Abstract
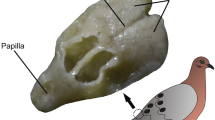
Surface structure and internal organization of prominent skin papillae in the mesopelagic eel Cyema atrum have been investigated by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Each papilla is club-shaped and possesses a pore at its distal end. A central rod, filled with cellular strands and surrounded by a 30 to 40 μm wide matrix of clear material, runs from the tip to the base of the papilla. A cluster of cells, located 60 μm below the surface of the skin, appears to be connected with the lateral line nerve. The lack of stereo- and kinocilia on the one hand, and the presence of a central rod and a terminal pore on the other, demonstrate that the cutaneous papillae in C. atrum cannot be regarded as typical lateral-line neuromasts. They share several features with electroreceptors, known from other fishes. It is postulated that C. atrum and other deep-sea species with similar skin papillae have been able to partially substitute vision and other senses useful for orientation by electroreception.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Barber, V.C.: Cilia in sense organs. In: Cilia and flagella, pp 403–433. Ed. by M.A. Sleigh. London & New York: Academic Press 1974
Bennett, M.V.L.: Electroreception. In: Fish physiology, Vol. V. pp 493–574. Ed. by W.S. Hoar and J.D. Randall. London & New York: Academic Press 1971a
— Electric organs. In: Fish physiology, Vol. V. pp 347–491. Ed. by W.S. Hoar and J.D. Randall. London & New York: Academic Press 1971b
Bergeijk, A. van: Introductory comments on lateral line function. In: Lateral line detectors, pp 73–81. Ed. by P. Cahn. Indiana: University Press 1967
Bertin, L.: Les poissons abyssaux du genre Cyema Günther (Anatomie, embryologie, bionomie). Dana Rep. 10, 1–30 (1937)
Bullock, T.H.: Seeing the world through a new sense: electroreception in fish. Am. Scient. 61, 316–325 (1973)
Dijkgraaf, S.: Biological significance of the lateral line organs. In: Lateral line detectors, pp 83–95. Ed. by P. Cahn. Indiana: University Press 1967
Enger, P.S., L. Kristensen and O. Sand: The perception of weak electric D.C. currents by the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 54A, 101–103 (1976)
Flock, Å.: The lateral line organ mechanoreceptors. In: Fish physiology, Vol. V. pp 241–263. Ed. by W.S. Hoar and J.D. Randall. London & New York: Academic Press 1971
Hama, K.: Some observations on the fine structure of the lateral line organ of the Japanese sea eel Lyncozymba nystromi. J. Cell Biol. 24, 193–210 (1965)
Iwai, T.: Structure and development of lateral line cupulae in teleost larvae. In: Lateral line detectors, pp 27–44. Ed. by P. Cahn. Indiana: University Press 1967
Kalmijn, A.J.: The electric sense of sharks and rays. J. exp. Biol. 55, 371–383 (1971)
Leonard, J.B. and R.G. Summers: The ultrastructure of the integument of the American eel Anguilla rostrata. Cell Tissue Res. 171, 1–30 (1976)
Marshall, N.B.: Explorations in the life of fishes, 204 pp. Cambridge: Harvard University Press 1971
— and J.C. Staiger: Aspects of the structure, relationships and biology of the deep-sea fish Ipnops murrayi. Bull. mar. Sci. 25, 101–111 (1975)
Meyer-Rochow, V.B.: The lateral-line organs of the larvae of the deep-sea fish Cataetyx memorabilis (Ophidiidae): a scanning-electron and light-microscope study. Mar. Biol. 12, 272–276 (1972)
—: Leptocephali and other transparent fish larvae from the South-Eastern Atlantic Ocean. Zool. Anz. 192, 240–251 (1974)
Roth, A. and H. Tscharntke: Ultrastructure of the ampullary electroreceptors in lungfish and Brachiopterygii. Cell Tissue Res. 173, 95–108 (1976)
Szamier, R.B. and A.W. Wachtel: Special cutaneous receptor organs of fish: VI. Ampullary and tuberous organs of Hypopomus. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 30, 450–471 (1970)
Thomopoulos, A.: Sur la ligne latérale des téléostéens. Bull. Soc. zool. Fr. 82, 347–442 (1957)
Tretiakov, D.K.: Outlines of the phylogeny of fishes, 176 pp. [In Russ.]. Leningrad: Akademiia Nauk SSSR; Zoologicheskii Institute 1944
Yamada, Y. and K. Hama: Fine structure of the lateral-line organ of the common eel, Anguilla japonica. Z. Zellforsch. 124, 454–464 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G.F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer-Rochow, V.B. Skin papillae as possible electroreceptors in the deep-sea eel Cyema atrum (Cyemidae: Anguilloidei). Mar. Biol. 46, 277–282 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390689
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390689