Summary
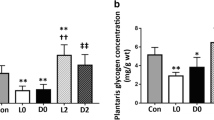
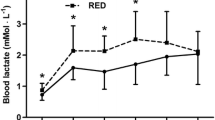
to study the effect of downhill running on glycogen metabolism, 94 rats were exercised by running for 3 h on the level or down an 18° incline. Muscle and liver glycogen concentrations were measured before exercise and 0, 48 and 52 h postexercise. Rats were not fed during the first 48 h of recovery but ingested a glucose solution 48 h postexercise. Downhill running depleted glycogen in the soleus muscle and liver significantly more than level running (P<0.01). The amount of glycogen resynthesized in the soleus muscle and liver in fasting or nonfasting rats was not altered significantly by downhill running (P>0.05). On every day of recovery the rats were injected with dexamethasone, which induced similar increases in glycogen concentration in the soleus muscle and liver after the 52nd h of the postexercise period in the case of downhill and level running. The glycogen depletion and repletion results indicated that, under our experimental conditions, downhill running in the rat, a known model of eccentric exercise, affected muscle glycogen metabolism differently from eccentric cycling in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong RB, Olgivie RW, Schwane JA (1983) Eccentric exercise-induced injury to rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 54:80–93
Cannon JG, Fielding RA, Fiatarone MA, Orencole SF, Dinarello CA, Evans WJ (1989) Increased interleukin-1 beta in human skeletal muscle after exercise. Am J Physiol 257:R451-R455
Costill DL (1988) Carbohydrates for exercise: dietary demands for optimal performance. Int J Sports Med 9:1–18
Costill DL, Pascoe DD, Fink WJ, Robergs RA, Barr SI, Pearson D (1990) Impaired muscle glycogen resynthesis after eccentric exercise. J Appl Physiol 69:46–50
Evans WJ, Meredith CN, Cannon JG, Dinarello CA, Frontera WR, Hugues VA, Jones BH, Knuttgen HG (1986) Metabolic changes following downhill running exercise in trained and untrained men. J Appl Physiol 61:1864–1868
Exton JH, Miller TB, Harper SC, Park CR (1976) Carbohydrate metabolism in perfused livers of adrenalectomized and steroid-replaced rats. Am J Physiol 230:163–170
Favier RJ, Koubi HE, Mayet MH, Semporé B, Simi B, Flandrois R (1987) Effects of gluconeogenic precursor flux alterations on glycogen resynthesis after prolonged exercise. J Appl Physiol 63:1733–1738
Fell RD, MacLane JA, Winder WW, Holloszy JO (1980) Glycogen repletion following continuous and intermittent exercise to exhaustion. Am J Physiol 238:R328-R332
Harris RC, Hultman E, Nordesjo LO (1976) Glycogen intermediates and high energy phosphates determined in biopsy samples of muscles quadriceps femoris of man at rest. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 33:109–120
Kilhstrom M, Salminen MA, Vihko V (1984) Prednisolone decreases exercise-induced acid hydrolase response in mouse skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 53:53–56
Olgivie RW, Armstrong RB, Baird KE, Bottoms CL (1988) Lesions in the rat soleus muscle following eccentrically biased exercise. Am J Anat 182:335–346
O'Reilly KP, Warhol MJ, Fielding RA, Frontera WR, Meredith CN, Evans WJ (1987) Eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage impairs muscle glycogen repletion. J Appl Physiol 63:252–256
Plato P, Sherman WM, Betts J, Lash JM (1989) Eccentric and concentric exercise and insulin action (abstract). Med Sci Sports Exerc 21:530
Poortmans JR (1986) La recuperation aprés l'exercice. Analyse de la repletion des reserves énergétiques. Sci Sports 1:209–230
Richter EA, Hansen SA, Hansen BF (1988) Mechanisms limiting glycogen storage in muscle during prolonged insulin stimulation. Am J Physiol 255:E621-E628
Smith LL (1991) Acute inflammation: the underlying mechanism in delayed onset muscle soreness. Med Sci Sports Exerc 23:542–551
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferry, A., Amiridis, I. & Men, M. Glycogen depletion and resynthesis in the rat after downhill running. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 64, 32–35 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376436
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376436