Summary
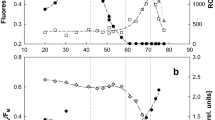
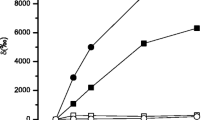
The uptake of labelled thallous ion into the interior of Chlorella fusca is enhanced by light. This is ascribed to active transport by way of the K (and Rb) pump. The Michaelis constants differ between the higher and the lower concentration ranges, but they are similar for Rb and Tl.
The additional, rapid, light-independent adsorption of Tl, mainly by the cell wall, is stronger than that of the alkali ions, but weaker than that of divalent cations. The adsorbed Tl is subject to elution by complexing agents (probably mainly glycolic acid) secreted by the cells, especially in the light.
In spite of the similarity of the Michaelis constants, the inhibition of the light-dependent uptake of labelled Rb by unlabelled Tl is far stronger than the inhibition of Tl uptake by Rb. The efficiency of Tl may be due to double action: namely, competition with Rb for the carrier and negative influence on a transport ATPase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Britten, J. S., Blank, M.: Thallium activation of the (Na−K) activated ATPase of rabbit kidney. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 159, 160–166 (1968).
Cohen, D.: Specific binding of rubidium in Chlorella. J. gen. Physiol. 45, 959–977 (1962).
Findenegg, G. R., Paschinger, H., Broda, E.: Untersuchung der Lichtabhängigkeit der Aufnahme von Rubidium, Zink, Kobalt, Blei und Cer durch Chlorella nach einer Flußmethode. Planta (Berl.) 99, 163–173 (1971).
—, Springer-Lederer, H.: Apparat zur laufenden Gewinnung von Chlorella-Algen für chemische Untersuchungen. Allg. prakt. Chem. 18, 279–280 (1967).
Gehring, P. J., Hammond, P. B.: The interrelation between thallium and potassium in animals. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 155, 187–201 (1967).
Hess, J. L., Tolbert, N. E.: Glycolate pathway in algae. Plant Physiol. 42, 371–379 (1967).
Inturrisi, C. E.: Thallium activation of K-activated phosphatases from beef brain. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 173, 567–569 (1969).
—: Thallium-induced dephosphorylation of a phosphorylated intermediate of the (sodium+thallium-activated) ATPase. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 178, 630–633 (1969).
Kayne, F. J.: Thallium activation of pyruvate kinase. Arch. Biochem. 143, 232–239 (1971).
Nightingale, E. R.: Phenomenological theory of ion solvation. Effective radii of hydrated ions. J. phys. Chem. 63, 1381–1387 (1959).
Schmid, W. E.: Influence of thallous ions on the transport of certain cations by excised barley roots. Trans. Ill. State Acad. Sci. 60, 61–67 (1967).
Springer-Lederer, H., Rosenfeld, D. L.: Energy sources for the absorption of rubidium by Chlorella. Physiol. Plantarum (Cph.) 21, 435–444 (1968).
Tolbert, N. E., Zill, L. P.: Excretion of glycolic acid by algae during photosynthesis. J. biol. Chem. 222, 895–906 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. H. Nowotny gewidmet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solt, J., Paschinger, H. & Broda, E. Die energieabhängige Aufnahme von Thallium durch Chlorella . Planta 101, 242–250 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386831
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386831