Abstract
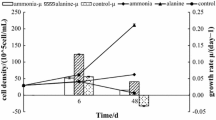
The marine pseudomonad bacterium PL1 contains an intracellular pool of free amino acids which consist mainly of glutamate with small amounts of glutamine and aspartate when grown in a nutrient medium containing 0.2 M NaCl. When the NaCl concentration of the growth medium is increased to 0.8 M, proline becomes a major component of the intracellular pool together with glutamate—at this molarity and under suitable nutrient conditions these amino acids comprise 20% of total bacterial amino acid nitrogen. When grown in a nutrient growth medium containing a constant level of NaCl, the intracellular pool size can vary by a factor of 4 depending on the concentration of carbon and nitrogen in the medium. Experiments show that the amino acid pool can act as a nitrogen reserve but has little function as a carbon reserve. At high NaCl concentrations there is a marked dependence for growth on the presence of sufficient potassium in the medium. However, no correlation between K+ and glutamate concentration in either nitrogen or K+-limited cultures has been found. None of the enzymes associated with glutamate biosynthesis was influenced by NaCl levels between 0.2 and 0.5 M. Neither Na+ or K+ stimulated the activity of these enzymes when tested in vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Benson, J.V., M.J. Gordon and J.A. Patterson: Accelerated chromatographic analysis of amino acids in physiological fluids containing glutamine and asparagine. Analyt Biochem. 18, 228–240 (1967)
Britten, R.J. and F.T. McClure: The amino acid pool of Escherichia coli. Bact. Rev. 26, 292–335 (1962)
Brown, C.M., D.S. MacDonald-Brown and J.L. Meers: Physiological aspects of microbial inorganic nitrogen metabolism. Adv. microb. Physiol. 11, 1–52 (1974)
—— and S.O. Stanley: Inorganic nitrogen metabolism in marine bacteria: nitrogen assimilation in some marine pseudomonads. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 52, 793–804 (1972)
———: The mechanisms of nitrogen assimilation in pseudomonads. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 39, 89–98 (1973)
———: Inorganic nitrogen metabolism in marine bacteria: nitrate uptake and reduction in a marine pseudomonad. Mar. Biol. 31, 7–13 (1975)
— and A.H. Rose: Effects of temperature on composition and cell volume of Candida utilis. J. Bact. 97, 261–272 (1969)
— and S.O. Stanley: Environment-mediated changes in the cellular content of the ‘pool’ constituents and their associated changes in cell physiology. J. appl. Chem. Biotechnol. 22, 363–389 (1972)
Drapeau, G.R. and R.A. MacLeod: Na+ dependent active transport of α-amino bytyric acid into cells of a marine pseudomonad. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 12, 111–115 (1963)
Gale, E.F. and E.S. Taylor: The assimilation of amino acids by bacteria. J. gen. Microbiol. 1, 77–84 (1947)
Griffiths, R.P., J.A. Baross, F.J. Hanus and R.Y. Morita: Some physical and chemical parameters affecting the formation and retention of glytamate pools in a marine psychrophilic bacterium. Z. allg. Mikrobiol. 14, 359–369 (1974)
Hussan, H.F. and R.A. MacLeod: Kinetics of Na+-dependent K+ ion transport in a marine pseudomonad. J. Bact. 121, 160–164 (1975)
Kay, W.W. and A.F. Grönlung: Amino acid pool formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bact. 97,282–291 (1969)
Moore, S. and W.H. Stein: Chromatography of amino acids on sulfonated polystyrene resins. J. biol. Chem. 192, 663–681 (1951)
——: A modified ninhydrin reagent for the photometric determination of amino acids and related compounds. J. biol. Chem. 211, 907–913 (1954)
Siegel, A. and E.T. Degens: Concentration of dissolved amino acids from saline waters by ligand-exchange chromatography. Science, N.Y. 151, 1098–1101 (1966)
Stanley, S.O. and C.M. Brown: Influence of temperature and salinity on the amino acid pools of some marine pseudomonads. In: Effects of ocean environment on microbial activity, pp 92–103. Ed. by R.R. Colwell and R.Y. Morita. Baltimore: University Park Press 1974
Tempest, D.W. and J.L. Meers: The influence of NaCl concentration of the medium on the potassium content of Aerobacter aerogenes and on the interrelationships between potassium, magnesium and ribonucleic acid in the growing bacteria. J. gen. Microbiol. 54, 319–325 (1968)
—— and C.M. Brown: Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J. gen. Microbiol. 64, 171–1850 (1970)
Thompson, J. and R.A. MacLeod: Functions of Na+ and K+ in the active transport of α-amino butyric acid in a marine pseudomonad. J. biol. Chem. 246, 4066–4074 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J.H.S. Blaxter, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanley, S.O., Brown, C.M. Inorganic nitrogen metabolism in marine bacteria: The intracellular free amino acid pools of a marine pseudomonad. Mar. Biol. 38, 101–109 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390763
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390763