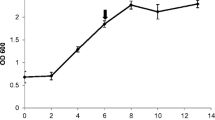
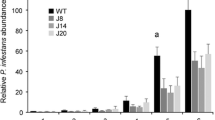
Abstract
Considerable amounts of the following substances were found in uninfected parsley (Petroselinum crispum) cotyledons: furanocoumarins, the putative phytoalexins of this and some related plant species, two enzymes of the furanocoumarin pathway (S-adenosyl-L-methionine: xanthotoxol and S-adenosyl-L-methionine: bergaptol O-methyltransferases), two hydrolytic enzymes (1,3-β-glucanase, EC 3.2.1.39, and chitinase, EC 3.2.1.14), and ‘pathogenesis-related’ proteins. The furanocoumarins and the methyltransferase activities reached their highest levels at the onset of cotyledon senescence as the hydrolytic enzymes increased from low to relatively high activity values. The relative amounts of pathogenesis-related proteins 1 and 2, as well as the corresponding mRNAs, also increased markedly. Two enzymes of general phenylpropanoid metabolism, L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and 4-coumarate: CoA ligase, decreased in activity in a biphasic fashion during cotyledon development. At all developmental stages, the levels of these putative defense-related agents in total cotyledon extracts were too high to enable detection of, possibly, additional changes upon infection with zoospores of Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea, a fungal pathogen to which parsley shows a non-host, hypersensitive resistance response.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMT:
-
S-adenosyl-L-methionine: bergaptol O-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.-)
- 4CL:
-
4-coumarate: CoA ligase (EC 6.1.1.12)
- CMT:
-
S-adenosyl-L-methionine: caffeate O-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.-)
- PAL:
-
L-phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.5)
- PR:
-
pathogenesis-related
- XMT:
-
S-adenosyl-L-methionine: xanthotoxin O-methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.-)
References
Beier, R.C., Oertli, E.H. (1983) Psoralen and other linear furanocoumarins as phytoalexins in celery. Phytochemistry 22, 2595–2597
Boller, T. (1985) Induction of hydrolases as a defense reaction against pathogens. In: Cellular and molecular biology of plant stress, pp. 247–262, Key, J.L., Kosuge, T., eds. Alan R. Liss, Inc., New York
Boller, T., Gehri, A., Mauch, F., Vögeli, U. (1983) Chitinase in bean leaves: induction by ethylene, purification, properties, and possible function. Planta 157, 22–31
Bonner, W.M., Laskey, R.A. (1974) A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur. J. Biochem. 46, 83–88
Bradford, M.M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254
Callow, J.A. (1983) Biochemical plant pathology. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, New York
Chappell, J., Hahlbrock, K. (1984) Transcription of plant defense genes in response to UV light or fungal elicitor. Nature 311, 76–78
Clark, G. (1981) Staining procedures, 4th edn., Williams and Wilkinson, Baltimore, London
Dixon, R.A. (1986) The phytoalexin response: elicitation, signalling and control of host gene expression. Biol. Rev. 61, 239–291
Fleming, A. (1922) On a remarkable bacteriolytic element found in tissues and secretions Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. B., 93, 306
Fraser, R.S.C. (1981) Evidence for the occurrence of the ‘pathogenesis-related’ proteins in leaves of healthy tobacco plants during flowering. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 19, 69–76
Hahlbrock, K., Scheel, D. (1987) Biochemical responses of plants to pathogens. In: Innovative approaches to plant disease control, pp. 229–254 Chet, I., ed. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, New York
Hahlbrock, K., Sutter, A., Wellmann, E., Ortmann, R., Grisebach, H. (1971) Relationship between organ development and activity of enzymes involved in flavone glycoside biosynthesis in young parsley plants. Phytochemistry 10, 109–116
Hahlbrock, K., Lamb, C.J., Purwin, C., Ebel, J., Fautz, E., Schäfer, E. (1981) Rapid response of suspension-cultured parsley cells to the elicitor from Phytophthora megasperma var. Sojae. Induction of enzymes of general phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Physiol. 67, 768–773
Hauffe, K.D., Hahlbrock, K., Scheel, D. (1986) Elicitor-stimulated furanocoumarin biosynthesis in cultured parsley cells. S-adenosyl-L-methionine: bergaptol and S-adenosyl-L-methionine: xanthotoxol O-methyltransferases. Z. Naturforsch. 41c, 228–239
Jahnen, W. (1986) Untersuchungen zur Histochemie und Biochemie der Nichtwirt-Pathogenbeziehung von Petersilie (Petroselinum crispum, Hoffm.) und Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea Dissertation, Köln
Kombrink, E., Bollmann, J., Hauffe, K.D., Knogge, W., Scheel, D., Schmelzer, E., Somssich, I., Hahlbrock, K. (1986) Biochemical responses of non-host plant cells to fungi and fungal elicitors. In: Biology and molecular biology of plant pathogen interactions, pp. 335–362 Bailey, J.A., ed. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Kombrink, E., Hahlbrock, K. (1986) Responses of cultured parsley cells to elicitors from phytopathogenic fungi. Plant Physiol. 81, 216–221
Kuhn, D.N., Chappell, J., Boudet, A., Hahlbrock, K. (1984) Induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and 4-coumarate: CoA ligase mRNAs in cultured plant cells by UV light or fungal elicitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 1102–1106
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685
Morrissey, J.H. (1981) Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal. Biochem. 117, 307–310
Murray, R.D.H., Mendez, J., Brown, S.A. (1982) The natural coumarins. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester New York
O'Farrell, P.H. (1975) High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 250, 4007–4021
Paxton, J.D. (1981) Phytoalexins—a working redefinition. Phytopathol. Z. 101, 106–109
Pelham, R.B., Jackson, R.J. (1976) An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur. J. Biochem. 76, 247–256
Scheel, D., Hauffe, K.D., Jahnen, W., Hahlbrock, K. (1986) Stimulation of phytoalexin formation in fungus-infected plants and elicitor-treated cell cultures of parsley. In: Recognition in microbe-plant symbiotic and pathogenic interactions, pp. 325–331, Lugtenberg, B., ed. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Somssich, I., Schmelzer, E., Bollmann, J., Hahlbrock, K. (1986) Rapid activation by fungal elicitor of genes encoding “pathogenesis-related” proteins in cultured parsley cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 2427–2430
Thomas, H., Stoddart, J.L. (1980) Leaf senescence. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31, 83–111
Tietjen, K.G., Hunkler, D., Matern, U. (1983) Differential response of cultured parsley cells to elicitors from two nonpathogenic strains of fungi. 1. Identification of induced products as coumarin derivatives. Eur. J. Biochem. 131, 401–407
Van Loon, L.C. (1985) Pathogenesis-related proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 4, 111–116
Van Loon, L.C., Van Kammen, A. (1970) Polyacrylamide disc electrophoresis of the soluble leaf proteins from Nicotiana tabacum var. ‘Samsum’ and ‘Samsum NN’. II. Changes in protein constitution after infection with tobacco mosaic virus. Virology 40, 199–211
Weber, K., Osborne, M. (1969) The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 244, 4406–4412
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knogge, W., Kombrink, E., Schmelzer, E. et al. Occurrence of phytoalexins and other putative defense-related substances in uninfected parsley plants. Planta 171, 279–287 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391105
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391105