Abstract
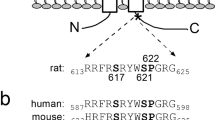
A potassium channel from rat brain was expressed in Xenopus oocytes in order to study modulation of channel function by phosphorylation via protein kinase A. Application of 8-Br-cAMP to oocytes expressing the drk1 channel (with the first 139 amino acids of the N terminus delected, ΔNdrk1) caused a voltage-independent elevation of current amplitude, which was not seen for endogenous currents or for wild-type full-length drk1 channel. This effect on ΔNdrk1 was blocked by pre-injection of oocytes with Walsh-peptide protein kinase A inhibitor, suggesting mediation via protein kinase A. The protein kinase inhibitor also reduced both ΔNdrk1 and full-length drk1 currents. Substitution of the serine residues by alanine at one or both of the two consensus protein kinase A phosphorylation sites on the C terminus (residues 440 and 492) of ΔNdrk1 resulted in a loss of function of the expressed channels. These results indicate that phosphorylation via protein kinase A modulates drk1 channel function and that both consensus phosphorylation sites seems to be essential for channels to function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong D, Eckert R (1987) Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2518–2522
Aviv H, Leder P (1972) Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 69:1408–1412
Blumenthal EM, Kaczmarek LK (1992) Modulation by cAMP of a slowly activating potassium channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Neurosci 12:290–296
Cheng H-C, Kemp BE, Pearson RB, Smith AJ, Misconi L, Van Patten SM, Walsh DA (1986) A potent synthetic peptide inhibitor of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 261:989–992
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate phenol chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Critz SD, Wible BA, Lopez HS, Brown AM (1993) Stable expression and regulation of a rat brain K+ channel. J Neurochem 60:1175–1178
Dumont JN (1972) Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). J Morphol 136:153–180
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Frech GC, VanDongen AMJ, Schuster G, Brown AM, Joho RH (1989) A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature 340:642–645
Gurdon JB (1974) The control of gene expression in animal development, Oxford University Press, Oxford
Hoger JH, Walter AE, Vance D, Yu L, Lester HA, Davidson N (1991) Modulation of cloned mouse brain potassium channel. Neuron 6:227–236
Kozak M (1989) The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol 108:229–241
Kunkel TA (1985) Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:488–492
Lopatin AN, Nicols CG (1993) 2,3-Butanedione monoxamine (BDM) inhibition of delayed rectifier DRK1 (Kv2.1) potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem 265:1011–1016
MacKinnon R (1991) Determination of the subunit stoichiometry of a voltage-activated potassium channel. Nature 350:232–235
Moran O, Dascal N, Lotan I (1991) Modulation of a Shaker potassium A-channel by protein kinase C activation. FEBS Lett 279:256–260
Pak MD, Baker K, Covarrubias M, Butler A, Ratcliffe A, Salkoff L (1991) mShal, a subfamily of A-type K+ channel cloned from mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4386–4390
Papazian DM, Schwarz TL, Tempel BL, Jan YN, Jan LY (1987) Cloning of genomic and complementary DNA from Shaker, a putative potassium channel gene from Drosophila. Science 237:749–753
Payet MD, Dupuis G (1992) Dual regulation of the n type K+ channel in Jurkat T lymphocytes by protein kinases A and C. J Biol Chem 267:18 270–18 273
Perozo E, Bezanilla F (1990) Phosphorylation affects voltage gating of the delayed rectifier K+ channel by electrostatic interactions. Neuron 5:685–689
Pongs O (1992) Molecular biology of voltage-dependent potassium channels. Phyisol Rev 72:S69-S88
Roberds SL, Tamkun MM (1991) Cloning and tissue-specific expression of five voltage-gated potassium channel cDNAs expressed in rat heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:1798–1802
Rudy B (1988) Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience 25:729–749
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, NY
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain termination inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Swanson R, Marshall J, Smith JS, Williams JB, Boyle MB, Folander K, Luneau CJ, Antanavage J, Oliva C, Buhrow SA, Bennett C, Stein RB, Kaczmarek LK (1990) Cloning and expression of cDNA and genomic clones encoding three delayed rectifier potassium channels in rat brain. Neuron 4:929–939
VanDongen AMJ, Frech GC, Drewe JA, Joho RH, Brown AM (1990) Alteration and restoration of K+ channel function by deletions at the N- and C-termini. Neuron 5:433–443
White MW, Aylwin M (1990) Niflumic and flufenamic acids are potent reversible blockers of Ca2+-activated Cl− channels in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Pharmacol 37:720–724
Yokoyama S, Imoto K, Kawamura T, Higashida H, Iwabe N, Miyata T, Numa S (1989) Potassium channels from NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Primary structure and functional expression from cDNAs. FEBS Lett 259:37–42
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, G.G., O'Neill, C.A., Sivaprasadarao, A. et al. Modulation by protein kinase A of a cloned rat brain potassium channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pflügers Arch 428, 186–193 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374857
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374857