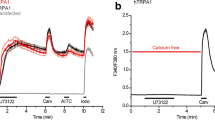
Abstract
Phospholipase C-mediated release of inositol trisposphate, followed by an increase in free intracellular calcium, is an important signal transduction pathway for several membrane receptors. In the present investigation, the coupling of various receptors to phospholipase C was studied in the human keratinocyte line HaCaT. Inositol trisphosphate formation was determined by anion-exchange chromatography, and the release of intracellular calcium was analysed with the fluorescence probe Fura-2 AM. Activation of HaCaT keratinocytes with bradykinin resulted in a time- and dose-dependent release of inositol trisphosphate and intracellular calcium, with an EC50 value of 50 nM for bradykinin-induced inositol trisphosphate formation. The mediators and cytokines IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, EGF and TGFα, as well as bombesin, prolactin, carbachol, substance P and retinoic acid, did not activate this pathway. The inability of the mediators examined to activate phospholipase C may be due to lack of the respective cognate receptors or to the use of other signal transduction pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge MJ (1983) Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyze polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J 212: 849–858
Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Marham A, Fusenig NE (1988) Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol 106: 761–771
Fisher GJ, Talwar HS, Ryder NS, Voorhees JJ (1989) Differential activation of human skin cells by platelet activating factor: stimulation of phosphoinositide turnover and arachidonic acid mobilization in keratinocytes but not in fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163: 1344–1350
Grynkiewicz G, Poenic M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260: 3340–3450
Hennings H, Cheng MD, Steinert P, Holbrook K, Yuspa SH (1980) Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell 19: 245–254
Meisenhelder J, Suh PG, Rhee SG, Hunter T (1989) Phospholipase C — gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein tyrosine kinase in vivo and in vitro. Cell 57: 1109–1122
Moscat J, Molloy CJ, Fleming TD, Aaronson SA (1988) Epidermal growth factor activates phosphoinositide turnover and protein kinase C in BALB/MK keratinocytes. Mol Endocrinol 2: 799–805
Nishizuka Y (1984) The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumor promotion. Nature 308: 693–697
Rees J (1992) The molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors: orphan of good family seeks home. Br J Dermatol 126: 97–104
Rosenbach T, Czarnetzki BM (1992) Signal transduction pathways in keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol 1: 59–66
Rosenbach T, Greenlee WF (1991) Inositol phosphate formation in the human squamous cell carcinoma line SCC-12F: Studies with bradykinin, the calcium ionophore A23187, and sodium fluoride. J Invest Dermatol 96: 116–122
Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I (1983) Release of Ca+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature 306: 67–69
Talwar HS, Fisher GJ, Harris VA, Voorhees JJ (1989) Agonist-induced hydrolysis of phosphoinositides and formation of 1,2,-diacylglycerol in adult human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 93: 241–245
Talwar HS, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ (1990) Bradykinin induces phosphoinositide turnover, 1,2-diacylglyceride formation, and growth in cultured adult human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 95: 705–710
Tang W, Ziboh VA, Isseroff R, Martinez BS (1989) Regulatory role of retinoic acid on cultured mouse keratinocyte inositol phospholipid metabolism: dose-dependent release of inositol triphosphate. J Invest Dermatol 92: 71–77
Tuschil A, Lam C, Haslberger A, Lindley I (1992) Interleukin-8 stimulates calcium transients and promotes epidermal cell proliferation. J Invest Dermatol 99: 294–298
Ullrich A, Schlessinger J (1990) Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61: 203–212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenbach, T., Liesegang, C., Binting, S. et al. Inositol phosphate formation and release of intracellular free calcium by bradykinin in HaCaT keratinocytes. Arch Dermatol Res 285, 393–396 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00372131
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00372131