Summary
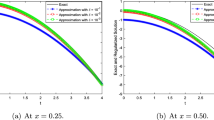
An approximate solution of heat-conduction problems can be obtained by the strip method. The method consists of an application of the finite-difference approximation in one physical coordinate and an analytic solution in other coordinates. A simple illustrative example is given and the result is compared with that obtained by the exact solution. By application of this method, an approximate solution is given for the steady heat conduction through a rectangular parallel composite wall with different rates of heat generation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carslaw, H. S. and J. C. Jaeger, Conduction of Heat in Solids, Oxford University Press, Oxford, England, 1959.
Schneider, P. J., Conduction Heat Transfer, Addison-Wesley Publication Company, Inc., Reading, Mass., 1955, pp. 129, 157.
Dusinberre, G. M., Heat Transfer Calculation by Finite Differences, International Textbook Co., Scranton, Penn., 1961.
Kärrholm, G., Parallelogram Plates Analysed by Strip Method, Chalmers Tekniska Högskola, Göteborg, 1956.
Eyres, N. R., D. R. Hartree, J. Ingham, R. Jackson, R. J. Sarjant and J. B. Wagstaff, Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond., A 240 (1946) 1.
Gantmacher, F. R., The Theory of Matrices, Chelsea Publishing Company, New York, N. Y., vol. I, 1959, pp. 110–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tien, C.L. Strip method for steady heat-conduction problems. Appl. sci. Res. 13, 209–223 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382048
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382048