Summary
-
1.
We have used histological and histochemical methods in order to follow the degradation of reserve fat in the cotyledons of the mustard seedling in darkness and under the influence of phytochrome. The results which have recently been obtained by Hock et al. (1965) with conventional methods of extraction and gravimetric determination of fat could be confirmed. Furthermore the detailed pattern of fat degradation in the cotyledons has been described.
-
2.
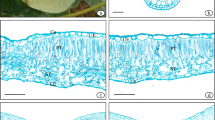
In the dormant seed the reserve fat is homogeneously distributed in the cotyledons. After the onset of germination this fat is degraded according to a complicated pattern.—In the dark grow seedling the rate of degradation is higher in the epidermis than in the mesophyll. Within the mesophyll degradation is more intense in the palisade parenchyma than in the spongy parenchyma (fig. 3). —There is still another gradient: the rate of degradation is greater in the centre and in the periphery of the lamina than in between (fig. 2). —In the light grown seedling (continuous far-red) the pattern of fat degradation is not changed compared with that in the dark grown seedling. The rate of degradation, however, is changed in a manner which is characteristic for “complex photoresponses” (Mohr, 1966): at first the rate is lower under the influence of far-red, later on it is higher than in the corresponding dark controls. We conclude: phytochrome does not change the pattern of fat degradation in the cotyledonary tissues; it does, however, exert a strong regulating influence on the rate of degradation.
-
3.
On the basis of the histochemical investigation of the epidermis it was concluded that phytochrome induced anthocyanin synthesis in this tissue is strictly correlated with an intense degradation of reserve fat within this tissue.
Zusammenfassung
-
1.
Es wurde in dieser Untersuchung mit histologisch-histochemischen Methoden der Abbau des Speicherfetts in den Kotyledonen des Senfkeimlings im Dunkel und unter Einfluß des Phytochroms verfolgt (vgl. Hock, Kühnert und Mohr, 1965).
-
2.
Das in den Kotyledonen ruhender Samen homogen verteilte Speicherfett wird nach einem komplizierten Muster abgebaut. Im Dunkelkeimling verläuft der Abbau in der Epidermis intensiver als im Mesophyll und in diesem wiederum im Palisadenparenchym stärker als im Schwammparenchym. Außerdem ist der Abbau stärker in der Blattmitte und im Spreitenrand.
-
3.
Im Licht (Dauer-Dunkelrot) zeigt der Abbau in den Geweben einen Verlauf, wie er für die “komplexen” Photomorphosen charakteristicch ist (Mohr, 1966): zuerst eine relative Verlangsamung (gegenüber den Dunkel-kontrollen) und später eine Beschleunigung. Das Muster des Fettabbaus bleibt indessen unter dem Einfluß des Phytochroms unverändert. Das Phytochrom reguliert lediglich die Intensität des Fettabbaus.
-
4.
Die histologische Untersuchung der Epidermis ergab, daß die phytochrominduzierte Anthocyansynthese in diesem Gewebe mit einem intensiven Abbau des Speicherfetts korreliert ist.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bertsch, W., u. H. Mohr: Ein Beitrag zur Interpretation der Dunkelrotbande der Hochenergiereaktion bei der Photomorphogenese (lichtabhängige Anthocyansynthese bei Senfkeimlingen, Sinapis alba L.). Planta (Berl.) 65, 245–258 (1965).
Eberhardt, F.: Über die Beziehung zwischen Atmung und Anthocyansynthese. Planta (Berl.) 43, 253–287 (1954).
Gardner, W. A.: Effect of light on germination of light=sensitive seeds. Bot. Gaz. 71, 249–288 (1921).
Grafe, V., u. V. Vouk: Untersuchungen über den Inulinstoffwechsel bei Cichorium intybus L. (Cichorie). I. Keimungsstoffwechsel. Biochem. Z. 43, 424–433 (1912).
Guerrant, N. B.: Some relations of the phospholipins in seeds to other constituents. J. Agricult. Res. 35, 1001–1019 (1927)
Hock, B., E. Kühnert u. H. Mohr: Die Regulation von Fettabbau und Atmung bei Senfkeimlingen durch Licht (Sinapis alba L.). Planta (Berl.) 65, 129–138 (1965).
, u. H. Mohr: Die Regulation der O2-Aufnahme von Senfkeimlingen (Sinapis alba L.) durch Licht. Planta (Berl.). 61, 209–228 (1964).
: Eine quantitative Analyse von Wachstumsvorgängen im Zusammenhang mit der Photomorphogenese von Senfkeimlingen (Sinapis alba L.). Planta (Berl.). 65, 1–16 (1965).
Jensen, W. A.: Botanical Histochemistry. Principles and Practice. San Francisco and London: W. H. Freeman & Co. 1962.
Kandeler, R.: Über die Lichtabhängigkeit der Anthocyanbildung. Flora (Jena) 149, 487–519 (1960).
Lange, H. u. H. Mohr: Die Hemmung der Phytochrom-induzierten Anthocyansynthese durch Actinomycin D und Puromycin. Planta (Berl.) 67, 107–121 (1965).
McLane, S. R.: Higher polyethylene glycols as a water soluble matrix for sectioning fresh or fixed plant tissues. Stain Technol. 26, 63–64 (1951).
Mohr, H.: Der Lichteinfluß auf das Wachstum der Keimblätter bei Sinapis alba L. Planta (Berl.) 53, 219–245 (1959).
: Steuerung der pflanzlichen Entwicklung durch Licht. Naturwiss. Rdsch. 18, 101–108 (1965).
Mohr, H.: Untersuchungen zur phytochrominduzierten Photomorphogenese des Senfkeimlings (Sinapis alba L.). Z. Pflanzenphysiol. (1966) (im Druck).
Ohlen, F. W. v.: A microchemical study of soybeans during germination, Amer. J. Bot. 18, 30–49 (1931).
Romeis, B.: Mikroskopische Technik, 12. Aufl. 1928 u. 15. Aufl. 1948. München: Lelbniz.
Tchakarof, E., and Z. Posalaky: Critical studies on the use of polyethylene glycols in lipid histochemistry. Acta histochem. (Jena) 15, 27–36 (1963).
Tschirch, A., u. O. Oesterile: Anatomischer Atlas der Pharmakognosie und Lebensmittelkunde, Bd. I. Leipzig: C. H. Tauchnitz 1900.
Toole, H. B.: The transformations and course of development of germinating maize. Amer. J. Bot. 11, 325–350 (1924).
White, H. B. jr.: Fat utilization and composition in germinating cotton seeds. Plant Physiol. 33, 218–226 (1958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Häcker, M., Stöhr, H. Der Abbau von Speicherfett in den Kotyledonen von Sinapis alba L. unter dem Einfluss des Phytochroms. Planta 68, 215–224 (1966). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385627
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385627