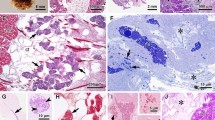
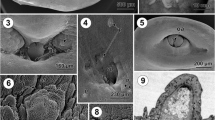
Abstract
The fine structure of the opercula of Spirobis borealis Daudin and S. pusilloides Bush, and the primary and secondary operculum of S. granulatus (L) have been examined by electron microscopy. In different regions, the epithelium of the operculum exhibits variations in thickness and fine structure which correspond to transitions from peduncular to opercular wall to opercular plate epithelia. Externally, the peduncle and walls of the operculum are covered by a cuticle which is composed of several layers of fibrils/fibres embedded in an amorphous matrix. It is regularly traversed by microvilli from underlying cells. At the operculum rim, the cuticle changes so that its appearance is thick and solid. It continues across the roof of the operculum as a thin layer overlying a calcareous plate. The secondary operculum of S. granulatus differs from those of the other species in that an internal calcareous plate and solid cuticle line the roof of the operculum. It differs further in possessing an opercular pore. The possibilities are discussed of the cuticle fibrils/fibres of the peduncle and the opercular wall being collagenous in nature, and later being transformed to a solid tanned structure overlying a calcareous plate. The modes of secretion of the cuticle and calcareous plate by underlying cells are also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Bergan, P.: On the anatomy and reproduction biology in Spirobis Daudin. Nytt. Mag. Zool. 1, 1–26 (1953).
Berlin, J. D.: The localisation of acid mucopolysaccharides in the Golgi complex of intestinal goblet cells. J. Cell Biol. 32, 760–766 (1967).
Borg, F.: Über die Spirorbisarten Schwedens. Zool. Bidr. Upps. 5, 15–38 (1917).
Bubel, A.: An electron-microscope investigation of the cells lining the outer surface of the mantle in some marine molluscs. Mar. Biol. 21, 245–255 (1973).
Ericsson, J. L. E., B. F. Trump, and J. Neibel: Electron microscopic studies of the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. II. Cytc-segresomes and cytosomes: their relationship to each other and the lysosome concept. Lab. Invest. 14, 1341–1365 (1965).
Friend, D. S.: Cytochemical staining of multivesicular body and Golgi vesicles. J. Cell Biol. 41, 269–279 (1969).
Ganagarajah, M. and A. S. M. Saleuddin: Electron histochemistry of the outer mantle epithelium in Helix pomatia during shell regeneration. Proc. malac. Soc. Lond. 40, 71–77 (1972).
Gravier, C.: La ponte et l'incubation chez les annelides polychètes. Annls Sci. nat. (Zool.) (Ser. 10) 6, 153–247 (1923).
Gupta, B. L. and C. Little: Studies on Pogonophora. 4. Fine structure of the cuticle and epidermis. Tissue Cell 2, 637–696 (1970).
Hare, P. E.: Amino acids in the proteins from aragonite and calcite in the shells of Mytilus californianus. Science, N.Y. 139, 216–217 (1963).
Hillman, R. E.: Formation of the periostracum in Mercenaria mercenaria. Science, N.Y. 134, 1754–1755 (1961).
Holman, W. and H. Schraer: The intracellular distribution of calcium in the mucosa of the avian shell gland. J. Cell Biol. 30, 317–331 (1966).
Krall, J. F.: The cuticle and epidermal cells of Dero obtusa (Family Naididae). J. Ultrastruct. Res. 25, 84–93 (1968).
Locke, M. and N. Krishnan: The distribution of phenoloxidases and polyphenols during cuticle formation. Tissue Cell 3, 103–126 (1971).
Matukas, V. J. and G. A. Krikos: Evidence for changes in protein polysaccharide associated with the onset of calcification in cartilage. J. Cell Biol. 39, 43–48 (1968).
Michel, C.: Ultrastructure et histochimie de la cuticule pharyngrenne chez Eulalia viridis Muller (annclide polychète errante, Phyllodccidae). Z. Zellforsch. mikrosk. Anat. 98, 54–73 (1969).
Nadol, J. B., J. R. Gibbins and K. R. Porter: A reinterpretation of the structure and development of the basement lamella: an ordered array of collagen in fish skin. Devl Biol. 20, 304–331 (1969).
Potswald, H. E.: The biology of fertilization and brood protection in Spirobis (Laoespira) morchi Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 135, 208–222 (1968).
Rambourg, A., W. Hernandez and C. P. Leblond: Detection of complex carbohydrates in the Golgi apparatus of rat cells. J. Cell Biol. 40, 395–414 (1969).
Rudall, K. M.: Comparative biology and biochemistry of collagen. In: Treatise on collagen. 2. Biology of collagen Part A, pp 83–137. Ed. by B. S. Gould. New York: Academic Press 1968.
Saleuddin, A. S. M. and W. Chan: Shell regeneration in Helix: shell matrix composition and crystal formation. Can. J. Zool. 47, 1107–1111 (1969).
Smith, R. E. and M. G. Farquhar: Lysosome function in the regulation of the secretory process in cell of the anterior pituitary gland. J. Cell Biol. 31, 319–347 (1966).
Storch, V. and U. Welsch: Über die Feistruktur der Polychaeten-Epidermis (Annelida). Z. Morph. Tiere 66, 310–322 (1970).
Thorp, C. H.: The reproductive cycles of Spirobinae (Polychaeta: Serepulida) and their synchrony with structural changes in the operculum. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Sheffield 1961.
Thorp, C. H.: Studies of the operculum in Spirobis. (Polychaeta: Serpulidae) I. The structure of the operculum in sinistral opercular incubators. (In preparation).
Thorson, G.: Reproduction and larval development of Danish marine bottom invertebrates. Meddr Kommn Danm. Fisk.-og Havunders. (Ser. Plankton) 3, 1–524 (1969).
Timmermans, L. P. M.: Studies on shell formation in molluscs. Neth. J. Zool. 19, 417–523 (1969).
Townsend, F. J. and M. A. Gibson: A histochemical study of glycogen metabolism in developing cartilage and bone. Can. J. Zool. 48, 87–95 (1970).
Wada, K.: Studies on the mineralisation of the calcified tissue in molluscs. X. Histochemical determination of the nature of acid mucopolysaccharide in organic crystals. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 30, 993–998 (1964).
Wilbur, K. M. and L. H. Jodrey: Studies on shell formation V. The inhibition of shell formation by carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 108, 359–365 (1955).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. H. S. Blaxter, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bubel, A. An electron-microscope investigation into the cuticle and associated tissues of the operculum of some marine serpulids. Mar. Biol. 23, 147–164 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389172
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00389172