Abstract
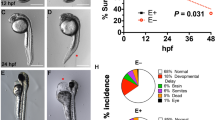
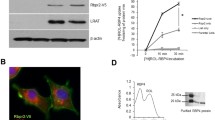
The vitamin A deficiency-associated lethal syndrome observed in avian embryos may be linked to dysfunction of vitamin A-dependent genes. We tested this hypothesis in a quail embryo model by examining the expression of retinoic acid receptors (RARs) and cytosolic retinoic acid binding protein (CRABP) in normal and vitamin A-deficient embryos during early development. RARα and RARγ mRNA were expressed at the same level in normal and vitamin A-deficient embryos during all stages studied. Expression of CRABP I was low in normal and vitamin A-deficient quail embryos during early development, but increased rapidly at later stages. Two transcripts of RARβ, 3.2 and 3.5 kb, were detected in quail embryos during developmental stages 6–12. In normal emryos the level of the 3.2-kb isoform increased as embryonic development advanced. The expression of the 3.5-kb transcript was significantly decreased in vitamin A-deficient embryos, while the 3.2-kb transcript was undetectable by northern analysis. In situ hybridization of stage 7–8 normal quail embryos using a chicken RARβ2 riboprobe revealed that RARβ2 expression was predominantly associated with the cell populations in heart-forming regions, somites, neural folds, notochord and the presumptive thyroid. In stark contrast, in the vitamin A-deficient quail embryo RARβ2 was not expressed in any of the above cell populations. We conclude that the expressions of RARβ and CRABP I are developmentally regulated. Additionally, the expression of RARβ2 during early embryogenesis is regulated by vitamin A status. We propose that RARβ2 plays an important role in the mechanism of action of retinoids in early avian development. The lack of expression of RARβ2 may be linked to abnormalities of the cardiovascular system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambon P (1994) The retinoid signaling pathway: molecular and genetic analyses. Semin Cell Biol 5:115–125
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Cullum ME, Zile MH (1985) Metabolism of all-trans-retinoic acid and all-trans-retinyl acetate. Demonstration of common physiological metabolites in rat small intestinal mucosa and circulation. J Biol Chem 260:10590–10596
Dersch H, Zile MH (1993) Induction of normal cardiovascular development in the vitamin A-deprived quail embryo by natural retinoids. Dev Biol 160:424–433
DeThé H, Marchio A, Tiollais P, Dejean A (1989) Differential expression and ligand regulation of the retinoic acid receptor α and β genes. EMBO J 8:429–433
DeThé H, Vivanco-Ruiz MDM, Tiollais P, Stunnenberg H, Dejean A (1990) Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor β gene. Nature 343:177–180
Eichele G (1993) Retinoids in embryonic development. Ann NY Acad Sci 678:22–36
Gorry P, Lufkin T, Dierich A, Rochette-Egly C, Decimo D, Dolle P, Mark M, Durand B, Chambon P (1994) The cellular retinoic acid binding protein I is dispensable. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9032–9036
Gudas LJ (1994) Retinoids and vertebrate development. J Biol Chem 269:15399–15402
Hale F (1937) Relation of maternal vitamin A deficiency to microphthalmia in pigs. Texas State J Med 33:228–232
Hamburger V, Hamilton HL (1951) A series of normal stages in the development of the chick embryo. J Morphol 88:49–92
Heine UI, Roberts AB, Munoz EF, Roche NS, Sporn MB (1985) Effects of retinoid deficiency on the development of the heart and vascular system of the quail embryo. Virchows Arch [Cell Pathol] 50:135–152
Hoffmann B, Lehmann JM, Zhang X-K, Hermann T, Husmann M, Graupner G, Pfahl M (1990) A retinoic acid receptor-specific element controls the retinoic acid receptor-β promoter. Mol Endocrinol 4:1727–1736
Hofmann C, Eichele G (1994) Retinoids in development. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS (eds) The retinoids, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 387–441
Jiang H, Gyda M III, Harnish DC, Chandraratna RA, Soprano KJ, Kochhar DM, Soprano DR (1994) Teratogenesis by retinoic acid analogs positively correlates with elevation of retinoic acid receptor-β2 mRNA levels in treated embryos. Teratology 50:38–43
Kastner P, Grondona JM, Mark M, Gansmuller A, LeMeur M, Decimo D, Vonesch J-L, Dolle P, Chambon P (1994) Genetic analysis of RXRα developmental function: convergence of RXR and RAR signaling pathways in heart and eye morphogenesis. Cell 78:987–1003
Kato S, Mano H, Kumazawa T, Yoshizawa Y, Kojima R, Masushige S (1992) Effect of retinoid status on α, β, and γ retinoic acid receptor mRNA levels in various rat tissues. Biochem J 286:755–760
Li E, Sucov HM, Lee K-F, Evans RM, Jaenisch R (1993) Normal development and growth of mice carrying a targeted disruption of the α1 retinoic acid receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1590–1594
Linney E, LaMantia A-S (1994) Retinoid signalling in mouse embryos. In: Wassermann P (ed) Advances in developmental biology, vol 3. JAI Press, Greenwich, Conn, pp 73–114
Lohnes D, Mark M, Mendelsohn C, Dolle P, Dierich A, Gorry P, Gansmuller A, Chambon P (1994) Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development. 1. Craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities in RAR double mutants. Development 120:2723–2748
Lufkin T, Lohnes D, Mark M, Dierich A, Gorry P, Gaub M-P, LeMeur M, Chambon P (1993) High postnatal lethality and testis degeneration in retinoic acid receptor a mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:7225–7229
Maden M (1994) Vitamin A in embryonic development. Nutr Rev 52:LS3-S12
Maden M, Hunt P, Eriksson U, Kuroiwa A, Krumlauf R, Summerbell D (1991) Retinoic acid-binding protein, rhombomeres and the neural crest. Development 111:35–44
Mangelsdorf DJ, Umesono K, Evans RM (1994) The retinoid receptors. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS (eds) The retinoids, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 319–350
Mason KE (1935) Foetal death, prolonged gestation, and difficult parturition in the rat as a result of vitamin A deficiency. Am J Anat 57:303–349
Mendelsohn C, Mark M, Dolle P, Dierich A, Gaub MP, Krust A, Lampron C, Chambon P (1994a) Retinoic acid receptor β2 (RARβ2) null mutant mice appear normal. Dev Biol 166: 246–258
Mendelsohn C, Lohnes D, Decimo D, Lufkin T, LeMeur M, Chambon P, Mark M (1994b) Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development. II. Multiple abnormalities at various stages of organogenesis in RAR double mutants. Development 120:2749–2771
Michaille J-J, Blanchet S, Kanzler B, Garnier J-M, Dhouailly D (1994) Characterization of cDNAs encoding the chick retinoic acid receptor γ2 and preferential distribution of retinoic acid receptor γ transcripts during chick skin development. Dev Dyn 201:334–343
Moore T (1957) Vitamin A. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Nohno T, Muto K, Noji S, Saito T, Taniguchi S (1991) Isoforms of retinoic acid receptor β expressed in the chicken embryo. Biochim Biophys Acta 1089:273–275
Ong DE, Newcomer ME, Chytil F (1994) Cellular retinoid-binding proteins. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS (eds) The retinoids, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 283–317
Osmond MK, Butler AJ, Voon FCT, Bellairs R (1991) The effects of retinoic acid on heart formation in the early chick embryo. Development 113:1405–1417
Pelt AMM van, Brink CE van den, Rooij DG de, Saag PT van der (1992) Changes in retinoic acid receptor messenger ribonucleic acid levels in the vitamin A-deficient rat testis after administration of retinoids. Endocrinology 131:344–350
Petkovich M (1992) Regulation of gene expression by vitamin A: the role of nuclear retinoic acid receptors. Annu Rev Nutr 12: 443–471
Riddle RD, Johnson RL, Laufer E, Tabin C (1993) Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Sonic Cell 75: 1401–1416
Ross CA (1993) Cellular metabolism and activation of retinoids: roles of cellular retinoid-binding proteins. FASEB 17:317–327
Rowe A, Brickell PM (1993) Current status review: the nuclear retinoid receptors. Int J Exp Pathol 74:117–126
Rowe A, Richman JM, Brickell PM (1991) Retinoic acid treatment alters the distribution of retinoic acid receptor-β transcripts in the embryonic chick face. Development 111: 1007–1016
Rowe A, Eager NSC, Richman JM, Brickell PM (1992) Retinoic acid receptors in the chick embryo. In: Morriss-Kay G (ed) Retinoids in normal development and teratogenesis. Oxford Science, Oxford, pp 85–98
Smith SM (1994) Retinoic acid receptor isoform β2 is an early marker for alimentary tract and central nervous system positional specification in the chicken. Dev Dyn 200:14–25
Smith SM, Eichele G (1991) Temporal and regional differences in the expression pattern of distinct retinoic acid receptor-β transcripts in the chick embryo. Development 111:245–252
Sucov HM, Dyson E, Gumeringer CL, Price J, Chien KR, Evans RM (1994) RXRα mutant mice establish a genetic basis for vitamin A signaling in heart morphogenesis. Genes Dev 8: 1007–1018
Sundin O, Eichele G (1992) An early marker of axial pattern in the chick embryo and its respecification by retinoic acid. Development 114:841–852
Thompson JN (1969) The role of vitamin A in reproduction. In: DeLuca HF, Suttie JW (eds) The fat soluble vitamins. University Wisconsin Press, Madison, pp 267–281
Twal W, Roze L, Zile MH (1995) Anti-retinoic acid antibody localizes all-trans-retinoic acid in target cells and blocks normal development in early quail embryo. Dev Biol 168:2225–2234
Ul-Haq R, Pfahl M, Chytil F (1991) Retinoic acid affects the expression of nuclear retinoic acid receptors in tissues of retinol-deficient rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:8272–8276
Underwood BA (1984) Vitamin A in animal and human nutrition. In: Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Goodman DS (eds) The retinoids, 1st edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 281–392
Verma AK, Shoemaker A, Simsiman R, Denning M, Zachman RD (1992) Expression of retinoic acid nuclear receptors and tissue transglutaminase is altered in various tissues of rats fed a vitamin A-deficient diet. J Nutr 22:2144–2152
Wilson JG, Roth CB, Warkany J (1953) An analysis of the syndrome of malformations induced by maternal vitamin A deficiency. Effects of restoration of vitamin A at various times during gestation. Am J Anat 92:189–217
Wolf G (1984) Multiple functions of vitamin A. Physiol Rev 64: 873–938
Zelent A, Mendelsohn C, Kastner P, Krust A, Garnier J-M, Ruffenach F, Leroy P, Chambon P (1991) Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor β are generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J 10:71–81
Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Reynolds K (1994) Tissue specific expression of the retinoic acid receptor-β2: regulation by short open reading frames in the 5′-noncoding region. J Cell Biol 127:1111–1119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostetskii, I., Linask, K.K. & Zile, M.H. Vitamin A deficiency and the expression of retinoic acid receptors during early cardiogenesis in quail embryo. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 205, 260–271 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00365804
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00365804