Summary
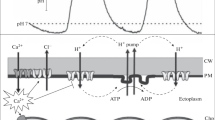
Some ionic relations of the filamentous green alga Mougeotia sp. have been analyzed under different light conditions. Data from influx and efflux measurements using 86Rb+ and 36Cl- fit the model of three cellular compartments (cell wall, cytoplasm, vacuole) in series. This result is remarkable, since in a Mougeotia cell at least two thirds of the cytoplasmic compartment are occupied by the cell-filling, flat and nearly rectangular chloroplast which is axially oriented. The chloroplast is concluded to be part of the cytoplasmic flux compartment.
Photosynthetically saturating irradiances of continuous white light enhance the active and passive fluxes of K+ and Cl- at the plasmalemma by a factor of 3. Photosystem II is responsible for the light-dependent increase of the uptake of Cl- (36Cl-) whereas the uptake of K+ (86Rb+) depends additionally on energy from photosystem I.
Ion flux measurements performed after irradiations with red and far-red, respectively, show that the fluxes of K+ and Cl- across the plasmalemma are not affected by the state of phytochrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber, J.: The efflux of potassium from Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 163, 531–538 (1968)
Bentrup, F. W.: Zur Funktion der Zellmembran bei der Cytomorphogenese. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 81, 311–314 (1968)
Briggs, W. R., Rice, H. V.: Phytochrome: Chemical and physical properties and mechanism of action. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 23, 293–334 (1972)
Cram, W. J.: Compartmentation and exchange of chloride in carrot root tissue. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 163, 339–353 (1968)
Cram, W. J.: Chloride fluxes in cells of the isolated root cortex of Zea mays. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 26, 757–779 (1973)
Filippis, L. F. de, Pallaghy, C. K.: Effect of light on the volume and ion relations of chloroplasts in detached leaves of Elodea densa. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 26, 1251–1265 (1973)
Gimmler, H., Ullrich, W., Domanski-Kaden, J., Urbach, W.: Excretion of glucolate during synchronous culture of Ankistrodesmus braunii in the presence of disalicylidenepropanediamine or hydroxypyridinemethanesulfonate. Plant and Cell Physiol. 10, 103–112 (1969)
Haupt, W.: Die Orientierung der Phytochrom-Moleküle in der Mougeotiazelle: Ein neues Modell zur Deutung der experimentellen Befunde. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 58, 331–346 (1968)
Haupt, W., Schönbohm, E.: Light-oriented chloroplast movements. In: Photobiology of microorganisms, P. Halldal, ed., pp. 283–307. New York-London-Sydney-Toronto: Wiley-Interscience 1970
Hope, A. B.: Ion transport and membranes. A biophysical outline. London: Butterworth 1971
Larkum, A. W.: Ionic relations of chloroplasts in vivo. Nature (Lond.) 218, 447–449 (1968)
MacRobbie, E. A. C.: The active transport of ions in plant cells. Quart. Rev. Biophys. 3, 251–294 (1970)
MacRobbie, E. A. C.: Fluxes and compartmentation in plant cells. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 22, 75–96 (1971)
MacRobbie, E. A. C., Dainty, J.: Sodium and potassium distribution and transport in the seaweed Rhodymenia palmata (L.). Grev. Physiol. Plantarum (Kbh.) 11, 782–801 (1958)
Nobel, P. S.: Light-induced changes in the ionic content of chloroplasts in Pisum sativum. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 172, 134–143 (1969)
Pierce, W. S., Higinbotham, N.: Compartments and fluxes of K+, na+ and Cl- in Avena coleoptile cells. Plant Physiol. 46, 666–673 (1970)
Pitman, M. G.: The determination of the salt relations of the cytoplasmic phase in cells of beetroot tissue. Aust. J. biol. Sci. 16, 647–668 (1963)
Rasmussen, H.: Cell communication, calcium ion and cyclic adenosine monophosphate. Science 170, 404–412 (1970)
Raven, J. A.: Action spectra for photosynthesis and light-stimulated ion transport processes in Hydrodictyon africanum. New Phytologist 68, 45–62 (1969a)
Raven, J. A.: Effects of inhibitors on photosynthesis and the active influxes of K and Cl in Hydrodictyon africanum. New Phytologist. 68, 1089–1113 (1969b)
Satter, R. L., Marinoff, P., Galston, A. W.: Phytochrome-controlled nyctinasty in Albizzia julibrissin. II. Potassium flux as a basis for leaflet movement. Amer. J. Bot. 57, 916–926 (1970)
Schäfer, E., Schmidt, W., Mohr, H.: Comparative measurements of phytochrome in cotyledons and hypocotyl hook of mustard (Sinapis alba L.). Photochem. Photobiol. 18, 331–334 (1973)
Sweet, H. C., Hillman, W. S.: Phytochrome control of nyctinasty in Samanea as modified by oxygen, submergence and chemicals. Physiol. Plantarum (Kbh.) 22, 776–786 (1969)
Umbreit, W. W., Burris, R. H., Stauffer, J. F.: Manometric techniques and tissue metabolism. Minneapolis: Burgess Publ. Co. 1951
Wagner, G.: Ionenflüsse und Phytochrom-abhängige Chloroplastenbewegung bei Mougeotia spec. Doct. dissert. Univ. Tübingen, W.-Germany (1974)
Wagner, G., Haupt, W., Laux, A.: Reversible inhibition of chloroplast movement by cytochalasin B in the green alga Mougeotia. Science 176, 808–809 (1972)
Weisenseel, M.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen zum Einfluß der Temperatur auf lichtinduzierte Chloroplastenverlagerungen. I. Die Wirkung verschiedener Licht-intensitäten auf die Chloroplastenanordnung und ihre Abhängigkeit von der Temperatur. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 59, 56–69 (1968)
Weisenseel, M., Smeibidl, E.: Phytochrome controls the water permeability in Mougeotia. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 70, 420–431 (1973)
Winocur, B. A., Macey, F. I., Tolberg, A. B.: Electrolyte exchange in isolated spinach chloroplasts. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 150, 32–40 (1968)
Yunghans, H., Jaffe, M. J.: Rapid respiratory changes due to red light or acetylcholine during the early events of phytochrome-mediated photomorphogenesis. Plant Physiol. 49, 1–7 (1972)
Ziegler, R., Egle, K.: Zur quantitativen Analyse der Chloroplastenpigmente. Beitr. Biol. Pflanzen 41, 11–37 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, G. Fluxes and compartmentation of potassium and chloride in the green alga Mougeotia . Planta 118, 145–157 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388390
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388390