Summary
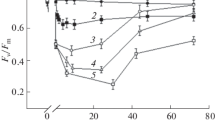
A new terminology for intermediates observed in the phototransformation of phytochrome (P) is proposed. At 0°C freeze dried tissue of Pisum sativum seedlings containing P in the red absorbing form (Pr) does not undergo complete photoconversion to the far red absorbing form (Pfr) but forms intermediates which revert to Pr in darkness. Use of low temperature techniques and comparison with reactions in fresh tissue allow identification of the intermediates with those observed earlier. They consist of a mixture of the first photoproduct, lumi-R and its dark relaxation product, meta-Ra. Similarly, Pfr forms a mixture of its first photoproduct, lumi-F and its dark relaxation product, meta-Fa. The dark reversion of lumi-R to Pr and of lumi-F to Pfr have also been observed in freeze-dried tissue. Reactions occurring in this material at 0°C are proposed to be essentially restricted to photoreactions of the chromophore and relaxations of the products. Before complete phototransformation of Pr to Pfr and vice versa is possible an aqueous matrix is required for protein/chromophore conformational relaxations to occur.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- P:
-
phytochrome
- Pr:
-
red absorbing form of P
- Pfr:
-
far red absorbing form of P
References
Balangé, A. P.: Spectral changes of phytochrome in glycerol solutions. Physiol. Vég. 12, 95–105 (1974)
Briggs, W. R., Fork, D. C.: Long-lived intermediates in phytochrome transformation. I. In vitro studies. Plant Physiol. 44, 1081–1088 (1969a)
Briggs, W. R., Fork, D. C.: Long-lived intermediates in phytochrome transformation. II. In vitro and in vivo studies. Plant Physiol. 44, 1089–1094 (1969b)
Briggs, W. R., Rice, H. V.: Phytochrome: chemical and physical properties and mechanism of action. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 23, 293–334 (1972)
Burke, M. J., Pratt, D. C., Moscowitz, A.: Low temperature absorption and circular dichroism studies of phytocnrome. Biochemistry 11, 4025–4031 (1972)
Butler, W. L., Hendricks, S. B., Siegelman, H. W.: Action spectra of phytochrome in vitro. Photochem. Photobiol. 3, 521–528 (1964)
Grill, R., Spruit, C. J. P.: Properties of phytochrome in gymnosperms. Planta (Berl.) 108, 203–213 (1972)
Kendrick, R. E.: Phytochrome intermediates in freeze-dried tissue. Nature (Lond.) 250, 159–161 (1974)
Kendrick, R. E., Frankland, B.: Photocontrol of germination in Amaranthus caudatus. Planta (Berl.) 85, 326–339 (1969)
Kendrick, R. E., Russell, J. H.: Photomanipulation of phytochrome in lettuce seeds. Plant Physiol. (in press)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P.: Light maintains high levels of phytochrome intermediates. Nature (Lond.) New Biol. 237, 281–282 (1972a)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P.: Phytochrome decay in seedlings under continuous incandescent light. Planta (Berl.) 107, 341–350 (1972b)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P.: Phytochrome intermediates in vivo. I. Effects of temperature, light intensity, wavelength and oxygen on intermediate accumulation. Photochem. Photobiol. 18, 139–144 (1973a)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P.: Phytochrome intermediates in vivo. III. Kinetic analysis of intermediate reactions at low temperature. Photochem. Photobiol. 18, 153–159 (1973b)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P.: Phytochrome properties and the molecular environment. Plant Physiol. 52, 327–333 (1973c)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P.: Inverse dark reversion of phytochrome: An explanation. Planta (Berl.) 120, 265–272 (1974)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P.: Intermediates in the photoconversion of phytochrome. In: Light and plant development (H. Smith, ed.). Proceedings of the 22nd Easter School in Agricultural Science, University of Nottingham. London: Butterworth (in press)
Kendrick, R. E., Spruit, C. J. P., Frankland, B.: Phytochrome in seeds of Amaranthus caudatus. Planta (Berl.) 88, 293–302 (1969)
Linschitz, H., Kasche, V., Butler, W. L., Siegelman, H. W.: The kinetics of phytochrome conversion. J. biol. Chem. 241, 3395–3403 (1966)
McArthur, J. A., Briggs, W. R.: Phytochrome appearence and distribution in the embryonic axis and seedlings of Alaska peas. Planta (Berl.) 91, 146–154 (1970)
Pratt, L. H., Butler, W. L.: Stabilization of phytochrome intermediates by low temperature. Photochem. Photobiol. 8, 477–485 (1968)
Rüdiger, W., Correll, D. L.: Über die Struktur des Phytochrom-Chromophors und seine Protein-Bindung. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 723, 208–212 (1969)
Smith, H., Kendrick, R. E.: The structure and properties of phytochrome. In: Chemistry and biochemistry of plant pigments (Goodwin, ed.), 2nd ed., volume 2. London and New York: Academic Press (in press)
Spruit, C. J. P.: Spectral observations related to the red-far red antagonism in plants. In: Currents in photosynthesis (J. B. Thomas and J. C. Goedheer, eds.), p. 67. Rotterdam: Donker 1966a
Spruit, C. J. P.: Thermal reactions following illumination of phytochrome. Meded. Land-bouwhogeschool Wageningen 66, 1–15 (1966b)
Spruit, C. J. P.: Photoreversible pigment transformations in etiolated plants. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 120, 186–188 (1966c)
Spruit, C. J. P.: Low temperature action spectra for phototransformation of photoperiodic pigments. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 120, 454–456 (1966d)
Spruit, C. J. P.: Spectrophotometers for the study of phytochrome in vivo. Meded. Landbouwhogeschool Wageningen 70, 1–14 (1970)
Spruit, C. J. P., Kendrick, R. E.: Phytochrome intermediates in vivo. II. Characterization of intermediates by difference spectrophotometry. Photochem. Photobiol. 18, 145–152 (1973)
Tobin, E. M., Briggs, W. R.: Phytochrome in embryos of Pinus palustris. Plant Physiol. 44, 148–150 (1969)
Tobin, E. M., Briggs, W. R., Brown, P. K.: The role of hydration in the phototransformation of phytochrome. Photochem. Photobiol. 18, 497–503 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spruit, C.J.P., Kendrick, R.E. & Cooke, R.J. Phytochrome intermediates in freeze-dried tissue. Planta 127, 121–132 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388373
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388373