Abstract
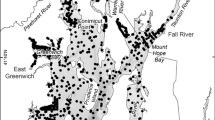
During two consecutive summers, the first quantitative bay-wide survey (207 stations) of benthic invertebrates was conducted in Delaware Bay (USA). In 1972, 109 species were collected at 105 stations; and in 1973, 125 species were collected at 102 stations. A total of 169 different species were collected for both summers. The number of species and number of individuals increased with increasing salinity and increasing median grain size. These relationships were compared and were found similar to those in estuaries and bays throughout the world. Average density was 722 individuals m2, which is low compared to other estuaries. The relationship of low secondary production to pollution, macroscopic algae, sediment transport, predation, and hydrography is discussed. Deposit feeders comparised the major feeding type. Local species composition was similar to that in Chesapeake Bay, and dominant species occurred in estuaries throughout the Mid-Atlantic Bight. The benthic invertebrates of Delaware Bay were related to the cosmopolitan mode of estuarine faunas. Faunal assemblages were identified by cluster analysis. The assemblages were associated with sediment type and salinity. It was concluded that Delaware Bay comprises a mosaic of animal assemblages, some of which have relatively sharp boundaries similar to classical level bottom type communities, whereas the boundaries of others are almost impossible to detect, and these represent species distributed along an environmental continum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abbott, R.T.: American seashells, 2nd ed. 633 pp. New York: Von Nostrand Reinhold Co. 1974
Bader, R.G.: The role of organic matter in determining the distribution of pelecypods in marine sediments. J. mar. Res. 13, 32–47 (1954)
Bloom, S.A., J.L. Simon and V.D. Hunter: Animalsediment relations and community analysis of a Florida estuary. Mar. Biol. 13, 43–56 (1972)
Boesch, D.F.: Classification and community structure of macrobenthos in the Hampton Roads area, Virginia. Mar. Biol. 21, 226–244 (1973)
Bousfield, E.L.: Adaptive radiation in sandburrowing amphipod crustaceans. Chesapeake Sci. 11, 143–154 (1970)
Brown, A.C.: Food relationships on the intertidal sandy beaches of the Cape Peninsula. S. Afr. J. Sci. 60, 35–41 (1964)
Carriker, M.R.: Observations on the penetration of tightly closing bivalves by Busycon and other predators. Ecology 32, 73–83 (1951)
—: Ecology of estuarine invertebrates: a perspective. In: Estuaries, pp 442–487. Ed. by G.H. Lauff. Washington, D.C.: American Association for the Advancement of Science 1967. (Publs Am. Ass. Advmt Sci. No. 83)
Christie, N.D.: A numerical analysis of the distribution of a shallow sublittoral sand macrofauna along a transect at Lamberts Bay, South Africa. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 42, 149–172 (1976)
Clifford, H.T. and W. Stephenson: An introduction to numerical classification, 229 pp. New York: Academic Press 1975
Cronin, L.E.: The role of man in estuarine processes. In: Estuaries, pp 667–689. Ed. by G.H. Lauff. Washington, D.C.: American Association for the Advancement of Science 1967. (Publs Am. Ass. Advmt Sci. No. 83)
Day, J.H.: The ecology of Morrumbene Estuary, Mocambique. Trans. R. Soc. S. Afr. 41, 43–97 (1974)
Fager, E.W.: Communities of organisms. In: The sea. Vol. 2. pp 415–437. Ed. by M.N. Hill. New York: Interscience Publishers 1963
Field, J.G.: A humerical analysis of changes in the soft-bottom fauna along a transect across False Bay, South Africa. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 7, 215–253 (1971)
Folk, R.L.: Petrology of sedimentary rocks, 170 pp. Austin, Texas: Hemphill's 1968
Gage, J.: A preliminary survey of the benthic macrofauna and sediments in Lochs Etive and Creran, sea-lochs along the West Coast of Scotland. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 52, 237–276 (1972)
—: Shallow-water zonation of sea-loch benthos and its relation to hydrographic and other physical features. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 54, 223–249 (1974)
Glemarec, G.: The benthic communities of the European North Atlantic continental shelf. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 11, 263–284 (1973)
Hampson, G.R.: A species pair of the genus Nucula (Bivalvia) from the eastern coast of the United States. Proc. malac. Soc. Lond. 39, 333–341 (1971)
Harrison, W. and M.L. Wass: Frequencies of infaunal invertebrates related to water content of Chesapeake Bay sediments. SEast. Geol. 6, 177–187 (1965)
Haskin, H.H. and S. Tweed: Oyster setting and early spat survival at critical salinity levels on natural seed oyster beds of Delaware Bay, 67 pp. Water Resources Research Institute, Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey 1976. (Internal publication)
Hedgpeth, J.W. (Ed.): Treatise on ecology and paleoecology. Vol. 1. Ecology 1296 pp. New York: Geological Society of America 1957. (Mem. geol. Soc. Am. No. 67)
Hidu, H. and H.H. Haskin: Setting of the American oyster related to environmental factors and larval behavior. Proc. natn. Shellfish. Ass. 61, 35–50 (1971)
Johnson, R.G.: Particulate matter at the sediment-water interface in coastal environments. J. mar. Res. 32, 313–330 (1974)
Kinner, P. and D. Maurer: Polychaetous annelids of the Delaware Bay area. Fish. Bull. U.S. (In press)
—— and W. Leathem: Benthic invertebrates in Delaware Bay: animal-sediment associations of the dominant species. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 59, 685–701 (1974)
Kraft, J.C.: Sedimentary facies patterns and geologic history of a Holocene marine transgression. Bull. geol. Soc. Am. 82, 2131–2158 (1971)
Leathem, W. and D. Maurer: The distribution and ecology of common marine and estuarine gastropods in the Delaware Bay area. Nautilus 89, 73–79 (1975)
Massé, H.: Quantitative investigations of sandbottom macrofauna along the Mediterranean North-West coast. Mar. Biol. 15, 209–220 (1972)
Maurer, D.: Pelecypod-sediment associations in Tomales Bay, California. Veliger 11, 243–249 (1969)
Maurer, D. Biological conditions of the deepwater portion of lower Delaware Bay, 94 pp. Rep. National Science Foundation/Research Applied to National Needs Program, College of Marine Studies, University of Delaware 1974. (Internal publication)
Maurer, D.: Estuarine benthic invertebrates of Indian River and Rehoboth Bays, Delaware. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. (In press)
—, J. Tinsman, W. Leathem and P. Kinner: Baseline study of Sussex County Delaware ocean outfalls, 287 pp. Sussex County, Delaware: Sussex County Engineers 1976
— and L. Watling: Studies on the oyster community in Delaware: the effects of the estuarine environment on the associated fauna. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 58, 161–201 (1973)
—— and G. Aprill: The distribution and ecology of common marine and estuarine pelecypods in the Delaware Bay area. Nautilus 88, 38–45 (1974)
McDermott, J.: The predations of oysters and barnacles by crabs of the family Xanthidae. Proc. Pa Acad. Sci. 34, 199–216 (1960)
—: Predation of the razor clam Ensis directus by the nemertean worm Cerebratulus lacteus. Chesapeake Sci. 17, 299–301 (1976)
McIntyre, A.D. and A. Eleftheriou: The bottom fauna of a flatfish nursery ground. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 48, 113–142 (1968)
Mills, E.L.: The community concept in marine zoology with comments on continua and instability in some marine communities. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 26, 1415–1428 (1969)
Muus, B.F.: The fauna of Danish estuaries and lagoons. Distribution and ecology of dominating species in the shallow reaches of the mesohaline zone. Meddr Danm. Fisk.-og Havunders. (N.S.) 5, 1–316 (1967)
O'Connor, J.S.: The macrofauna of Moriches Bay, New York. Biol. Bull. mar biol. Lab., Woods Hole 142, 84–102 (1972)
Oostdam, B.L.: Suspended sediment transport in Delaware Bay, 303 pp. Ph. D. Dissertation, University of Delaware 1971
Orth, R.J.: Benthic infauna of eelgrass, Zostera marina, beds. Chesapeake Sci. 14, 258–269 (1973)
Phelps, D.K.: Functional relationships of benthos in a coastal lagoon, 146 pp. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Rhode Island 1964
Polis, D.F. and S.L. Kupferman: Physical oceanography. Rep. Ser. Delaware Bay, Coll. mar. Stud. 4, 1–143 (1973)
Pratt, S.D.: Benthic fauna. Univ. Rhode Island Occ. Publs (Mar. Publ. Ser. No. 2) (1973)
Richards, H.G.: A faunistic survey of the marine invertebrates of New Jersey, with especial reference to the Cape May region, 108 pp. M. S. Thesis, University of Pennsylvania 1929
Rosenberg, R.: Succession in benthic macrofauna in a Swedish fjord subsequent to the closure of a sulphite pulp mill. Oikos 24, 244–258 (1973)
Rowe, G.T., P.T. Polloni and J.I. Rowe: Benthic community parameters in the lower Mystic River. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 57, 573–584 (1972)
Sanders, H.L.: Oceanography of Long Island Sound 1952–1954. X. Biology of marine bottom communities. Bull. Bingham oceanogr. Coll. 15, 345–414 (1956)
—: Benthic studies in Buzzards Bay. I. Animalsediment relationships. Limnol. Oceanogr. 3, 245–258 (1958)
—: Benthic studies in Buzzards Bay. III. The structure of the soft-bottom community. Limnol. Oceanogr. 5, 138–153 (1960)
—: Marine benthic diversity — a comparative study. Am. Nat. 102, 243–282 (1968)
Shuster, C.N.: Xiphosura. In: Treatise on ecology and paleoecology, pp 1171–1174. Ed. by J. W. Hedgpeth. New York: Geological Society of America 1957. (Mem. geol. Soc. Am. No. 67)
Smith, O.R.: Notes on the ability of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus, to locate soft-shell clams, Mya arenaria. Ecology 34, 636–637 (1953)
Smith, R.W.: An analysis of the summer flounder Paralichthys dentatus (Linnaeus), population in the Delaware Bay, 72 pp. Master's Thesis, University of Delaware 1969
Sneath, P.H.A. and R.R. Sokal: Numerical taxonomy, the principles and practice of numerical classification, 573 pp. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman & Co. 1973
Stephenson, W., Y.I. Raphael and S.D. Cook: The macrobenthos of Bramble Bay. Moreton Bay, Queensland. Mem. Qd Mus. 17, 425–447 (1976)
—, W.T. Williams and S.D. Cook: Computer analyses of Petersen's original data on bottom communities. Ecol. Monogr. 42, 387–415 (1972)
Thorson, G.: Bottom communities (sublittoral or shallow shelf). In: Treatise on marine ecology and paleoecology, pp 461–534. Ed. by J.W. Hedgpeth. New York: Geological Society of America 1957. (Mem. geol. Soc. Am. No. 67)
Watling, L.: Analysis of structural variations in a shallow estuarine deposit-feeding community. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 19, 275–313 (1975)
—, W. Leathem, P. Kinner, C. Wethe and D. Maurer: Evaluation of sludge dumping off Delaware Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 5, 39–42 (1974a)
—, J. Lindsay, R. Smith and D. Maurer: The distribution of Isopoda in the Delaware Bay region. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 59, 343–351 (1974b)
— and D. Maurer: Marine shallow water amphipods of the Delaware Bay area, U.S.A.. Crustaceana 1972 (Suppl. 3), 251–266 (1972a)
——: Shallow water hydroids of the Delaware Bay region. J. nat. Hist. 6, 643–649 (1972b)
Watling, L. and D. Maurer (Eds.): Ecological studies on benthic and planktonic assemblages in Lower Delaware Bay, 634 pp. Rep. National Science Foundation/ Research Applied to national Needs Program. College of Marine Studies, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 1976. (Internal publication)
Weil, C.: Dynamics of sedimentary facies in Delaware Bay, 300 pp. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Delaware 1976
Zaneveld, J.S.: The benthic marine algae of Delaware, U.S.A. Chesapeake Sci. 13, 120–138 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M.R. Tripp, Newark
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurer, D., Watling, L., Kinner, P. et al. Benthic invertebrate assemblages of Delaware Bay. Mar. Biol. 45, 65–78 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388978
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388978