Abstract
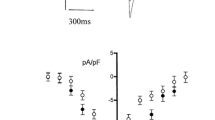
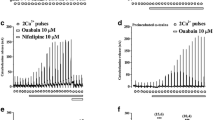
We have studied the pathways by which extra-cellular bradykinin and adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) elicit changes in intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+]i) in nerve-growth-factor(NGF)- treated rat pheochromocytoma (PC 12) cells. Both substances caused a significant rise in [Ca2+]i as assessed by fura-2 based micro-fluorimetry. The bradykinin-induced response consisted of an initial Ca2+ mobilization from an internal pool followed by a sustained increase in [Ca2+]i, which was due to activation of a small inward current. The initial response always started at a localized site opposite to the cell nucleus. The inward current was partially carried by Ca2+ and began with a time lag of about 4 s after the start of the initial transient signal. Stepwise hyperpolarization of the plasma membrane, after activation of the inward current by bradykinin, caused a simultaneous increase in current amplitude and in [Ca2+]i, due to an increase in the driving force for Ca2+ influx. With ATP as an agonist the onset of inward current coincided with an increase in [Ca2+]i. Inward current and [Ca2+]i were enhanced during hyperpolarizing steps indicating a substantial Ca2+ influx through ATP-activated channels. No release of Ca2+ from internal stores, but a large Na+ inward current, was observed in Ca2+-free external solution after addition of ATP. While the bradykinin-induced responses were much more pronounced in cell bodies than in growth cones, the ATP effects were somewhat variable in cell bodies and more homogeneous in growth cones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bean BP, Friel DD (1990) ATP-activated channels in excitable cells. In: Naharashi T (ed) Ion channels (vol 2). Plenum, New York, pp 169–203
Bean BP, Williams ChA, Ceelen PW (1990) ATP-activated channels in rat and bullfrog sensory neurons: current-voltage relation and single-channel behavior. J Neurosci 10:11–19
Buchan KW, Martin W (1991) Bradykinin induces elevations of cytosolic calcium through mobilization of intracellular and extra-cellular pools in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 102:35–40
Burgess GM, Mullaney I, McNeill M, Dunn PhM, Rang HP (1989) Second messenger involved in the mechanism of action of bradykinin in sensory neurons in culture. J Neurosci 9:3314–3325
Fasolato C, Pandiella A, Meldolesi J, Pozzan T (1988) Generation of inositol phosphates, cytosolic Ca2+ and ionic fluxes in PC12 cells treated with bradykinin. J Biol Chem 263:17350–17359
Fasolato C, Pizzo P, Pozzan T (1990) Receptor-mediated calcium influx in PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 265:20351–20355
Greene LA, Tischler AS (1976) Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:2424–2428
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3340–3450
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Lee Ch, Chen LB (1988) Dynamic behavior of endoplasmic reticulum in living cells. Cell 54:27–46
Lipscombe D, Madison DV, Poenie M, Reuter H, Tsien RW, Tsien RY (1988) Imaging of cytosolic Ca2+ transients arising from Ca2+ stores and Ca2+ channels in sympathetic neurons. Neuron 1:355–365
Nakazawa K, Fujimori K, Takanaka A, Inoue K (1990) An ATP-activated conductance in pheochromocytoma cells and its suppression by extracellular calcium. J Physiol (Lond) 428:257–272
Neuhaus R, Reber BFX, Reuter H (1991) Bradykinin-and ATP-induced membrane currents in NGF-differentiated PC 12 cells (abstract). Experientia 47:A9
Neuhaus R, Reber BFX, Reuter H (1991) Regulation of bradykinin-and ATP-activated Ca2+ permeable channels in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Neurosci 11:3984–3990
Ogura A, Myojo Y, Higashida H (1990) Bradykinin-evoked acetylcholine release via inositol-trisphosphate-dependent elevation in free calcium in neuroblastomaxglioma hybrid NG 108-15 cells. J Biol Chem 265:3577–3584
Reber BFX, Reuter H (1991) Dependence of cytosolic calcium in differentiating rat pheochromocytoma cells on calcium channels and intracellular stores. J Physiol (Lond) 435:145–162
Reber BFX, Reuter H (1991) Intracellular calcium pools in differentiating PC 12 cells (abstract). Experientia 47:A59
Schilling WP, Raijan L, Strobl-Jager E (1989) Characterization of the bradykinin-stimulated calcium influx pathway of cultured vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 264:12838–12848
Shuttleworth TJ, Thompson JL (1991) Effect of temperature on receptor-activated changes in [Ca2+]i and their determination using fluorescent probes. J Biol Chem 266:1410–1414
Thayer StA, Perney TM, Miller JR (1988) Regulation of calcium homeostasis in sensory neurons by bradykinin. J Neurosci 8:4089–4097
Weiss C, Sela D, Atlas D (1990) Divalent cations effectively replace Ca2+ and support bradykinin-induced noradrenaline release. Neurosci Lett 119:241–244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reber, B.F.X., Neuhaus, R. & Reuter, H. Activation of different pathways for calcium elevation by bradykinin and ATP in rat pheochromocytoma (PC 12) cells. Pflügers Arch. 420, 213–218 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374993
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374993