Abstract
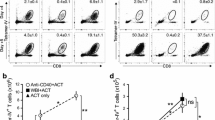
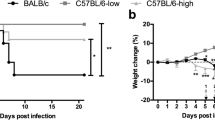
The hybrid resistance (Hr) effect operates in the lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) in vivo transfer model to inhibit both the level of cytotoxicity T lymphocyte (CTL) generation in spleen and the induction of inflammation in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The effect is seen when LCM virus-immune T cells that are homozygous for H-2D b are injected into virus-infected, immunosuppressed recipients that are heterozygous for this allele, or into radiation chimeras that express an appropriate F1 phenotype. Evidence that Hr to T -cell transfer is cell-dose-dependent and tends to diminish with age was found in both chimeric and normal F1 mice. Inhibition of the capacity of injected T cells to cause meningitis is a more sensitive measure of Hr than is the further stimulation of CTL effectors in recipient lymphoid tissue. The injection of large numbers of H-2b virus-immune T cells into (H-2 k X H-2 bF1→H-2 k) virus-infected recipients did not induce any cellular extravasation into CSF, though potent H-2b-restricted CTL effectors were generated in recipient spleen. Evidence of minimal inflammatory process was found in one experiment where these chimeras were given a comparable dose of (H-2 b X H-2 d)F1 immune spleen cells. Development of this Tcell-mediated immunopathological process depends essentially on the expression of the appropriate H-2 restriction element on radiation-resistant host cells which, in this case, presumably constitute part of the physiological barrier between blood and CSF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan, J. E. and Doherty, P. C.: Consequences of cyclophosphamide-treatment in murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis: Evidence for cytotoxic T cell replication in vivo. Scand. J. Immunol. 22: 367–379, 1985a
Allan, J. E. and Doherty, P. C.: Immune T cell can protect or induce fatal neurological disease in murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Cell Immunol. 90: 401–407, 1985b
Allan, J. E. and Doherty, P. C.: Natural killer cells contribute to inflammation but do not appear to be essential for the induction of clinical lymphocytic choriomeningitis. Scand. J. Immunol. 24: 153–162, 1986
Clark, E. A. and Harmon, R. C.: Genetic control of cytotoxicity and hybrid resistance. Adv. Cancer Res. 31: 227–285, 1980
Cudkowicz, G. and Hochman, P. S.: Do natural killer cells engage in regulated reactions against self to ensure homeostasis? Immunol. Rev. 44: 13–49, 1979
Dixon, J. E., Allan, J. E., and Doherty, P. C.: The acute inflammatory process in murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis is dependent on Lyt2+ immune T cells. Cell. Immunol., in press, 1987
Doherty, P. C. and Allan, J. E.: Hybrid resistance modulates the inflammatory process induced by lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-immune T cells. Immunology 57: 515–519, 1986a
Doherty, P. C. and Allan, J. E.: Role of the major histocompatibility complex in targeting effector T cells into a site of virus infection. Eur. J. Immunol., in press, 1986b
Doherty, P. C. and Korngold, R.: Characteristics of poxvirus-induced meningitis: Virus-specific and non-specific cytotoxic effectors in the inflammatory exudate. Scand. J. Immunol. 18: 1–7, 1983
Doherty, P. C., Dunlop, M. B. C., Parish, C. R., and Zinkernagel, R. M.: Inflammatory process in marine LCM is maximal in H-2K or H-2D compatible interactions. J. Immunol. 117: 187–190, 1976
Elkins, W. L.: An immunogenetic approach to the graft-versus-host reaction and secondary disease. In R. P. Gale and C. F. Fox (eds.): Biology of Bone Marrow Transplantation, pp. 195–208, Academic Press, New York, 1980
Gorer, P. A.: Some recent work on tumor immunity. Adv. Cancer Res. 4: 149–186, 1956
Gorer, P. A. and Boyse, E. A.: Pathological changes in F 1 hybrid mice following transplantation of spleen cells from donors of the parental strains. Immunology 2: 182–193, 1959
Korngold, R. and Doherty, P. C.: Sequential analysis of virus-immune responder characteristics of thymocytes from Fl-parent radiation chimeras. Thymus 4: 119–133, 1982
Korngold, R. and Doherty, P. C.: Treatment of mice with polyinosinicpolycytidilic polyribonucleotide reduces T cell involvement in a localized inflammatory response to vaccinia virus challenge. J. Viral. 53: 489–494, 1985
Korngold, R., Blank, K. J., and Murasko, D. M.: Effect of interferon on thoracic duct lymph output: Induction with either polyl: polyC or vaccinia virus. J. Immunol. 130: 2236–2240, 1983
Longo, D. L. and Schwartz, R. H.: T cell specificity for H-2 and Ir gene phenotype correlates with the phenotype of thymic antigen-presenting cells. Nature 287: 44–60, 1980
Perry, V. H., Hume, D. A., and Gordon, S.: Immunohistochemical localization of macrophages and microglia in the adult and developing mouse brain. Neuroscience 15: 313–326, 1985
Shearer, G. M.: Natural resistance to parental T-lymphocyte-induced immunosuppression in F1 hybrid mice: Implications for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Immunol. Rev. 73: 115–126, 1983
Sprent, J. and Korngold, R.: A comparison on lethal graft-versus-host disease in minor-versus-major histocompatibility differences in mice. Implications for marrow transplantation in man. Prog. Immunol. 5: 1461–1475, 1983
Welsh, R. M., Jr., Zinkernagel, R. M., and Hallenbeck, L. A.: Cytotoxic T cells induced during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of mice. II. Specificity of the natural killer cells. J. Immunol. 122: 475–481, 1979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doherty, P.C., Allan, J.E. Differential effect of hybrid resistance on the localization of virus-immune effector T cells to spleen and brain. Immunogenetics 24, 409–415 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00377960
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00377960