Summary
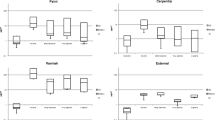
The relation between the mean all-shift concentration of xylene vapor in the atmosphere and the amount of conjugated toluic acids excreted in urine of exposed persons, was derived from the results of 38 experiments with pure xylene isomers and with a mixture of isomers at ratio 1:1:1.
It was proved by statistical processing of experimental data that the decisiveness of the exposure test depends on the way of expressing the excreted amount of metabolites. The data of the concentration (mg metabolite/1 1 l of urine) show the largest dispersion of results. Least variable are the results obtained when using the data of the amount of the metabolite excreted within a defined period and recalculated to 1 kg weight of the exposed person. It is possible to use either the actual weights of the persons for the recalculation, or so-called ideal weights, the numeric value of which equals the body height (in cm) decreased by 100.
The other methods (concentration data recalculated to standard density of urine 1.024 g/ml, data recalculated to 1 g of excreted creatinine, data on the amount of metabolite excreted within a defined period) yield results, the reliability of which lies between the margin values expressed in mg/l and in mg/weight.
It has been proved by studies of the course of toluic acid excretion that short-term samples of urine from the last 2 h of the shift are not suitable for estimation of the level of exposure, if the exposure is interrupted or if the vapor concentration in the atmosphere changes. In such cases it is necessary to use all-shift, or better all-day urine samples.
The biologic limits corresponding to an 8-h exposure to a concentration of xylene vapors 200 μg/l (= Czechoslovak MAC) were determined for various urine samples (short-term, all-shift, all-day) as well as for different data on the excreted amount of metabolite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardoděj, Z.: Exposure tests (in Czech.). Enclosure nr.5 to Informační zprávy z oboru hygieny práce a nemocí z povolaní, p.7, Prague, July 1965
Buchwald, H.: The expression of urine analysis results. Observations on the use of a specific gravity correction. Ann.occup.Hyg. 7, 125 (1964)
Elkins, H.B., Pagnotto,L.D.: Is the 24-hour urine sample a fallacy? Amer.industr.Hyg.Ass.J. 26, 456 (1965)
Flek, J., Šedivec, V.: Determination of toxic substances and their metabolites in biological fluids by gas chromatography. VII. Toluric or toluic acids in urine. Coll.Czechoslov.Chem.Comm. 38, 1754 (1973)
Ikeda, M., Ohtsuji, H..: Hippuric acid, phenol and trichloroacetic acid levels in the urine of Japanese subjects with no known exposure to organic solvents. Brit.J.industr.Med. 26, 162 (1969)
Ikeda, M., Ohtsuji, H.: Significance of urinary hippuric acid determination as an index of toluene exposure. Brit.J.industr.Med. 26, 244 (1969)
Imamura, T., Ikeda, M.: Lower fiducial limit of urinary metabolite level as an index of excessive exposure to industrial chemicals. Brit.J.industr. Med. 30, 289 (1973)
Jackson, S.: Creatinine in urine as an index of urinary excretion rate. Hlth Phys. 12, 843 (1966)
Ogata, M., Takatsuka, Y., Tomokuni, K.: Excretion of hippuric acid and m- or p-methylhippuric acid in the urine of persons exposed to vapours of toluene and m- or p-xylene in an exposure chamber and in workshops, with specific reference to repeated exposures. Brit.J.industr.Med. 28, 382 (1971)
Ogata, M., Tomokuni, K., Takatsuka, Y.: Quantitative determination in urine of hippuric acid and m- or p-methylhippuric acid, metabolites of toluene and m- or p-xylene. Brit.J.industr.Med. 26, 330 (1969)
Ogata, M., Tomokuni, K., Takatsuka, Y.: Urinary excretion of hippuric acid and m- or p-methylhippuric acid in the urine of persons exposed to vapours of toluene and m- or p-xylene as a test of exposure. Brit.J. industr.Med. 27, 43 (1970)
Šedivec, V., Flek, J.: The absorption, metabolism, and excretion of xylenes in man. Int. Arch. Occup.Environ.Hlth 37, 205–217 (1976)
Šedivec, V., Flek, J., Mráz, M.: Preparation of an atmosphere with defined contents of studied substances (in Czech., English summary). Pracovní Lékařství 26, 48 (1974)
Smith, J.C., Kench, J.E.: Observations on urinary cadmium and protein excretion in men exposed to cadmium oxide dust and fume. Brit.J.industr. Med. 14, 240 (1957)
Teisinger, J.: Critical evaluation of the methods expressing the amount of excreted substances via urine (in Czech.). Pracovní Lekařství 25, 303 (1973)
Teisinger, J., Škramovský, S., Srbová, J.: Chemical methods for investigation of biologic material in industrial toxicology (in Czech.), pp.84, 108, and 119. Prague: SZdN 1956
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šedivec, V., Flek, J. Exposure test for xylenes. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 37, 219–232 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378420
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378420