Abstract
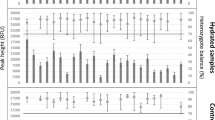
The aim of the reported study was to investigate the reproducibility of the single-cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) assay in the determination of DNA single-strand breaks (SSBs) and to estimate the statistical requirements when the SCGE assay is used for the detection of genotoxicity in humans. In human peripheral mononuclear leukocytes (PMLs), we repeatedly measured the rate of SSBs after in vitro incubation of cells for 1 h at 4°C in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, basal) or 10 μM or 50 μM H2O2 (induced). Intra-assay variation was determined from cryopreserved PMLs of a single donor. To assess intrasubject and intersubject variation, PMLs of ten healthy, nonsmoking subjects (aged 19–37 years) were tested 5–9 times. Cryopreserved cells revealed a mean coefficient of variation of 18% (PBS) and 7%–9% (H2O2). There were statistically significant differences between individuals in the rate of SSBs after incubation in PBS (P < 0.01), 10 μM H2O2 (P < 0.001), and 50 μM H2O2 (P < 0.001). The range of interindividual variability was 26% for basal and 12%–13% for induced SSBs, and the coefficient of intraindividual variation was 18%–72% (PBS) and 7%–23% (H2O2). Neither basal nor induced rates of DNA damage were related to gender or age. Estimates of the minimum detectable effects were based on these observed sources of variability (power 90%, level of significance 5%, assumed sample size 50). With two different groups, a difference of 31% in basal SSBs or 12% in induced SSBs would be detectable. Repeated measurement within one group could detect a difference of 26% in basal and 9% in induced SSBs. In summary, the SCGE assay appears to be suitable for the detection of single-strand breaks, e.g., in biomonitoring or environmental medicine, and the statistical requirements could be derived from our analysis of the sources of variability.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson D, Yu TW, Phillips BJ, Schmezer P (1994) The effect of various antioxidants and other modifying agents on oxygen-radical-generated DNA damage in human lymphocytes in the comet assay. Mutat Res 307:261–271
Boyum A (1977) Separation of lymphocytes, lymphocyte subgroups and monocytes. A review. Lymphology 10:71–76
Carrano AV, Minkler JL, Stetka DG, Moore DH II (1980) Variation in the baseline sister chromatid exchange frequency in human lymphocytes. Environ Mutagen 2:325–337
De Meo M, Laget M, Castegnaro M, Dumenil G (1991) Genotoxic activity of potassium permanganate in acidic solutions. Mutat Res 260:295–306
Gedik CM, Ewen SWB, Collins AR (1991) Single cell gel electrophoresis applied to the analysis of UV-C damage and its repair in human cells. Int J Radiat Biol 62:313–320
Hartung J, Elpelt B, Klösener KH (1985) Statistik. R. Oldenbourg, Munich Vienna
Holz O, Meißner R, Einhaus M, Koops F, Warncke K, Scherer G, Adlkofer F, Baumgartner E, Rüdiger HW (1993) Detection of DNA single-strand breaks in lymphocytes of smokers. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 65:83–88
Kohn KW, Ewing RAG, Erickson LC, Zwelling DA (1981) In: EC Friedberg EC, Hanawalt PC (eds) DNA repair. Lab manual. Marcel Decker, New York, 379–401
Krause T, Einhaus M, Holz O, Meißner R, Baumgartner E, Rudiger HW (1993) A novel technique for the detection of DNA single-strand breaks in human white blood cells and its combination with the unscheduled DNA synthesis assay. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 65:77–82
McKelvey-Martin VJ, Green MHL, Schmezer P, Pool-Zobel BL, DeMeo MP, Collins A (1993) The single cell gel electrophoresis assay (comet assay): a European review. Mutat Res 288:47–63
0esch F, Aulmann W, Platt KL, Doerjer G (1987) Individual differences in DNA repair in man. Arch Toxicol Suppl 10:172–179
Olive PL, Wlodek D, Durand RE, Banath JP (1992) Factors influencing DNA migration from individual cells subjected to gel electrophoresis. Exp Cell Res 198:259–267
Ostling O, Johanson KJ (1984) Microelectrophoretic study of radiation-induced DNA damages in individual mammalian cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 123:291–298
Pero RW, Anderson MW, Doyle GA, Anna CH, Romagna F, Markowitz M, Bryngelsson C (1990) Oxidative stress induces DNA damage and inhibits the repair of DNA lesions induced by N-acetoxy-2-acetylaminofluorene in peripheral mononuclear leukocytes. Cancer Res 50:4619–4625
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Singh NP, Danner DB, Tice RR, Pearson JD, Brant LJ, Morrel CH, Schneider EL (1991) Basal DNA damage in individual human lymphocytes with age. Mutat Res 256:1–6
Tice RR, Strauss GHS, Peters WP (1992) High-dose combination alkylating agents with autologous bone-marrow support in patients with breast cancer: preliminary assessment of DNA damage in individual peripheral blood lymphocytes using the single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Mutat Res 271:101–113
Vähäkangas K, Trivers GE, Plumer S, Hayes RB, Krokan H, Rowe M, Swartz RP, Yeager H, Harris CC (1991) 06-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase and uracil DNA glycosylase in human broncho-alveolar lavage cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from tobacco smokers and non-smokers. Carcinogenesis 8:1389–139
Ward JF, Blakeley WF, Joner EI (1985) Mammalian cells are not killed by DNA single-strand breaks caused by hydroxyl radicals from hydrogen peroxide. Radiat Res 103:383–392
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work is part of a thesis by A. Kästner for a medical doctorate at the University of Hamburg.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holz, O., Jörres, R., Kästner, A. et al. Reproducibility of basal and induced DNA single-strand breaks detected by the single-cell gel electrophoresis assay in human peripheral mononuclear leukocytes. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 67, 305–310 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385645
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385645