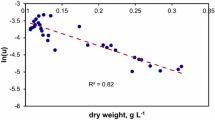
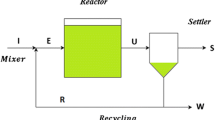
Abstract
Traditional application of computer to fermentation processes has focused on the measurement and control of parameters such as temperature, pH, vessel pressure, sparge rate, dissolved oxygen, substrate concentration, and product concentration. In a fed-batch reactor with the photosynthetic green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum which converts hydrogen sulfide to elementary sulfur or sulfate, separate measurement of cell mass concentration and sulfur particle concentration turbidimetrically was difficult due to their combined contributions to the total turbidity. Instead of on-line measurement of many process variables, a model-based control of feed rate and illuminance was designed. Optimal operation condition relating feed rate vs. light intensity was obtained to suppress the accumulation of sulfate and sulfide, and to save light energy in a 4-1 photosynthetic fed-batch reactor. This relation was correlated with the inreasing cell mass concentration. A model which describes the cell growth by considering the light attenuation effects due to scattering and absorption, and to crowding effect of the cells, was established beforehand with the results from the experiments. Based on these optimal operating conditions and the cell growth model, automatic controls of feed rate and illuminance were carried out alternatively to the traditional application of computer to fermentation with on-line measurement, realtime response and adjustment of process variables.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- F ml/min:
-
Flow rate of gas mixture
- hV lux:
-
Average illuminance
- Q mmol/(l h):
-
Removal rate of hydrogen sulfide
- X mg protein/l:
-
Cell mass concentration as protein
- X 0 mg protein/l:
-
Initial cell mass concentration
- X m mg protein/l:
-
Maximum cell mass concentration
- μ a h−1 :
-
Apparent specific growth rate
References
Sublette, K. L.; Sylvester, N. D.: Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide by Thiobacillus denitrificans: Desulfurization of natural gas. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 29 (1987) 249–257
Buisman, C. J. N.; Geraats, B. G.; Ijspeert, P.; Lettinga, G.: Optimization of sulphur production in a biotechnological sulphideremoving reactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 35 (1990) 50–56.
Cork, D. J.; Garunas, R.; Sajjad, A.: Chlorobium limicola forma thiosulfatophilum: Biocatalyst in the production of sulfur and organic carbon from a gas stream containing H2S and CO2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45 (1983) 913–918.
Kim, B. W.; Chang, H. N.: Removal of hydrogen sulfide by Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum in immobilized-cell and sulfursettling free-cell recycle reactors. Biotechnol. Progr. 7 (1991) 495–510
Kim, B. W.; Kim, I. K.; Chang, H. N.: Bioconversion of hydrogen sulfide by free and immobilized cells of Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Biotechnol. Lett. 12 (1990) 381–386
Kim, B. W.; Kim, E. H.; Chang, H. N.: Application of light emitting diodes as a light source to a photosynthetic culture of Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum. Biotechnol. Tech. 5 (1991) 343–348
Kim, B. W.; Chang, H. N.; Kim, I. K.; Lee, K. S.: Growth kinetics of the photosynthetic bacterium Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum in a fed-batch reactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. (1992, accepted)
Fuchs, G.; Stupperich, E.; Jaenchen, R.: Autotrophic CO2 fixation in Chlorobium limicola. Arch. Microbiol. 128 (1980) 56–63
Bradford, M. M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal. Chem. 72 (1976) 248–254
Greenberg, A. E.; Connors, J. J.; Jenkins, D. (Eds.): Standard method for the examination of water and wastewater. 15th edition. American Public Health Association, Washington (1981) 439–450
Truepper, H. G.; Hathaway, J. C.: Orthorhombic sulphur formed by photosynthetic sulfur bacteria. Nature 215 (1967) 435–436
Lee, H. Y.; Erickson, L. E.; Yang, S. S.: Kinetics and bioenergetics of light limited photoautotrophic growth of Spirulina platenis. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 29 (1987) 832–843
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.W., Kim, E.H., Lee, S.C. et al. Model-based control of feed rate and illuminance in a photosynthetic fed-batch reactor for H2S removal. Bioprocess Engineering 8, 263–269 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369839
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369839