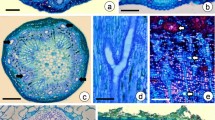
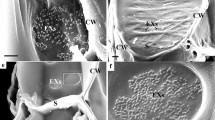
Abstract
The peripheral secretion tissue of the root cap of Lepidium sativum L. was investigated by electronmicroscopy and freeze-fracturing in order to study structural changes of membranes involved in the secretion process of polysaccharide slime. Exocytosis of slime-transporting vesicles occurs chiefly in the distal region of the anticlinal cell walls. The protoplasmic fracture face (PF) of the plasmalemma of this region is characterized by a high number of homogenously distributed intramembranous particles (IMPs) interrupted by areas nearly free of IMPs. Near such areas slime-transporting vesicles are found to be underlying the plasma membrane. It can be concluded that areas poor in particles are prospective sites for membrane fusion. During the formation of slime-transporting vesicles, the number of IMPs undergoes a striking change in the PF of dictyosome membranes and their derivatives. It is high in dictyosome cisternae and remarkably lower in the budding region at the periphery of the cisternae. Slime-transporting vesicles are as poor in IMPs as the areas of the plasmalemma. Microvesicles rich in IMPs are observed in the surroundings of dictyosomes. The results indicate that in the plasmalemma and in membranes of the Golgi apparatus special classes of proteins — recognizable as IMPs — are displaced laterally into adjacent membrane regions. Since the exoplasmic fracture face (EF) of these membranes is principally poor in particles, it can be concluded that membrane fusion occurs in areas characterized by a high quantity of lipid molecules. It is obvious that the Golgi apparatus regulates the molecular composition of the plasma membrane by selection of specific membrane components. The drastic membrane transformation during the formation of slime-transporting vesicles in the Golgi apparatus causes the enrichment of dictyosome membranes by IMPs, whereas the plasma membrane probably is enriched by lipids. The structural differentiations in both the plasma membrane and in Golgi membranes are discussed in relation to membrane transformation, membrane flow, membrane fusion, and recycling of membrane constituents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PF:
-
protoplasmic fracture face
- EF:
-
exoplasmic fracture face
- IMP:
-
intramembranous particle
References
Branton, D., Bullivant, S., Gilula, N.B., Karnovsky, M.J., Moor, H., Mühlethaler, K., Northcote, d.H., Packer, L., Satir, B., Satir, P., Speth, V., Staehelin, L.A., Steere, R.L., Weinstein, R.S. (1975) Freeze-etching nomenclature. Science 190, 54–56
Branton, D., Deamer, D.W. (1972) Membrane structure. In: Protoplasmatologia, vol. II/E/1, Alfert, M., Bauer, H., Sandritter, W., Sitte, P., eds. Springer, Wien New York
Branton, D., Moor, H. (1964) Fine structure in freeze-etched Allium cepa L. root tips. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 11, 401–411
Camilli de, P., Peluchetti, D., Meldolesi, J. (1976) Dynamic changes of the luminal plasmalemma in stimulated parotic acinar cells. A freeze-fracture study. J. Cell Biol. 70, 59–74
Chailley, B. (1979) Etude par cryofracture des membranes impliquées dans la sécrétion. Biol. Cellulaire 35, 55–70
Chandler, D.E., Heuser, J. (1979) Membrane fusion during secretion. Cortical granule exocytosis in sea urchin eggs as studied by quick-freezing and freeze-fracture. J. Cell Biol. 83, 91–108
Chandler, D.E., Heuser, J.E. (1980) Arrest of membrane fusion events in mast cells by quick-freezing. J. Cell Biol. 86, 666–674
Chi, E.Y., Lagunoff, D., Koehler, J.K. (1976) Freeze-fracture study for mast cell secretion. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 73, 2823–2827
Giddings, T.H. Jr., Brower, D.L., Staehelin, L.A. (1980) Visualization of particle complexes in the plasma membrane of Micraterias denticulata associated with the formation of cellulose fibrils in primary and secondary cell walls. J. Cell Biol. 84, 327–339
Gros, D., Potreau, D., Mocquard, J.-P. (1980) The myocardial plasma membrane during development: Influence of glutaraldehyde fixation on the density and size of intramembranous particles. J. Cell Sci. 43, 301–317
Grove, S.N., Bracker, C.E., Morré, D.J. (1968) Cytomembrane differentiation in the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi apparatusvesicle complex. Science 161, 171–173
Hasty, D.L., Hay, E.D. (1978) Freeze-fracture studies of the developing cell surface. II. Particle-free membrane blisters on glutaraldehyde-fixed corneal fibroblasts are artefacts. J. Cell Biol. 78, 756–768
Hemmes, D.E., Pinto da Silva, P. (1980) Localization of secretion-related, calcium-binding substrates in encysting zoospores of Phytophthora palmivora. Biol. Cellulaire 37, 235–240
Keenan, T.W., Morré, D.J. (1970) Phospholipid class and fatty acid composition of Golgi apparatus isolated from rat liver and comparison with other cell fractions. Biochemistry 9, 19–25
Kiermayer, O. (1970) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zum Problem der Cytomorphogenese von Micrasterias denticulata Bréb. I. Allgemeiner Überblick. Protoplasma 69, 97–132
Kiermayer, O., Dobberstein, B. (1973) Membrankomplexe dictyosomaler Herkunft als “Matrizen” für die extraplasmatische Synthese und Orientierung von Mikrofibrillen. Protoplasma 77, 437–451
Kiermayer, O., Sleytr, U.B. (1979) Hexagonally ordered “rosettes” of particles in the plasma membrane of Micrasterias denticulata Bréb. and their significance for microfibril formation and orientation. Protoplasma 101, 133–138
Kiermayer, O., Staehelin, L.A. (1972) Feinstruktur von Zellwand und Plasmamembran bei Micrasterias denticulata Bréb. nach Gefrierätzung. Protoplasma 74, 227–237
Lawson, D., Raff, M.C., Gomperts, B., Fewtrell, C., Gilula, N.B. (1977) Molecular events during membrane fusion. A study of exocytosis in rat peritoneal mast cells. J. Cell Biol. 72, 242–259
Lüttge, U., Schnepf, E. (1976) Organic substances. In: Encyclopedia of plant physiology, vol. 2, pt. B, pp. 244–277, Lüttge, U., Pitman, M.G., eds. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Mollenhauer, H.H., Hass, B.S., Morré, D.J. (1976) Membrane transformations in Golgi apparatus of rat spermatids. A role for thick cisternae and two classes of coated vesicles in acrosome formation. J. Microsc. Biol. Cell 27, 33–36
Mollenhauer, H.H., Morré, D.J. (1966) Golgi apparatus and plant secretion. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 17, 27–46
Mollenhauer, H.H., Whaley, W.G., Leech, J.H. (1961) A function of the Golgi apparatus in outer rootcap cells. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 5, 193–200
Moor, H., Mühlethaler, K. (1963) Fine structure in frozen-etched yeast cells. J. Cell Biol. 17, 609–628
Morré, D.J., Jones, D.D., Mollenhauer, H.H. (1967) Golgi apparatus mediated polysaccharide secretion by outer root cap cells of Zea mays. I. Kinetics and secretory pathway. Planta 74, 286–301
Morré, D.J., Mollenhauer, H.H., Bracker, C.E. (1971) Origin and continuity of Golgi apparatus. In: Results and problems in cell differentiation, vol. 2, pp. 82–126, Reinert, J., Ursprung, H., eds. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Morré, D.J., Ovtracht, L. (1977) Dynamics of the Golgi apparatus: Membrane differentiation and membrane flow. Int. Rev. Cytol. Suppl. 5, 61–188
Northcote, D.H., Lewis, D.R. (1968) Freeze-etched surfaces of membranes and organelles in the cells of pea root tips. J. Cell Sci. 3, 199–206
Northcote, D.H., Pickett-Heaps, J.D. (1966) A function of the Golgi apparatus in polysaccharide synthesis and transport in root-cap cells of wheat. Biochem. J. 98, 159–167
Orci, L., Perrelet, A., Friend, S. (1977) Freeze-fracture of membrane fusions during exocytosis in pancreatic B-cells. J. Cell Biol. 75, 23–30
Papahadjopoulos, D., Poste, G., Schaeffer, B.E., Vail, W.J. (1974) Membrane fusion and molecular segregation in phospholipid vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 352, 10–28
Peng, H.B., Jaffe, L.F. (1976) Cell-wall formation in Pelvetia embryos. A freeze-fracture study. Planta 133, 57–71
Pinto da Silva, P., Nougeira, M.L. (1977) Membrane fusion during secretion. A hypothesis based on electron microscope observation of Phytophthora palmivora zoospores during encystment. J. Cell Biol. 73, 161–181
Robinson, D.G., Preston, R.D. (1971) Fine structure of swarmers of Cladophora and Chaetomorpha. I. The plasmalemma and Golgi apparatus in naked swarmers. J. Cell Sci. 9, 581–601
Schnepf, E. (1969) Sekretion und Exkretion bei Pflanzen. In: Protoplasmatologia, vol. VIII/8, Alfert, M., Bauer, H., Harding, C.V., Sandritter, W., Sitte, P., eds. Springer, Wien New York
Severs, N.J., Hicks, R.M. (1979) Analysis of membrane structure in the transitional epithelium of rat urinary bladder. 2. The discoidal vesicles and Golgi apparatus: Their role in luminal membrane biogenesis. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 69, 279–296
Sievers, A. (1967) Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur geotropischen Reaktion. II. Die polare Organisation des normal wachsenden Rhizoids von Chara foetida. Protoplasma 64, 255–253
Sievers, A. (1973) Golgi-Apparat. In: Grundlagen der Cytologie, pp. 281–296, Hirsch, G.C., Ruska, H., Sitte, P., eds. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart
Staehelin, L.A., Kiermayer, O. (1970) Membrane differentiation in the Golgi complex of Micrasterias denticulata Bréb. visualized by freeze-etching. J. Cell Sci. 7, 787–792
Vian, B. (1974) Précisions fournies par le cryodécapage sur la restructuration et l'assimilation au plasmalemme des membranes des dérivés golgiens. C.R. Acad. Sci., D, 278, 1483–1486
Whaley, W.G. (1966) Proposals concerning replication of the Golgi apparatus. In: Funktionelle und morphologische Organisation der Zelle. 3. wiss. Konf. Ges. Dtsch. Naturf. u. Ärzte: Probleme der biologischen Reduplikation, pp. 340–371, Sitte, P., ed. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Whaley, W.G., Dauwalder, M. (1979) The Golgi apparatus, the plasma membrane, and functional integration. Int. Rev. Cytol. 58, 199–245
Yunghans, W., Keenan, T.W., Morré, D.J. (1970) Isolation of a Golgi apparatus-rich cell fraction from rat liver. III. Lipid and protein composition. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 12, 36–45
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkmann, D. Structural differentiation of membranes involved in the secretion of polysaccharide slime by root cap cells of cress (Lepidium sativum L.). Planta 151, 180–188 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387821
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387821