma 115, 70–80
Dustin, P. (1978) Microtubules. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Franke, W.W. (1971a) Relationship of nuclear membranes with filaments and microtubules. Protoplasma 73, 263–292
Franke, W.W. (1971b) Cytoplasmic microtubules linked to endoplasmic reticulum with cross-bridges. Exp. Cell Res. 66, 486–489
Galatis, B. (1977) Differentiation of stomatal meristemoids and guard mother cells into guard-like cells in Vigna sinensis leaves after colchicine treatment. Planta 136, 103–114
Galatis, B. (1980) Microtubules and guard-cell morphogenesis in Zea mays L. J. Cell Sci. 45, 211–244
Galatis, B. (1982) The organization of microtubules in guard cell mother cells of Zea mays. Can. J. Bot. 60, 1148–1166
Galatis, B., Apostolakos, P., Katsaros, C. (1983) Microtubules and their organizing centres in differentiating guard cells of Adiantum capillus veneris. Protoplasma 115, 176–192
Gunning, B.E.S. (1980) Spatial and temporal regulation of nucleating sites for arrays of cortical microtubules in root tip cells of the water fern Azolla pinnata. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 23, 53–65
Gunning, B.E.S. (1981) Microtubules and cytomorphogenesis in a developing organ: the root primordium of Azolla pinnata. In: Cell biology monographs, vol. 8: Cytomorphogenesis in plants, pp. 301–325, Kiermayer, O., ed. Springer, Wien New York
Gunning, B.E.S., Hardham, A.R. (1982) Microtubules. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 33, 651–698
Gunning, B.E.S., Hardham, A.R., Hughes, J.E. (1978) Evidence for initiation of microtubules in discrete regions of the cell cortex in Azolla root-tip cells, and an hypothesis on the development of cortical arrays of microtubules. Planta 143, 161–179
Hardham, A.R. (1982) Regulation of polarity in tissues and organs. In: The cytoskeleton in plant growth and development, pp. 377–403, Lloyd, C.W., ed. Academic Press, London
Hardham, A.R., Gunning, B.E.S. (1978) Structure of cortical microtubule arrays in plant cells. J. Cell Biol. 77, 14–34
Hardham, A.R., Gunning, B.E.S. (1979) Interpolation of microtubules into cortical arrays during cell elongation and differentiation in roots of Azolla pinnata. J. Cell Sci 37, 411–442
Harris, P. (1975) The role of membranes in the organization of the mitotic apparatus. Exp. Cell Res. 94, 409–425
Heath, I.B. (1975) The effect of antimicrotubule agents on the growth and ultrastructure of the fungus Saprolegnia ferax and their ineffectiveness in disrupting hyphal microtubules. Protoplasma 85, 147–176
Heath, I.B., Heath, M.C. (1978) Microtubules and organelle movements in the rust fungus Uromyces phaseoli var. vignae. Cytobiologie 16, 393–411
Hensel, W. (1984) Microtubules in statocytes from roots of cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Protoplasma 119, 121–134
Hensel, W., Sievers, A. (1981) Induction of gravity-dependent plasmatic responses in root statocytes by short time contact between amyloplasts and the distal endoplasmic reticulum complex. Planta 153, 303–307
Hepler, P.K. (1980) Membranes in the mitotic apparatus of barley cells. J. Cell Biol 86, 490–499
Hepler, P.K. (1981) Morphogenesis of tracheary elements and guard cells. In: Cell biology monographs, vol. 8: Cytomorphogenesis in plants, pp. 327–347, Kiermayer, O., ed. Springer, Wien New York
Hillmann, G., Ruthmann, A. (1982) Effect of mitotic inhibitors on the ultrastructure of root meristem cells. Planta 155, 124–132
Kirschner, M.W. (1978) Microtubule assembly and nucleation. Int. Rev. Cytol. 54, 1–71
Kristen, U. (1978) Ultrastructure and a possible function of the intercisternal elements in dictyosomes. Planta 138, 29–33
Lloyd, C.W., ed. (1982) The cytoskeleton in plant growth and development. Academic Press, London
Mandelkow, E., Mandelkow, E.M., Bordas, J. (1983) Synchrotron radiation as a tool for studying microtubule self-assembly. Trends Biochem. Sci. 8, 374–377
Melkonian, M., Kröger, K.-H., Marquardt, K.G. (1980) Cell shape and microtubules in zoospores of the green alga Chlorosarcinopsis gelatinose (Chlorosarcinales): effects of low temperature. Protoplasma 104, 283–293
Mollenhauer, H.H. (1965) An intercisternal structure in the golgi apparatus. J. Cell Biol 24, 504–511
Mollenhauer, H.H., Morré, D.J. (1975) A possible role for intercisternal elements in the formation of secretory vesicles in plant golgi apparatus. J. Cell Sci 19, 231–237
Palevitz, B.A. (1981) Microtubules and possible microtubule nucleation centers in the cortex of stomatal cells as visualized by high voltage electron microscopy. Protoplasma 107, 115–125
Palevitz, B.A. (1982) The stomatal complex as a model of cytoskeletal participation in cell differentiation. In: The cytoskeleton in plant growth and development, pp. 345–376, Lloyd, C.W., ed. Academic Press, London
Plattner, H., Westphal, C., tiggemann, R. (1982) Cytoskeleton-secretory vesicle interactions during the docking of secretory vesicles at the cell membrane in Paramecium tetraurelia cells. J. Cell Biol. 92, 368–377
Quatrano, R.S. (1978) Development of cell polarity. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 29, 487–510
Robinson, D.G. (1977) Structure, synthesis and orientation of microfibrils. IV. Microtubules and microfibrils in Glaucocystis. Cytobiologie 15, 475–484
Robinson, D.G., Herzog, W. (1977) Structure, synthesis and orientation of microfibrils. III. A survey of the action of microtubule inhibitors on microtubules and microfibril orientation in Oocystis solitaria. Cytobiologie 15, 463–474
Schmiedel, G., Reiss, H.-D., Schnepf, E. (1981) Associations between membranes and microtubules during mitosis and cytokinesis in caulonema tip cells of the moss Funaria hygrometrica. Protoplasma 108, 173–190
Schmiedel, G., Schnepf, E. (1979) Side branch formation and orientation in the caulonema of the moss, Funaria hygrometrica: experiments with inhibitors and centrifugation. Protoplasma 101, 47–59
Schmiedel, G., Schnepf, E. (1980) Polarity and growth of caulonema tip cells of the moss Funaria hygrometrica. Planta 147, 405–413
Schnepf, E. (1981) Polarity and gradients in tip growing plant cells. In: International cell biology 1980–1981, pp. 485–488, Schweiger, H.G., ed. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Schnepf, E. (1982) Morphogenesis in moss protonemata. In: The cytoskeleton in plant growth and development, pp. 321–344, Lloyd, C.W., ed. Academic Press, London
Schnepf, E. (1984) Pre- and postmitotic reorientation of microtubule arrays in young Sphagnum leaflets: transitional stages and initiation sites. Protoplasma 120, 100–112
Schnepf, E., Hrdina, B., Lehne, A. (1982) Spore germination, development of the microtubule system and protonema cell morphogenesis in the moss, Funaria hygrometrica: effects of inhibitors and growth substances. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 177, 461–482
Seagull, R.W., Heath, I.B. (1979) The effect of tannic acid on the in vivo preservation of microfilaments. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 20, 184–188
Seagull, R.W., Heath, I.B. (1980) The organization of cortical microtubule arrays in the radish root hair. Protoplasma 103, 205–229
Sievers, A., Behrens, H.M., Buckhout, T.J., Gradmann, D. (1984) Can a Ca2+ pump in the endoplasmic reticulum of the Lepidium root be the trigger for rapid changes in membrane potential after gravistimulation? Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 114, 195–200
Sievers, A., Hensel, W. (1982) The nature of graviperception. In: Plant growth substances 1982, pp. 497–506, Wareing, P.F., ed. Academic Press, London
Sievers, A., Schnepf, E. (1981) Morphogenesis and polarity of tubular cells with tip growth. In: Cell biology monographs, vol. 8: Cytomorphogenesis in plants. pp. 265–299, Kiermayer, O., ed. Springer, Wien New York
Sievers, A., Volkmann, D. (1972) Verursacht differentieller Druck der Amyloplasten auf ein komplexes Endomembransystem die Geoperzeption in Wurzeln? Planta 102, 160–172
Sievers, A., Volkmann, D., Hensel, W., Sobick, V., Briegleb, W. (1976) Cell polarity in root statocytes in spite of simulated weightlessness. Naturwissenschaften 63, 343
Traas, J.A. (1984) Visualization of the membrane bound cytoskeleton and coated pits of plant cells by means of dry cleaving. Protoplasma 119, 212–218
Volkmann, D. (1981) Structural differentiation of membranes involved in the secretion of polysaccharide slime by root cap cells of cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Planta 151, 180–188
Volkmann, D., Sievers, A. (1975) Wirkung der inversion auf die Anordnung des Endoplasmatischen Reticulums und die Polarität von Statocyten in Wurzeln von Lepidium sativum. Planta 127, 11–19
Volkmann, D., Sievers, A. (1979) Graviperception in multicellular organs. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, N.S., vol. 7: Physiology of movements, pp. 573–600, Haupt, W., Feinleib, M.E., eds. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Wardrop, A.B. (1983) Evidence for the possible presence of a microtrabecular lattice in plant cells. Protoplasma 115, 81–87
Weisenseel, M.H., Kicherer, R.M. (1981) Ionic currents as control mechanism in cytomorphogenesis. In: Cell biology monographs, vol. 8: Cytomorphogenesis in plants, pp. 379–399, Kiermayer, O., ed. Springer, Wien New York
Wick, S.M., Hepler, P.K. (1980) Localization of Ca++-containing antimonate precipitates during mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 86, 500–513
Wilson, H.J. (1970) Endoplasmic reticulum and microtubule formation in dividing cells of higher plants — a postulate. Planta 94, 184–190
Woodcock, C.L.F. (1971) The anchoring of nuclei by cytoplasmic microtubules in Acetabularia. J. Cell Sci. 8, 611–621
Wunderlich, F., Speth, V. (1970) Antimitotic agents and macronuclear divisions of ciliates. IV. Reassembly of microtubules in macronuclei of Tetrahymena adapting to colchicine. Protoplasma 70, 139–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hensel, W. A role of microtubules in the polarity of statocytes from roots of Lepidium sativum L.. Planta 162, 404–414 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393452
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00393452