Abstract
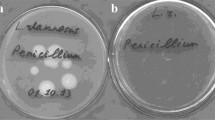
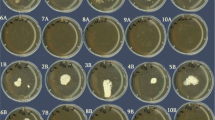
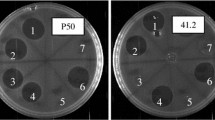
Of nine strains of lactic acid bacteria commonly used as starter cultures for the dalry industry and ensiling, six (Lactobacillus bulgaricus, L. casei, L. acidophilus CH=5, L. plantarum, Streptococcus latis and Strep. taecium) had antibiotic activity. Gram-positive bacteria were more sensitive than Gram-negative bacteria to the antibiotics. The most sensitive strain of Staphylococcus aureus was used as a target micro-organism for the characterization of the antimicrobial substance. The cultures of Streptococcus faecium and L. plantarum gave the most intense antimicrobial activity. Adding CaCO3 to the medium (to bind accumulated lactic acid) increased the antibiotic activity of the lactic acid bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, R. 1986 Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus and spheroplast of Gram-negative bacteria by an antagonistic compound produced by strain of Lactobacillus plantarum. International Journal of Food Microbiology 3, 149–160.
Barker, S.B. & Summerson, W.H. 1941 The colorimetric determination of lactic acid in biological material. Journal of Biological Chemistry 138, 535–554.
Daeschel, M.A., Andersson, R.E. & Fleming, H.P. 1987 Microbial ecology of fermenting plant materials. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 46, 357–367.
Fernandes, C.F., Shahani, K.M. & Amer, M.A. 1987 Therapeutic role of dietary lactobacilli and lactobacillic fermented dairy products. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 46, 343–356.
Gilliland, S.E. 1979 Beneficial interrelationships between certain microorganisms and humans. Candidate microorganisms for use as dietary adjuncts. Journal of Food Protection 42, 164–167.
Gurr, M.I. 1987 Nutritional aspects of fermented miik products. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 46, 337–342.
Hamdan, J. & Mikolajcik, E.M. 1974 Acidolin: an antibiotic produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Journal of Antibiotics 27, 631–636.
Klaenhammer, T.R. 1988 Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie 70, 337–349.
Additional information
The authors are with the Department of Biochemical Engineering, Faculty of Food Technology and Biotechnology, University of Zagreb, Pierottijeva 6, 41000 Zagreb, Yugoslavia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blažeka, B., Šušković, J. & Matošić, S. Antimicrobial activity of lactobacilli and streptococci. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 7, 533–536 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00368356
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00368356