Abstract
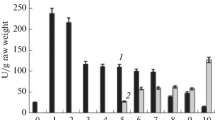
The total activity of aldolase (EC 4.1.2.13) and the activities of cytosol and chloroplast aldolase were determined in seeds, cotyledons, primary leaves and secondary leaves of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L., cv. Monopa) during germination. Total aldolase activity in cotyledons increased from low levels to a low maximum in the dark after one week and to a high maximum in white light after three to four weeks and declined thereafter. The activity in primary and secondary leaves started to rise strongly from the 18th and 26th days, respectively, up to the 42nd day of germination. The levels of aldolase activity paralleled the development of leaf area, chlorophyll content and protein content per leaf except that the leaf area of cotyledons continued to increase steadily up to the 42nd day after the maximum of aldolase activity was reached. Resolution of cytosol- and chloroplast-specific isoenzymes by chromatography on diethylaminoethylcellulose indicated that in the light the cytosol enzyme represented approx. 8% of the total activity in cotyledons, primary and secondary leaves throughout germination, and the chloroplast enzyme represented the remaining 92%. Only in cotyledons of dark-grown seedlings was the cytosol aldolase between 25 and 50% of the total activity. Seeds contained almost exclusively a cytosol aldolase. In cotyledons the increase of total activity in the light was specifically the consequence of an increase in chloroplast aldolase while the cytosol aldolase was little affected by light. The light effect was mediated by phytochrome as demonstrated by classical induction and reversion experiments with red and far-red light and by continuous far-red light treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DEAE-cellulose:
-
diethylaminoethylcellulose
References
Anderson, L.E., Advani, V.R. (1970) Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. Three distinct isoenzymes associated with the reductive pentose phosphate cycle. Plant Physiol. 45, 583–585
Anderson, L.E., Levin, D.A. (1970) Chloroplast aldolase is controlled by a nuclear gene. Plant Physiol. 46, 819–820
Anderson, L.E., Pacold, I. (1972) Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. IV. Pea leaf fructose 1,6-diphosphate aldolases. Plant Physiol. 49, 393–397
Arnon, D.I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24, 1–15
Bradbeer, J.W. (1969) The activities of the photosynthetic carbon cycle enzymes of greening bean leaves. New Phytol. 68, 233–245
Bradbeer, J.W. (1971) Plastid development in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. The effect of short blue, red, far-red and white light treatments on dark grown plants. J. Exp. Bot. 22, 382–390
Bukowiecki, A.C., Anderson, L.E. (1974) Multiple forms of aldolase and triose phosphate isomerase in diverse plant species. Plant Sci. Lett. 3, 381–386
Cerff, R., Quail, P.H. (1974) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenases and glyoxylate reductase. II. Far red light-dependent development of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase isoenzyme activities in Sinapis alba cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 54, 100–104
Davis, B.J. (1964) Disc gel electrophoresis — II. Method and application to human serum proteins. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 121, 404–427
Gasperini, C., Pupillo, P. (1983) Aldolase isoenzymes of maize leaves. Plant Sci. Lett. 28, 163–171
Kelly, G.J., Latzko, E. (1977) Chloroplast phosphofructokinase. I. Proof of phosphofructokinase activity in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 60, 290–294
Kessler, St.W. (1975) Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-binding adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes. J. Immunol. 115, 1617–1624
Krüger, I., Schnarrenberger, C. (1983) Purification, subunit structure and immunological comparison of fructose-bisphosphate adolases from spinach and corn leaves. Eur. J. Biochem. 136, 101–106
Krüger, I., Schnarrenberger, C., Salnik, J., Amiri, T. (1984) Purification and structural comparison of aldolases. Plant Physiol. 75 (Suppl.), 162
Latzko, E., Zimmermann, G., Feller, U. (1974) Evidence for a hexosediphosphatase from the cytoplasm of spinach leaves. Hoppe-Seyler's Z. Physiol. Chem. 355, 321–326
Lebherz, H.G., Leadbetter, M.M., Bradshaw, R.A. (1984) Isolation and characterization of the cytosolic and chloroplast form of spinach leaf fructose diphosphate aldolase. J Biol. Chem. 259, 1011–1017
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, M.J., Farr, A.L., Randall, R.J., (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275
Mohr, H. (1966) Untersuchungen zur phytochrominduzierten Photomorphogenese des Senfkeimlings (Sinapis alba L.). Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 54, 63–83
Mohr, H., Meyer, U., Hartmann, K.M. (1964) Die Beeinflussung der Farnsporenkeimung durch Phytochrom und Photosynthese. Planta 60, 483–496
Mühlbach, H., Schnarrenberger, C. (1978) Properties and intracellular distribution of two phosphoglucomutases from spinach leaves. Planta 141, 65–70
Murphy, D.J., Walker, D.A. (1981) Aldolase from wheat leaves — its properties and subcellular distribution. FEBS Lett. 134, 163–166
Nishimura, M., Beevers, H. (1981) Isoenzymes of sugar phosphate metabolism in endosperm of germinating castor beans. Plant Physiol. 67, 1255–1258
Scandalios, J.G. (1974) Isoenzymes in development and differentiation. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25, 225–258
Schnarrenberger, C., Herbert, M., Krüger, I. (1983) Intracellular compartmentation of isozymes of sugar phosphate metabolism in green leaves. In: Isozymes, vol. 8, pp. 23–51, Rattazzi, M.C., Scandalios, J.G., Whitt, G.S., eds. Liss, New York
Schnarrenberger, C., Oeser, A. (1974) Two isoenzymes of glucosephosphate isomerase from spinach leaves and their intracellular compartmentation. Eur. J. Biochem. 45, 77–82
Schnarrenberger, C., Oeser, A., Tolbert, N.E. (1973) Two isoenzymes each of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in spinach leaves. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 154, 438–448
Schnarrenberger, C., Tetour, M., Herbert, M. (1975) Development and intracellular distribution of enzymes of the oxidative pentose phosphate cycle in radish cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 56, 836–840
Steup, M., Latzko, E. (1979) Intracellular localization of phosphorylases in spinach and pea leaves. Planta 145, 69–75
Walker, D.A. (1976) Interactions between cytoplasm and plastids. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, N.S., vol. 3: Transport in plants III, pp. 85–136, Stocking, C.R., Heber, U., eds. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Weeden, N.F., Gottlieb, L.D. (1980) The genetics of chloroplast enzymes. J. Hered. 71, 392–396
Wu, R., Racker, E. (1959) Regulatory mechaniisms in carbohydrate metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 234, 1029–1035
Zucker, M. (1972) Light and enzymes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 23, 133–156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krüger, I., Schnarrenberger, C. Development of cytosol and chloroplast aldolases during germination of spinach seeds. Planta 164, 109–114 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391034
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391034