Abstract
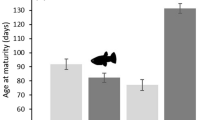
Four sibships of Hyla chrysoscelis larvae were used to examine the effects of parentage on mass at day 23 of growth and on vulnerability to predation. The H. chrysoscelis larvae were raised alone, in competition with Rana clamitans larvae, and in competition with siblings. Vulnerability to predation by adult Notophthalmus viridescens dorsalis was evaluated for Hyla that had been raised in competition with siblings. Sibships differed in body mass and vulnerability to predation. Competition with Rana or with siblings resulted in a major reduction in body mass. There were no interactions between the effects of parentage and level of competition on body mass. Vulnerability to predation by newts appeared to be determined partially by body mass and partially by parental influences on factors other than body mass. If the differences observed between factors determining body mass and vulnerability to predation reflect negative genetic correlations among these determinants, tradeoffs between selection for increased competitive ability and reduced vulnerability to predators may partially account for the existence of genetic variation for growth rate in larval Hyla.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford RA (1986) Habitat use and positional behavior of anuran larvae in a northern Florida temporary pond. Copeia 1986 (2) (in press)
Alford RA, Wilbur HM (1985) Priority effects in experimental pond communities: competition between Bufo and Rana. Ecology 66:1097–1105
Antonovics J (1976) The nature of limits to natural selection. Ann Missouri Bot Garden 63:224–227
Brockelman WY (1969) An analysis of density effects and predation in Bufo americanus tadpoles. Ecology 50:632–644
Brooks JL, Dodson SI (1965) Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150:28–35
Caldwell JP, Thorp JH, Jervey TO (1980) Predator-prey relationships among larval dragonflies, salamanders, and frogs. Oecologia (Berlin) 46:285–289
Calef GW (1973) Natural mortality of tadpoles in a population of Rana aurora. Ecology 54:741–758
Christiansen FB, Fenchel TM (1977) Theories of Populations in Biological Communities. Springer, New York
Heyer WR, Muedeking MW (1976) Notes on tadpoles as prey for naiads and turtles. J Wash Acad Sci 66:235–239
Heyer WR, McDiarmid RW, Weigmann DL (1975) Tadpoles, predation, and pond habitats in the tropics. Biotropics 7:100–111
Kinsman S (1982) Herbivore Responses to Oenothera biennis (Onagraceae): Effects of the Host Plant's Size, Genotype, and Resistant Conspecific Neighbors. Ph. D. thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York
Morin PJ (1981) Predatory salamanders reverse the outcome of competition among three species of anuran tadpoles. Science 212:1284–1286
Morin PJ (1983) Predation, competition, and the composition of larval anuran guilds. Ecol Monogr 53:119–138
Pollard AJ, Briggs D (1982) Genecological studies of Urtica dioica L. I. The nature of intraspecific variation in U. dioica. New Phytol 92:453–470
Pollard AJ, Briggs D (1984) Genecological studies of Urtica dioica L. III. Stinging hairs and plant-herbivore interactions. New Phytol 97:507–522
Pritchard G (1965) Prey capture by dragonfly larvae (Odonata: Anisoptera). Can J Zool 43:271–289
Samollow P (1980) Selective mortality and reproduction in a natural population of Bufo boreas. Evolution 34:18–39
Steinwascher K (1978) Interference and exploitation competition among tadpoles of Rana utricularia. Ecology 59:1039–1046
Steinwascher K (1979) Competitive interactions among tadpoles: responses to resource level. Ecology 60:1172–1183
Travis J (1980a) Phenotypic variation and the outcome of interspecific competition in hylid tadpoles. Evolution 34:40–50
Travis J (1980b) Genetic variation for larval specific growth rate in the frog Hyla gratiosa. Growth 44:167–181
Travis J (1981) Control of larval growth variation in a population of Pseudacris triseriata (Anura: Hylidae). Evolution 35:423–432
Travis J (1983a) Variation in development patterns of larval anurans in temporary ponds. I. Persistent variation within a Hyla gratiosa population. Evolution 37:496–512
Travis J (1983b) Variation in growth and survival of Hyla gratiosa larvae in experimental enclosures. Copeia 1983:232–237
Wilbur HM (1972) Competition, predation, and the structure of the Ambystoma-Rana sylvatica community. Ecology 53:2–21
Wilbur HM (1976) Competition, predation, and the structure of the Ambystoma-Rana sylvatica community. Ecology 53:2–21
Wilbur HM (1976) Density-dependent aspects of metamorphosis in Ambystoma and Rana sylvatica. Ecology 57:1289–1296
Wilbur HM (1977) Interactions of food level and population density in Rana sylvatica. Ecology 58:206–209
Wilbur HM (1980) Complex life cycles. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 11:67–93
Wilbur HM, Alford RA (1985) Priority effects in experimental communities: response of Hyla to Bufo and Rana. Ecology 66:1106–1114
Wright AH, Wright AA (1949) Handbook of Frogs and Toads, Third Edition. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alford, R.A. Effects of parentage on competitive ability and vulnerability to predation in Hyla chrysoscelis tadpoles. Oecologia 68, 199–204 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384787
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00384787