Summary
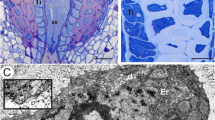
Portions of the hypocotyls of 16-day-old Cucurbita maxima plants, from which the cotyledons and first foliage leaves had been removed 2 days earlier, were fixed in glutaraldehyde and postfixed in osmium tetroxide for electron microscopy. In well over 90% of the mature sieve elements examined the P-protein was entirely parietal in distribution in both the lumina and sieve-plate pores. In addition to the parietal P-protein, the unoccluded sieve-plate pores were lined by narrow callose cylinders and the plasmalemma. Segments of endoplasmic reticulum also occurred along the margins of the pores.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R., Cronshaw, J.: Sieve-plate pores in tobacco and bean. Planta (Berl.) 91, 173–180 (1970).
Cronshaw, J., Anderson, R.: Sieve plate pores of Nicotiana. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 27, 134–148 (1969).
Cronshaw, J., Anderson, R.: Phloem differentiation in tobacco pith culture. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 34, 244–259 (1971).
Cronshaw, J., Esau, K.: P protein in the phloem of Cucurbita. I. The development of P-protein bodies. J. Cell Biol. 38, 25–39 (1968a).
Cronshaw, J., Esau, K.: P protein in the phloem of Cucurbita. II. The P protein of mature sieve elements. J. Cell Biol. 38, 292–303 (1968b).
Esau, K., Cronshaw, J.: Endoplasmic reticulum in the sieve elements of Cucurbita. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 23, 1–14 (1968).
Evert, R. F., Bornman, C. H., Butler, V., Gilliland, M. G.: Structure and development of the sieve-cell protoplast in leaf veins of Welwitschia. Protoplasma (Wien), in press (1972a).
Evert, R. F., Bornman, C. H., Butler, V., Gilliland, M. G.: Structure and development of sieve areas in leaf veins of Welwitschia. Protoplasma (Wien), in press (1972b).
Evert, R. F., Deshpande, B. P.: Electron microscope investigation of sieve-element ontogeny and structure in Ulmus americana. Protoplasma (Wien) 68, 403–432 (1969).
Evert, R. F., Eschrich, W., Eichhorn, S. E.: Sieve-plate pores in leaf veins of Hordeum vulgare. Planta (Berl.) 100, 262–267 (1971).
Evert, R. F., Murmanis, L., Sachs, I. B.: Another view of the ultrastructure of Cucurbita phloem. Ann. Bot. 30, 563–585 (1966).
Evert, R. F., Tucker, C. M., Davis, J. D., Deshpande, B. P.: Light microscope investigation of sieve-element ontogeny and structure in Ulmus americana. Amer. J. Bot. 56, 999–1017 (1969).
Fensom, D. S.: A theory of translocation in phloem of Heracleum by contractile protein microfibrillar material. Canad. J. Bot. 50, 479–497 (1972).
Johnson, R. P. C.: Microfilaments in pores between frozen-etched sieve elements. Planta (Berl.) 81, 314–332 (1968).
Kleinig, H., Dörr, I., Weber, C., Kollmann, R.: Filamentous proteins from plant sieve tubes. Nature N. B. (Lond.) 229, 152–153 (1971).
Kollmann, R., Schumacher, W.: Über die Feinstruktur des Phloems von Metasequoia glyptostroboides und seine jahreszeitlichen Veränderungen. V. Die Differenzierung der Siebzellen im Verlaufe einer Vegetationsperiode. Planta (Berl.) 63, 155–190 (1964).
MacRobbie, E. A. C., Phloem translocation. Facts and mechanisms: a comparative survey. Biol. Rev. 46, 429–481 (1971).
Maxe, M.: Étude de la dégénérescence nucléaire dans les cellules criblées de Polypodium vulgare (Polypodiacée). C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 262, 2211–2214 (1966).
Mishra, U., Spanner, D. C.: The fine structure of the sieve tubes of Salix caprea (L.) and its relation to the electro-osmotic theory. Planta (Berl.) 90, 43–56 (1970).
Siddiqui, A. W., Spanner, D. C.: The state of the pores in functioning sieve plates. Planta (Berl.) 91, 181–189 (1970).
Singh, A. P., Srivastava, L. M.: The fine structure of corn phloem. Canad. J. Bot. 50, 839–846 (1972).
Spanner, D. C.: Transport in the phloem. Nature (Lond.) 232, 157–160 (1971).
Spanner, D. C., Jones, R. L.: The sieve tube wall and its relation to translocation. Planta (Berl.) 92, 64–72 (1970).
Thaine, R.: A translocation hypothesis based on the structure of plant cytoplasm. J. exp. Bot. 13, 152–160 (1962).
Thaine, R.: Movement of sugars through plants by cytoplasmic pumping. Nature (Lond.) 222, 873–875 (1969).
Webb, J. A., Gorham, P. R.: Translocation of photosynthetically assimilated C14 in straight-necked squash. Plant Physiol. 39, 663–672 (1964).
Williamson, R. E.: An investigation of the contractile protein hypothesis of phloem translocation. Planta (Berl.) 106, 149–159 (1972).
Wooding, F. B. P.: Fine structure and development of phloem sieve tube content. Protoplasma (Wien) 64, 315–324 (1967).
Wooding, F. B. P.: P protein and microtubular systems in Nicotiana callus phloem. Planta (Berl.) 85, 284–298 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evert, R.F., Eschrich, W. & Eichhorn, S.E. P-protein distribution in mature sieve elements of Cucurbita maxima . Planta 109, 193–210 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387084
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387084