Abstract
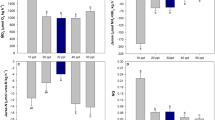
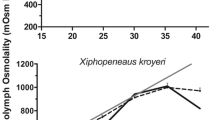
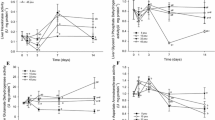
Mytilus edulis L. were exposed to abrupt (30‰→15‰ and 15‰→30‰) and fluctuating (sinusoidal 12 h cycles of 30‰→15‰→30‰) changes in salinity, and the changes in the total osmoconcentration of the haemolymph were recorded. The response of nitrogen metabolism to the altered extracellular osmotic concentrations was investigated in terms of the concentrations of the total NPS (ninhydrin-positive substances) pool and the individual amino acids of the tissues, the concentration of the amino acids of the haemolymph, and the rates of excretion of ammonia and amino acids by whole individuals. The haemolymph became isosmotic with the seawater with abrupt changes in salinity, but with fluctuating salinity was slightly hyperosmotic as the salinity decreased and then slightly hypo-osmotic as the salinity increased. This resulted in a reduction in the extent of the extracellular osmotic change compared to the change in fluctuating salinity to which it was exposed. Total NPS of the tissues decreased with an abrupt decrease in salinity and increased with an abrupt increase in salinity, but a seasonal dependence of the response was indicated. The short-term response of tissue NPS to fluctuating salinity was equivocal, but with long-term exposure the concentration declined. Ammonia and amino acid excretion increased with both an abrupt decrease in salinity and fluctuating salinity and decreased with an abrupt increase in salinity. Haemolymph amino acids increased with an abrupt decrease in salinity. The increased rates of nitrogen excretion accounted for the reductions in the NPS concentrations of the tissues except in the early stages of fluctuating salinity. Taurine, aspartate, threonine, serine, glycine and arginine declined with an abrupt decrease in salinity while alanine and glutamate increased slightly. With an abrupt increase in salinity, alanine and ammonia accumulated in the tissues and then declined while the other amino acids increased slowly over a longer time-course. Similar individual amino acid responses were seen with long-term exposure to fluctuating salinity, except for taurine which did not decrease in concentration. On the basis of the changes in tissue amino acids and ammonia, it is suggested that the “alanine dehydrogenase reaction” is the primary nitrogen-fixing reaction in marine bivalves such as M. edulis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Anderson, J.W. and W.B. Bedford: The physiological responses of the estuarine clam, Rangia cuneata (Gray), to salinity. II. Uptake of glycine. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 144, 229–247 (1973)
Baginski, R.M. and S.K. Pierce, Jr.: Anaerobicsis: a possible source of osmotic solute for high-salinity acclimation in marine molluscs. J. exp. Biol. 62, 589–598 (1975)
——: The time course of intracellular free amino acid accumulation in tissues of Modiolus demissus during high salinity adaptation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 57A, 407–412 (1977)
——: A comparison of amino acid accumulation during high salinity adaptation with anaerobic metabolism in the ribbed mussel, Modiolus demissus. J. exp. Zool. 203, 419–428 (1978)
Barnes, H. and J. Blackstock: The separation and estimation of free amino acids, trimethyl-amine oxide, and betaine in tissues and body fluids of marine invertebrates. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 16, 29–45 (1974)
Bartberger, C.A. and S.K. Pierce, Jr.: Relationship between ammonia excretion rates and hemolymph nitrogenous compounds of a euryhaline bivalve during low salinity acclimation. Biol. Bull. mar. Biol. Lab., Woods Hole 150, 1–14 (1976)
Bayne, B.L.: Aspects of physiological condition in Mytilus edulis L., with special reference to the effects of oxygen tension and salinity. Proc. 9th Eur. mar. Biol. Symp. 213–238 (1975). (Ed. by H. Barnes. Aberdeen: Aberdeen University Press)
— and C. Scullard: Rates of nitrogen excretion by species of Mytilus (Bivalvia: Mollusca). J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57, 355–369 (1977)
—, R.J. Thompson and J. Widdows: Physiology: I. In: Marine mussels. International Biological Programme Vol. 10, pp 121–206. Ed. by B. L. Bayne. Cambridge: University Press 1976a)
—, J. Widdows and R.J. Thompson: Physiology: II. In: Marine mussels. International Biological Programme, Vol. 10, pp 207–260. Ed. by B.L. Bayne. Cambridge: University Press 1976b)
Bedford, J.J.: Osmoregulation in Melanopsis trifasciata Gray 1843 — III. The intracellular nitrogenous compounds. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 40A, 899–910 (1971a)
—: Osmoregulation in Melanopsis trifasciata — IV. The possible control of intracellular isosmotic regulation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 40A, 1015–1027 (1971b)
Bishop, S.H.: Nitrogen metabolism and excretion: regulation of intracellular amino acid concentrations. In: Estuarine processes, Vol. I. pp 414–431. Ed. by M. Wiley, New York: Academic Press Inc. 1976
Bricteux-Gregoire, S., G. Duchâteau-Bosson, C. Jeuniaux et M. Florkin: Constituants osmotiquement actifs des muscles adducteurs de Mytilus edulis adaptée à l'eau saumâtre. Archs int. Physiol. Biochim. 72, 116–123 (1964)
Campbell, J.W. and S.H. Bishop: Nitrogen metabolism in molluscs. In: Comparative biochemistry of nitrogen metabolism, Vol. I. pp 103–206. Ed. by J.W. Cambell. New York and London: Academic Press 1970
DuPaul, W.D. and K.L. Webb: The effect of temperature on salinity-induced changes in the free amino acid pool of Mya arenaria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 32, 785–801 (1970)
Florkin, M. and E. Schoffeniels: Molecular approaches to ecology, 203 pp. New York and London: Academic Press 1969)
Furlong, C.E. and L.A. Heppel: Leucine binding proteins from Escherichia coli. Meth. Enzym. 17 (B), 639–643 (1971)
Gabbot, P.A. Energy metabolism. In: Marine mussels. International Biological Programme Vol. 10, pp 293–355. Ed. by B. L. Bayne. Cambridge: University Press 1976
Gilles, R.: Osmoregulation in three molluscs: Acanthochitona discrepans (Brown), Glycymeris glycymeris (L.) and Mytilus edulis (L.). Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 142, 25–35 (1972)
Hand, S.C. and W.B. Stickle: Effects of tidal fluctuations of salinity on pericardial fluid composition of the American oyster Crassostrea virginica. Mar. Biol. 42, 259–271 (1977)
H.M. Stationery Office: Interpolation and allied tables, 80 pp. London: 1956
Hoyaux, J., R. Gilles and Ch. Jeuniaux: Osmoregulation in molluscs of the intertidal zone. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 53A, 361–365 (1976)
Lange, R.: The osmotic function of amino acids and taurine in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 10, 173–179 (1963)
—: Some recent work on osmotic, ionic and volume regulation in marine animals. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 10, 97–135 (1972)
Livingstone, D.R. and B.L. Bayne: Pyruvate kinase from the mantle tissue of Mytilus edulis L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 48B, 481–497 (1974)
Matheson, A.T. and B.L. Tattrie: A modified Yemm and Cocking ninhydrin reagent for peptidase assay. Can. J. Biochem. 42, 95–103 (1964)
North, B.B.: Primary amines in California coastal waters: utilization by phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20, 20–27 (1975)
Dierce, S.K. Jr.: A source of solute for volume regulation in marine mussels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 38A, 619–635 (1971)
— and M.J. Greenberg: The nature of cellular volume regulation in marine bivalves. J. exp. Biol. 57, 681–692 (1972)
Potts, W.T.W.: The inorganic composition of the blood of Mytilus edulis and Anodonta cygnea. J. exp. Biol. 31, 376–385 (1954)
—: The inorganic and amino acid composition of some lamellibranch muscles. J. exp. Biol. 35, 749–764 (1958)
Reiss, P.M., S.K. Pierce and S.H. Bishop: Glutamate dehydrogenases from tissues of the ribbed mussel Modiolus demissus: ADP activation and possible physiological significance. J. exp. Zool. 202, 253–258 (1977)
Schoffeniels, E. and R. Gilles: Ionoregulation and osmoregulation in Mollusca. In: Chemical zoology, Vol. VII. pp 393–420. Ed. by M. Florkin and B.T. Scheer. New York and London: Academic Press 1972
Shumway, S.E.: Effect of salinity fluctuation on the osmotic pressure and Na+, Ca2+ and Mg2+ ion concentrations in the hemolymph of bivalve molluscs. Mar. Biol. 41, 153–177 (1977a)
—: The effect of fluctuating salinity on the tissue water content of eight species of bivalve molluscs. J. comp. Physiol. (Part B) 116, 269–285 (1977b)
—, P.A. Gabbott and A. Youngson: The effect of fluctuating salinity on the concentrations of free amino acids and ninhydrin-positive substances in the adductor muscles of eight species of bivalve molluscs. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 29, 131–150 (1977)
Solórzano, L.: Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenol-hypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 799–801 (1969)
Stickle, W.B. and R. Ahokas: The effects of tidal fluctuations of salinity on the perivisceral fluid composition of several echinoderms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 47A, 469–476 (1974)
——: The effects of tidal fluctuations of salinity on the hemolymph composition of several molluscs. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 50A, 291–296 (1975)
Virkar, R.A. and K.L. Webb: Free amino acid composition of the soft-shell clam Mya arenaria in relation to salinity of the medium. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 32, 775–783 (1970)
Widdows, J.: The effects of fluctuating and abrupt changes in salinity on the feeding and metabolic responses of Mytilus edulis. (In preparation)
Widdows, J. and D.R. Livingstone: Adaptation of Mytilus edulis to fluctuating and abrupt changes in salinity. Volume regulation and water content. (In preparation)
Zwaan, A. de: Anaerobic energy metabolism in bivalve molluscs. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 15, 103–187 (1977)
— and W.J.A. van Marrewijk: Anaerobic glucose degradation in the sea mussel Mytilus edulis L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 44B, 429–439 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Mauchline, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Livingstone, D.R., Widdows, J. & Fieth, P. Aspects of nitrogen metabolism of the common mussel Mytilus edulis: Adaptation to abrupt and fluctuating changes in salinity. Mar. Biol. 53, 41–55 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386528
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386528