Abstract
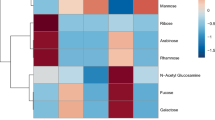
The chemical composition of the mucus from three hard corals (Acropora formosa, Pachyseris speciosa and Fungia fungites) and three soft corals (Sarcophyton sp., Lemnalia sp., and Cespitularia sp.) collected on the Great Barrier Reef (1982–1985) was determined. Significant variation exists in the composition and structure of the six mucus samples, indicating the absence of a common structure for coral mucus. In all cases protein and/or carbohydrate polymers are the major components of the mucus, and lipids are present only in small amounts. The glycose composition varied between species, with fucose (F. fungites and Lemnalia sp.), arabinose (A. formosa), galactose (P. speciosa) and N-acetyl glucosamine (Sarcophyton sp.) being present in high concentrations. With the exception of Sarcophyton sp. and Lemnalia sp., all mucus samples were acidic and contained significant sulphate but no uronic or sialic acids. The amino acid composition of the mucus samples was not unusual, apart from A. formosa, which contained a high percentage of serine and threonine, and F. fungites, which had high levels of glutamic acid present.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Allen, A. (1983). Mucus — a protective secretion of complexity. Trends biochem. Sciences 8: 169–173
Benson, A. A., Muscatine, L. (1974). Wax in coral mucus: energy transfer from corals to reef fishes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19: 810–814
Crossland, C. J., Barnes, D. J., Borowitzka, M. A. (1980a). Diurnal lipid and mucus production in the staghorn coral Acropora acuminata. Mar. Biol. 60: 81–90
Crossland, C. J., Barnes, D. J., Cox, T., Devereux, M. (1980b). Compartmentation and turnover of organic carbon in the staghorn coral Acropora formosa. Mar. Biol. 59: 181–187
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P. A., Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analyt. Chem. 28: 350–356
Ducklow, H. W., Mitchell, R. (1979). Composition of mucus released by coral reef coelenterates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24: 706–714
Goreau, T. (1956). Histochemistry of mucopolysaccharide-like substances and alkaline phosphatase in Madreporaria. Nature, Lond. 177: 1029–1030
Hartree, E. F. (1972). Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Analyt. Biochem. 48: 422–427
Johannes, R. E. (1967). Ecology of organic aggregates in the vicinity of a coral reef. Limnol. Oceanogr. 12: 189–195
Krupp, D. A. (1982). The composition and production of the mucus of the solitary mushroom coral, Fungia scutaria (Lamarck). Ph. D. thesis, University of Hawaii
Lewis, J. B., Price, W. S. (1976). Patterns of ciliary currents in Atlantic reef corals and their functional significance. J. Zool., Lond. 178: 77–89
Marcus, J., Thorhaug, A. (1982). Pacific versus Atlantic responses of the subtropical hermatypic coral Porites sp. to temperature and salinity effects. Proc. 4th int. Symp. coral Reefs 2: 15–20 [Gomez, E. D. et al. (eds.) Marine Sciences Center, University of the Philippines, Quezon City]
Meikle, P., Richards, G. N., Yellowlees, D. (1987). Structural characterisation of the oligosaccharide side chains from a glycoprotein isolated from the mucus of the coral Acropora formosa. J. biol. Chem. 262: 16941–16947
Molchanova, V. I., Ovodova, R. G., Ovodov, Y. S., Elkin, Y. H. (1985). Studies of the polysaccharide moiety of corallan, a glycoprotein from Pseudopteragorgia americana. Carbohydr. Res. 141: 289–293
Murty, V. L. N., Sarosiek, J., Slomiany, A., Slomiany, B. L. (1984). Effect of lipids and proteins on the viscosity of gastric mucus glycoprotein. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 121: 521–529
Sarosiek, J., Slomiany, A., Takagi, A., Slomiany, B. L. (1984). Hydrogen ion diffusion in dog gastric mucus glycoprotein: effect of associated lipids and covalently bound fatty acids. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 118: 523–531
Schuhmacher, H. (1977). Ability of fungiid corals to overcome sedimentation. Proc. 3rd int. Symp. coral Reefs 1: 503–510 [Taylor, D. L. (ed.) School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences, University of Miami]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meikle, P., Richards, G.N. & Yellowlees, D. Structural investigations on the mucus from six species of coral. Mar. Biol. 99, 187–193 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391980
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391980