Summary
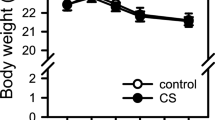
Exposure of rabbits to 0.5 ppm hydrogen cyanide alone or in combination with 200 ppm carbon monoxide for one and four weeks or combined exposure to 0.5 ppm hydrogen cyanide, 200 ppm carbon monoxide, and 5 ppm nitric oxide for two weeks did not cause morphological changes in lungs, pulmonary arteries, coronary arteries, or aorta. The need for selective toxicity studies with tobacco smoke constituents is stressed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astrup, P., Kjeldsen, K., Wanstrup, J.: Enhancing influence of carbon monoxide on the development of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J. Atheroscler. Res. 7, 343–354 (1967)
Brunnemann, K. D., Yu, L., Hoffmann, D.: Chromatographic determination of hydrogen cyanide and cyanogen in tobacco smoke. World Smoking Health 2, 23–28 (1977)
Elkins, H. B.: The chemistry of industrial toxicology, 2nd ed., p. 345. New York: Wiley 1959
Fisher, A. B., Hyde, R. W., Bone, A. E., Reif, J. S., Kelly, D. F.: Effect of carbon monoxide on function and structure of the lung. J. Appl. Physiol. 26, 4–12 (1969)
Freeman, G., Furiosi, N. J., Haydon, G. B.: Effects of continuous exposure of 0.8 ppm NO2 on respiration of rats. Arch. Environ. Health 13, 454–456 (1966)
Haydon, G. B., Freeman, G., Furiosi, N. J.: Covert pathogenesis of NO2 induced emphysema in the rat. Arch. Environ. Health 11, 776–783 (1965)
Hazucha, M., Bates, D. V.: Combined effect of ozone and sulphur dioxide on human pulmonary function. Nature 257, 50–51 (1975)
Hugod, C., Hawkins, L. H., Kjeldsen, K., Thomsen, H. K., Astrup, P.: Effect of carbon monoxide exposure on aortic and coronary intimal morphology in the rabbit. Atherosclerosis 30, 333–342 (1978)
Hugod, C.: Effect on rabbit lung of exposure to 43 ppm nitric oxide and 3.6 ppm nitrogen dioxide. — A light and electron microscopic study. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 42, 159–167 (1979)
Hugod, C.: Ultrastructural changes of the rabbit lung after a 5 ppm nitric oxide exposure. Arch. Environ. Health 34, 12–17 (1979)
Hugod, C.: The effect of carbon monoxide exposure on morphology of lungs and pulmonary arteries in rabbits. — A light and electron microscopic study. (In prep.)
Hugod, C., Hawkins, L. H.: Method for the creation and measurement of low levels of hydrogen cyanide in air. (In prep.)
Niden, A. H., Schultz, H.: The ultrastructural effects of carbon monoxide inhalation on the rat lung. Virchows Arch. [Pathol. Anat.] 339, 283–292 (1965)
Stephens, R. J., Freeman, G., Evans, M. J.: Early response of lungs to low levels of nitrogen dioxide. Arch. Environ. Health 24, 160–179 (1972)
Wagner, W. D., Duncan, B. R., Wright, P. G., Stokinger, H. E.: Experimental study of threshold limit of NO2. Arch. Environ. Health 10, 455–466 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Forschungsgesellschaft Rauchen und Gesundheit, Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hugod, C. Effect of exposure to 0.5 ppm hydrogen cyanide singly or combined with 200 ppm carbon monoxide and/or 5 ppm nitric oxide on coronary arteries, aorta, pulmonary artery, and lungs in the rabbit. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 44, 13–23 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381205
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381205