Abstract
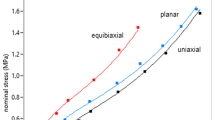
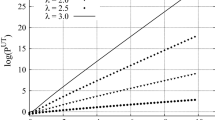
A non-linear thermo-elastic constitutive model for the large deformations of isotropic materials is formulated. This model is specialized to account for the physics and thermodynamics of the elastic deformation of rubber-like materials, and based on these molecular considerations a constitutive model for compressible elastomeric solids is proposed. The new constitutive model generalizes the incompressible and isothermal model of Arruda and Boyce (1993) to include the compressibility and thermal expansion of these materials. The model is fit to existing experimental data on vulcanized natural rubbers to determine the material parameters for the rubbers examined. The fit between the simple model and the data is found to be very good for large stretches and moderate volume changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- x\s=f(p):
-
Deformation function
- p:
-
Material point of a body in a reference configuration
- x:
-
Place occupied by material point p in the current configuration
- F(p)\eq(\t6/\t6p) f(p):
-
Deformation gradient
- J\s=det F\s>0:
-
Determinant of F
- F\s=RU\s=VR:
-
Polar decompositions of F
- U, V:
-
Right and left stretch tensors; positive definite and symmetric
- R:
-
Rotation tensor; proper orthogonal
- U=Σ 31−1 λ 21 r1⊗r1 :
-
Spectral representation of U
- V=Σ 31=1 λ 2t 1t⊗11 :
-
Spectral representation of V
- λt > 0:
-
Principal stretches
- {ri}:
-
Right principal basis
- {li}:
-
Left principal basis
- C\s=FTF, B\s=FFT :
-
Right and left Cauchy-Green strain tensors
- \gq\s>0:
-
Absolute temperature
- \ge:
-
Internal energy density/unit reference volume
- \gh:
-
Entropy density/unit reference volume
- \gy\s=\ge\t-\gq\gh:
-
Helmholtz free energy/unit reference volume
References
Adams, L. H.; Gibson, R. E. 1930: The Compressibility of Rubber. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 20: 213–223
Arruda, E.; Boyce, M. C. 1993: A Three-Dimensional Constitutive Model for the Large Stretch Behavior of Rubber Elastic Materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 41: 389–412
Ericksen, J. L. 1991: Introduction to the Thermodynamics of Solids. London: Chapman & Hall
Flory, P. J. 1961: Thermodynamic Relations for High Elastic Materials. Trans. Faraday Soc. 57: 829–838
Fong, J. T.; Penn, R. W. 1975: Construction of a Strain-Energy Function for Isotropic Elastic Material. Transactions of the Society of Rheology 19: 99–113
Gurtin, M. 1981: An Introduction to Continuum Mechanics. pp. 175–177. New York: Academic Press
James, H. M.; Guth, E. 1943: Theory of the Elastic Properties of Rubber. Journal of Chemical Physics 11: 455–481
Jones, D. F.; Treloar, L. R. G. 1975: The Properties of Rubber in Pure Homogeneous Strain. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 8: 1285–1304
Kuhn, W.; Grün, F. 1942: Beziehungen zwischen elastischen Konstanten und Dehnungsdoppelbrechung höchelastischer Stoffe. Kolloidzeitschrift 101: 248–271
Meyer, K. H.; Ferri, C. 1935: Sur l'élasticité du caoutchouc. Helv. Chim. Acta. 18: 570–589
Ogden, R. W. 1982: Elastic Deformations of Rubber-like Solids. In: Hopkins H. G.; Sewell, M. J. (eds.) Mechanics of Solids, The Rodney Hill 60th Anniversary Volume, pp. 499–537 Oxford: Pergamon Press
Ogden, R. W. 1984: Non-Linear Elastic Deformations. New York: John Wiley & Sons
Peng, S. T. J.; Landel, R. F. 1975: Stored Energy Function and Compressibility of Compressible Rubber-like Materials under Large Strain. Journal of Applied Physics 46: 2599–2604
Penn, R. W. 1970: Volume Changes Accompanying the Extension of Rubber. Transactions of the Society of Rheology 14: 509–517
Treloar, L. R. G. 1944: Stress-strain Data for Vulcanized Rubber under Various Types of Deformation. Trans. Faraday Soc. 40: 59–70
Treloar, L. R. G. 1975: The Physics of Rubber Elasticity Oxford: Clarendon Press
Truesdell, C.; Noll, W. 1965: The Non-Linear Field Theories of Mechanics, Handbuch Der Physik, Vol III/3: 294–304
Weiner, J. H. 1983: Statistical Mechanics of Elasticity. Chap. 5. New York: John Wiley & Sons
Wood, L. A.; Martin, G. M. 1964: Compressibility of Natural Rubber at Pressures below 500 kg/cm2. Journal of Research of the National Bureau of Standards—A. Physics and Chemistry 68 A: 259–268
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. N. Atluri, 27 March 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand, L. A constitutive model for compressible elastomeric solids. Computational Mechanics 18, 339–355 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376130
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00376130