Summary
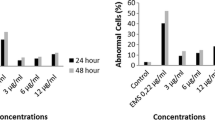
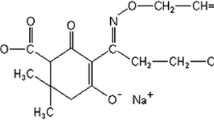
Paraoxon and methyl-parathion (Wofatox), frequently used organophosphate pesticides, were tested for cytogenetic effects in lymphocytes of persons with different phenotypes of paraoxonase activity. Sister chromatid exchanges (SCE), chromosome breaks, and cell cycle traverse were studied in ten individuals. Paraoxon showed no significant effects whereas methylparathion showed a dose-dependent increase in the SCE and a definite delay in the cell cycle as assessed by fluorescence plus Giemsa technique. No significant clastogenic effects and no difference in response were observed among individuals with different phenotypes of paraoxonase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen JW, Shuler CF, Mendes RW, Latt SA (1977) A simplified technique for in vivo analysis of sister-chromatid exchanges using 5-bromodeoxyuridine tablets. Cytogenet Cell Genet 18:231–237
Bao T van, Szabó I, Ruzieska P, Czeizel A (1974) Chromosome aberrations in patients suffering acute organic phosphate insecticide intoxication. Hum Genet 24:33–57
Bauknecht R, Vogel W, Bayer U, Wied D (1977) Comparative in vivo mutagenicity testing by SCE and micronucleus induction in mouse bone marrow. Hum Genet 35:299–307
Beek B, Obe G (1975) The human leucocyte test system. VI. The use of sister chromatid exchanges as possible indicators for mutagenic activities. Hum Genet 29:127–139
Böhlke JU, Singh S, Goedde HW (1983) Cytogenetic effects of acetaldehyde in lymphocytes of Germans and Japanese: SCE, clastogenic activity, and cell cycle delay. Hum Genet 63:285–289
Carrano AV, Thompson CH, Lindland PA, Minkler JL (1978) Sister chromatid exchanges as an indicator of mutagenesis. Nature [Lond] 271:551–553
Chen HH, Hsueh JL, Sirianni SR, Huang CC (1981) Induction of sister chromatid exchanges and cell cycle delay in cultured mammalian cells treated with eight organophosphorus pesticides. Mut Res 88:307–316
Gebhart E (1981) Sister chromatid exchange (SCE) and structural chromosome aberration in mutagenicity testing. Hum Genet 58:235–254
Geldmacher-v. Mallinckrodt M, Lindorf HH, Petenyí M, Flügel M, Fischer T, Hiller T (1973) Genetisch determinierter Polymorphismus der menschlichen Serum-Paraoxonase (EC 3.1.1.2). Hum Genet 17:331–335
Griffen III DE, Hill WE (1978) In vitro breakage of plasmid DNA by mutagens and pesticides. Mutat Res 52:161–169
Hollaender A (ed) (1971) Chemical mutagens. Principles and methods for their protection, vol I–II. Plenum Press, New York London
Huang CC (1973) Effect on growth but not on chromosomes of the mammalian cells after treatment with three organophosphorus insecticides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 142:36–40
Kato H, Shimada H (1975) Sister chromatid exchanges induced by mitomycin C: a new method of detecting DNA damage at chromosomal level. Mutat Res 28:459–464
Krisch K (1968) Enzymatische Hydrolyse von Diäthyl-p-nitro-phenylphosphat (E 600) durch menschliches Serum. Z Klin Chem Biochem 6:41–45
Latt SA (1975) Sister chromatid exchanges, indices of human chromosome damage and repair: detection by fluorescence and induction by mitomycin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci [USA] 71:3162–3166
Lobdell BJ, Johnston CD (1966) Methyl-parathion — three generation reproduction study in the rat. Woodard Res Corp, Herndon, Va, pp 1–64 (quoted in Stocco et al. 1982)
Marquardt H, Bayer U (1977) The induction in vivo of sister chromatid exchanges in the bone marrow of the Chinese hamster I. The sensitivity of the system (methyl methane sulphonate). Mutat Res 56:169–176
Mohn G (1973) 5-Methyltryptophan resistance mutations in escherichia coli K 12, mutagenic activity of monofunctional alkylating agents including organophosphorus insecticides. Mutat Res 20:7–15
Müller RF, Hornung S, Furlong CE, Anderson T, Giblett ER, Motulsky AG (1983) Plasma paraoxinase polymorphism: a new enzyme assay, population, family, biochemial and linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet 35:393–408
Perry P, Evans HJ (1975) Cytological detection of mutagen-carcinogen exposure by sister chromatid exchange. Nature [Lond] 258:121–125
Perry P, Wolff S (1974) New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature [Lond] 251:156–158
Playfer JR, Eze LC, Bullen MF, Evans DA (1976) Genetic polymorphism and interethnic variability of plasma paraoxonase activity. J Med Genet 13:337–342
Seiler JP (1973) A survey on the mutagenicity of various pesticides. Experientia [Basel] 29:622–623
Simmon KF, Mitchell AD, Jorgensen TA, Newell GW (1975) Summary report on methyl-parathion, in vitro and in vivo studies of selected pesticides to evaluate their potential as chemical mutagens. Unpublished report submitted to NIOSH by Stanford Research Institute, Menlo Park, CA (quoted in Stocco et al. 1982)
Solomon E, Bobrow M (1975) Sister chromatid exchanges - a sensitive assay of agents damaging human chromosomes. Mutat Res 30:273–278
Stocco R de Cassio, Beçak W, Gaeta R, Rabello-Gay MN (1982) Cytogenetic study of workers exposed to methyl-parathion. Mutat Res 103:71–76
Tanimura T, Katsuya T, Nishimura H (1967) Embryotoxicity of acute exposure to methyl-parathion in rats and mice. Arch Environ Health 15:609–613
Vogel F, Röhrborn G (eds) (1970) Chemical mutagenesis in mammals and man. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Waters MD, Simmon VF, Mitchell AD, Jorgenson TA, Valencia R (1980) An overview of short-term tests for the mutagenic and carcinogenic potential of pesticides. J Environ Sci Health, Part B: Pesticides, food contaminants and agricultural wastes (quoted in Chen et al. 1981)
Yoder J, Watson M, Beson WW (1973) Lymphocyte chromosome analysis of agricultural workers during extensive occupational exposure to pesticides. Mutat Res 21:335–340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work is dedicated to Dr. Hasso Schroeder on the occasion of his 60th birthday
This work is part of the thesis of B. Lehmann-Grube for Fachbereich Medizin, Universität Hamburg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Lehmann-Grube, B. & Goedde, H.W. Cytogenetic effects of paraoxon and methyl-parathion on cultured human lymphocytes: SCE, clastogenic activity and cell cycle delay. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 54, 195–200 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379049
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00379049