Summary
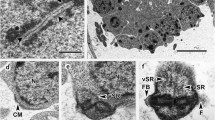
The fine structure of the deutomerite of D. gigantea was investigated. The development of the nuclear apparatus, the nuclear division, and the Golgi apparatus are emphasized. In its earliest stage, the young trophozoite has only one nucleus displaying a rather dense but heterogeneous karyosome. The adult trophozoite has nuclei with a homogeneous nucleolus. During the evolution of the trophozoite — even before the association of two individuals to a syzygy — appear very rapid successive nuclear divisions (Fig. 3), so that adult syzygies may display several hundred nuclei in each individual (Fig. 5). The spherical structure (Fig. 1) considered by Legar (1892) as nucleus has been revealed to be a large vaculole with fine granular or fibrillar material (Fig. 6). Rather often nuclei are surrounded by cyternae of endoplasmic reticulum (Fig. 7) or display large cytoplasmic invaginations (Fig. 8). The intranuclear spindle-apparatus is characterized by a polar centrocone-like structure (Figs. 9–12). Intranclear microtubuli can often be observed (Figs. 9, 10, 15, 18). The nucleolus is separating just before the definite nuclear division (Figs. 13–15). New nuclear division can start even if the preceding one is not yet finished (Fig. 18). The Golgi apparatus is rather complex. There can be observed dictyosomes in relation with the nuclear envelope, and endoplasmic reticulum serves in the case as intermediate organite (Figs. 18–27, 31). Besides these dictyosomes exist other dictyosomes free of endoplasmic reticulum and containing dense material in their vesicles (Figs. 29, 30). These two types of dictyosomes are probably different evolution stages of one whole Golgi apparatus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Andreassen, J., Behnke, O.: Fine structure of merozoïtes of a rat coccidian Eimeria migairii, with a comparison of the fine structure of other Sporozoa. J. Parasitol. 54, 150–163 (1968)
Belar, K.: Zur Cytologie von Aggregata eberthi (Bemerkungen zu der Arbeit “The life history and chromosome cycle of Aggregata eberthi” von C.C. Dobell). Arch. Protistenkd. 53, 312–325 (1926)
Cordua, C.A.: Untersuchungen über die Gregarinenfektion der Dungskäfer. Arch. Protistenkd. 98, 469–506 (1953)
Desportes, I.: Ultrastructure des Grégarines du genre Stylocephalus. La phase enkystée. Ann. Sci. Nat. Zool. Biol. Anim. 12ème série 12, 74–169 (1970)
Dubremetz, J.F.: L'ultrastructure du centriole et du centrocône chez la coccidie Eimeria necatrix. Etude au cours de la schizogonie. J. Micr. 12, 453–458 (1971)
Dubremetz, J.F.: Etude ultrastructurale de la mitose schizogonique chez la coccidie Eimeria necatrix (Johnson, 1930). J. Ultrast. Res. 42, 354–376 (1973)
Foerster, H.: Gregarinen in schlesischen Insekten. Z. Parasitenkd. 10, 157–209 (1938a)
Foerster, H.: Beobachtungen über das Auftreten von Gregarinen in Insekten. Z. Parasitenkd. 10, 644–673 (1938b)
Francisco, A. de, Roth, L.E.: The marine diatom, Striatella unipunctata. I. Cytoplasmic fine structure with emphasis on the Golgi apparatus. Cytobiologie 14, 191–206 (1977)
Grell, K.G.: The protozoan nucleus. In: The Cell, J. Brachet et A. Mirsky, eds., Vol. 6, pp. 1–79. New York: Academic Press, 1964
Hammond, D.M., Scholtyseck, E., Chobotar, B.: Fine structure study of the microgametogenesis of Eimeria auburnensis. Z. Parasitenkd. 33, 65–84 (1969)
Hildebrand, H.F.: Etude au microscope électronique de l'évolution nucléaire progamique chez la Grégarine Didymophyes gigantea Stein., parasite intestinal de la larve du Scarabeide Oryctes nasicornis L. J. Protozool. 19 (suppl.), 67 (1972)
Hildebrand, H.F.: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an den Entwicklungsstadien des Trophozoiten von Didymophyes gigantea (Sporozoa, Gregarinida). I. Die Feinstruktur des Proto-und Epimeriten und die Beziehung zwischen Wirt und Parasit. Z. Parasitenkd. 49, 193–215 (1976)
Hildebrand, H.F., Vinckier, D.: Nouvelles observations sur la Grègarine Didymophyes gigantea Stein. J. Protozool. 22, 200–213 (1975)
Hollande, A., Enjumet, M.: Contribution à l'étude biologique des Sphaerocollides (Radiolaires collodaires et radiolaires polycythaires) et leurs parasites. Ann. Sci. Nat. Zool. lle série 15, 99–183 (1953)
Howells, R.E., Davies, E.E.: Nuclear division in the oocyst of Plasmodium berghei. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 65, 451–460 (1971)
Kushida, H.: A styrene-methacrylate resin embedding method for ultrathin sectioning. J. Electron. Microsc. 10, 16–19 (1961)
Léger, L.: Recherches sur les Grégarines. Tabl. Zool. 3, 1–183 (1892)
Lipa, E., Jr.: Tribolium destructor Uytt (Copeoptera, Tenebrionidae) nouvel hôte de la Grégarine Didymorphes minuta (Ishii) Watson (Gregarinidae, Didymophyidae). Zool. Zh. SSSR 45, 1130–1133 (1966)
Ludwig, P.W.: Studies on the protozoan fauna of the larvae of the crane fly, Tipula abdominalis L. I. Flagellates, amoebae and gregarines. Trans. Amer. micr. Soc. 65, 189–214 (1964)
Marshall, W.S.: Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Gregarinen. Arch. Naturgesch. 59, 25–44 (1893)
Nahib, A.: Studien über die Gattung Klossia und Beschreibung des Lebenszyklus von Klossia loosi (nov. sp.). Arch. Protistenk. 91, 474–515 (1938)
Obata, K.: Reports on some gregarines from Japanese insects. J. Sci. Hiroshima Univ. 14, 1–34 (1953)
Ogino, N., Yoneda, C.: The fine structure and mode of division of Toxoplasma gondii. Arch. Ophthalmol. 75, 218–227 (1966)
Ormières, R.: Eugrégarines parasites d'Aphodius (Coleop., Scarab.) des environs de Besse. Données nouvelles sur le genre Didymophyes Stein. Ann. Stat. Biol. Besse-en-Chaudesse 3, 209–220 (1968)
Porchet-Henneré, E., Richard, A.: La sporogénèse chez la Coccidie Aggregata eberthi. Etude en microscopie électronique. J. Protozool. 18, 614–628 (1971)
Porchet-Henneré, E., Vivier, E.: Ultrastructure comparée des germes infectueux (sporozoites, merozoites, schizoites, endozoites etc.) chez les sporozoaires. Ann. Biol. 10, 77–113 (1971)
Prensier, G.: Contribution à l'étude ultrastructurale des différents stades du cycle de Diplauxis hatti (Grégarine monocystidée) parasite de Perinereis cultrifera Grübe. Thèse de 3ème Cycle. Lille (1971)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain for electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208 (1963)
Schrevel, J.: Biologie, cytologie, physiologie des Grégarines parasites d'Annélides Polychètes. Thèse de Doctorat ès Sciences Naturelles, Lille 1969
Sénaud, J.: Contribution à l'étude des sarcosporidies et des toxoplasmes (Toxoplasma). Protistologica 3, 170–216 (1967)
Sheffield, H.G.: Electron microscopy study of the proliferative form of Besnoitia jellisoni. J. Parasitol. 52, 583–594 (1966)
Sheffield, H.G., Melton, M.L.: The fine structure and reproduction of Toxoplasma gondii. J. Parasitol. 54, 209–226 (1968)
Stein, F.: Über die Natur der Gregarinen. Arch. Anat. Phys. Med. (Müllers Arch.) 182, 223 (1848)
Stockem, W.: Die Eignung von Pioloform F für die Herstellung elektronenmikroskopischer Träger filme. Mikroskopie 26, 185–189 (1970)
Stockem, W., Komnick, H.: Erfahrungen mit der Styrol-Methacrylat-Einbettung als Routinemethode für die Licht- und Elektronenmikroskopie. Mikroskopie 26, 199–203 (1970)
Terzakis, J.A.: Uranyl acetate, a stain and fixative. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 22, 168–184 (1968)
Theodorides, J.: Contribution à l'étude des parasites et phorétiques de coléoptères terrestres. Vie et Milieu, Suppl. 4, 1–310 (1955)
Theodorides, J., Jolivet, P.: Eugrégarines parasites de coléoptères. Exp. Pc. Nat. Albert, 2ème série 8, 3–95 (1959)
Theodorides, J., Ormières, R.: Sur un cas tératologique chez Didymophyes guttiformis Cordua. Remarques sur la position systématique du genre Didymophyes Stein (Eugregarina-Didymophyidae). Ann. Parasitol. hum. comp. 31, 177–181 (1956)
Tucker, J.B.: Changes in nuclear structure during the binary fission in the ciliate Nassula. J. Cell Sci. 2, 481 (1967)
Vivier, E.: Sur quelques particularités de certains organites cytoplasmiques (mitochondries et appareil de Golgi) chez les Sporozoaires. J. Micr. 4, 168–169 (1965)
Vivier, E., Henneré, E.: Ultrastructure des stades végétatifs de la coccidie Coelotropha durchoni. Protistologica 1, 89–104 (1965)
Vivier, E., Petitprez, A.: Données ultrastructurales complémentaires, morphologiques et cytochimiques, sur Toxoplasma gondii. Protistologica 8, 199–221 (1972)
Vivier, E., Schrevel, J.: Les ultrastructures cytoplasmiques de Selenidium hollandei, n. sp. Grégarine parasite de Sabellaria alveolata L. J. Micr. 5, 213–228 (1966)
Watson, M.E.: Studies on gregarines. Illinois Biol. Mon. 2, 1–258 (1916)
Wohlfarth-Bottermann, K.E.: Die Kontrastierung tierischer Zellen und Gewebe im Rahman ihrer elektronenmikroskopischen Untersuchung an ultradünnen Schnitten. Naturwissenschaften 44, 287–288 (1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hildebrand, H.F. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an den Entwicklungsstadien des Trophozoiten von Didymophyes gigantea (Sporozoa, Gregarinida). Z. F. Parasitenkunde 55, 9–27 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00383471
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00383471