Abstract
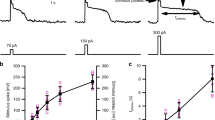
The cytoplasm of subepidermal parenchyma cells of Avena sativa L. coleoptiles was collected at one end of the cell by centrifugation. The electrical properties of both plasmalemma and tonoplast were then examined with microelectrodes inserted into both cytoplasm and vacuole of the same cell. The input resistance of the cytoplasm measured with either electrode was 7.5±0.8 MΩ while that of the vacuole measured with the single vacuolar electrode and a bridge circuit was 29.2±3.1 MΩ. The latter value was not significantly different from that of control, uncentrifuged cells. The resistance of the tonoplast is therefore several times larger than the input resistance of the cytoplasm, but the specific resistance of the plasma membrane cannot be calculated without knowledge of the extent and pattern of intercellular coupling. Electrical coupling of the cytoplasms of adjacent cells was observed in only two out of eight experiments. The mean potential of the vacuoles,-77.8±6.4 mV, was not significantly different from that of the cytoplasm; however, all the available evidence indicates that variable tip potentials in impaled cells made absolute determination of the membrane potential uncertain. In fusicoccin, the cells hyperpolarized by 20 mV within 10 min. This reponse occurred entirely at the plasmalemma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, W.P., Hendrix, D.L., Higinbotham, N.: Higher plant cell membrane resistance by a single intracellular electrode method. Plant Physiol. 53, 122–124 (1974)
Cleland, R.E.: Kinetics of hormone-induced H+ excretion. Plant Physiol. 58, 210–213 (1976a)
Cleland, R.: Fusicoccin-induced growth and hydrogen ion excretion of Avena coleoptiles: relation to auxin responses. Planta 128, 201–206 (1976b)
Cleland, R.E.: Rapid stimulation of K+−H+ exchange by a plant growth hormone. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 69, 333–338 (1976c)
Cleland, R.E., Prins, H.B.A., Harper, J.R., Higinbotham, N.: Rapid hormone-induced hyperpolarization of the oat coleoptile transmembrane potential. Plant Physiol. 59, 395–397 (1977)
Dohrmann, U., Hertel, R., Pesci, P., Cocucci, S.M., Marrè, E., Randazzo, G., Ballio, A.: Localization of in vitro binding of the fungal toxin fusicoccin to plasma-membrane-rich fractions from corn coleoptiles. Plant Sci. Lett. 9, 291–299 (1977)
Etherton, B., Keifer, D.W., Spanswick, R.M.: Comparison of three methods for measuring electrical resistances of plant cell membranes. Plant Physiol. 60, 684–688 (1977)
Goldsmith, M.H.M., Fernandez, H.R., Goldsmith, T.H.: Electrical properties of parenchymal cell membranes in the oat coleoptile. Planta 102, 302–323 (1972)
Goldsmith, M.H.M., Ray, P.M.: Intracellular localization of the active process in polar transport of auxin. Planta 111, 297–314 (1973)
Goldsmith, T.H., Goldsmith, M.H.M.: The interpretation of intracellular measurements of membrane potential, resistance and coupling in cells of higher plants. Planta 143, 267–274 (1978)
Greenham, C.G.: The relative resistances of the plasmalemma and tonoplast in higher plants. Planta 69, 150–157 (1966)
Higinbotham, N., Hope, A.B., Findlay, G.P.: Electrical resistance of cell membranes of Avena coleoptiles. Science 143, 1448–1449 (1964)
Jacobs, M., Ray, P.M.: Rapid auxin induced decrease in free space pH and its relationship to auxin induced growth in maize and pea. Plant Physiol. 58, 203–209 (1976)
Marrè, E., Lado, P., Caldogno, F.R., Colombo, R.: Correlation between cell enlargement in pea internode segments and decrease in the pH of the medium of incubation. I. Effects of fusicoccin, natural and synthetic auxins and mannitol. Plant Sci. Lett. 1, 179–184 (1973)
Marrè, E., Lado, P., Ferroni, A., Denti, A.B.: Transmembrane potential increase induced by auxin, benzyladenine, and fusicoccin. Correlation with proton extrusion and cell enlargement. Plant Sci. Lett. 2, 257–265 (1974)
Spanswick, R.M.: Electrical coupling between cells of higher plants: A direct demonstration of intracellular communication. Planta 102, 215–227 (1972)
Zeiger, E., Moody, W., Hepler, P.: Light sensitive membrane potentials in onion guard cells. Nature 270, 270–271 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldsmith, M.H.M., Cleland, R.E. The contribution of tonoplast and plasma membrane to the electrical properties of a higher-plant cell. Planta 143, 261–265 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391996
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391996