Summary
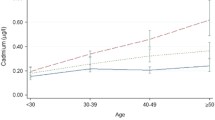
Cadmium in blood (CdB), cadmium in urine (CdU) and beta2-microglobulins (β2MU) were determined in 83 male workers exposed to cadmium fumes. CdU was measured both on 24-h urine samples and on spot samples. The behaviour of the biological indicators of cadmium was assessed in relation to degree of current exposure, length of exposure and cumulative exposure (computed as concentration of cadmium at the workplace multiplied by duration of exposure). CdB values were significantly higher in the subgroups of subjects with higher current cadmium exposure and in the subgroups of subjects with greater cumulative exposure, but the test levels were not influenced by duration of exposure. CdU levels were significantly higher in the subgroups of subjects with greater cumulative exposure, but were less influenced by current exposure or duration of exposure. Considering the entire population, a rather close correlation (r = 0.69) was observed between CdB and CdU. When the population was divided according to level of current exposure, a close relationship was observed between the two indicators in all subgroups; nevertheless, for identical CdU values, the CdB values were higher in the subjects with heavier current exposure. Even if in all Cd workers the β2MU levels were in the range of reference values, the highest β2MU levels were found in the subjects with CdU > 10 μg/l. The data confirm that CdU is prevalently influenced by the body burden of metal, but they also suggest that the CdB levels are not influenced solely by the intensity of current exposure but also depend to a considerable degree on the body burden.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alessio L, Odone P, Bertelli G, Foà V (1983) Cadmium. In: Alessio L, Berlin A, Roi R, Boni A (eds) Human biological monitoring of industrial chemicals. Commission of the European Communities, Luxembourg, pp 23–44, EUR 8476EN
Alessio L, Zocchetti C, Odone P, Toffoletto F, Ghezzi I, Berlin A (1983) Problems concerning the usefulness of creatinine adjustment for urinary cadmium. Int Conf Heavy Metals in the Environment, Amsterdam, pp 58–61
Allain P, Mauras Y (1979) Micromethode de dosage du plomb et du cadmium dans le sang et l'urine par absorption atomique au four graphite. Clin Chim Acta 91:41–46
Bernard A, Buchet JP, Roels H, Masson P, Lauwerys R (1979) Renal excretion of proteins and enzymes in workers exposed to cadmium. Eur J Clin Invest 9:11–12
Buchet JP, Roels H, Bernard A, Lauwerys R (1980) Assessment of renal function of workers exposed to inorganic lead, cadmium or mercury vapor. J Occup Med 22:741–750
Castoldi MR, Calzaferri G, Odone P, Dell'Orto A, Zocchetti C, Alessio L (1983) Behaviour of cadmium biological indicators in subjects living in the Milan area. Med Lav 74:442–452
Evrin PE, Peterson PA, Wide L, Berggård I (1971) Radioimmunoassay of β2-microglobulin in human biological fluid. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 28:439–443
Friberg L, Kjellstrom T, Nordberg GF, Piscator M (1979) Cadmium: In: Friberg L, Nordberg GF, Vouk VB (eds) Handbook on the toxicology of metals. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 355–381
Lauwerys R (1982) The toxicology of cadmium. Environment and quality of life. Commission of the European Communities, Luxembourg, EUR 7649EN
Lauwerys R (1983) Industrial chemical exposure: guidelines for biological monitoring. Biomedical Publications, Davis, pp 17–22
Nie NH, Hadlai Hull C, Jenkins JG, Steinbrenner K, Bent DH (1975) Statistical package for social science, 2nd edn. McGraw Hill, New York
NIOSH (1977) Manual of analytical methods. U.S. Department of Health, Education and Welfare DREW, Publication No. 77-157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghezzi, I., Toffoletto, F., Sesana, G. et al. Behaviour of biological indicators of cadmium in relation to occupational exposure. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 55, 133–140 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378375
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378375