Abstract
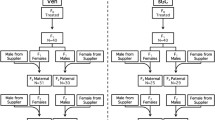
Different strains of H-2 congenic mice have different susceptibilities to corticosteroid-induced fetal loss and cleft palate. Applying this knowledge, we tested the null hypothesis, which assumes that there are no statistically significant differences in the frequency of abnormality among various types of treated backcross offspring and, thus, no evidence of a cytoplasmic effect. In the present study this null hypothesis was frequently, but not consistently, rejected. Therefore, there was some evidence of a cytoplasmic effect. One possible explanation of these results is seen when one considers the phenotypic effects of “gene-gene interaction” between variant H-2 genotypes and an invariant mitochondrial genotype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biddle, F. G. and Fraser, F. C.: Maternal and cytoplasmic effects in experimental teratology. In J. G. Wilson and F. C. Fraser (eds.): Handbook of Teratology, Volume 3, pp. 3–33, Plenum Press, New York, 1977
Bonner, J. J. and Slavkin, H. C.: Cleft palate susceptibility linked to histocompatibility-2 (H-2) in the mouse. Immunogenetics 2: 213–218, 1975
Cochran, W. G.: Testing a linear relationship among variances. Biometics 7: 17–32, 1951
Dagg, C. P., Schlager, G., and Doerr, A.: Polygenic control of the teratogenicity of 5-fluorouracil in mice. Genetics 53: 1101–1117, 1966
Ferris, S. D., Sage, R. D., and Wilson, A. C.: Evidence for mtDNA sequences that common laboratory strains of inbred mice are descended from a single female. Nature 295: 163–165, 1982
Gasser, D. L., Mele, L., Lees, D. D., and Goldman, A. S.: Genes in mice that affect susceptibility to cortisone-induced cleft palate are closely linked to Ir genes on chromosomes 2 and 17. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78: 3147–3150, 1981
Gaylor, D. W.: Methods and concepts of biometrics applied to teratology. In J. G. Wilson and F. C. Fraser (eds.): Handbook of Teratology, Volume 4, pp. 429–444, Plenum Press, New York, 1978
Goldman, A. S., Katsumata, M., Yaffe, S. J., and Gasser, D. L.: Palatal cytosol corticoid receptors and teratogens for cleft palate. Nature 265: 634–645, 1977
Melnick, M., Jaskoll, T., and Slavkin, H. C.: Corticosteroid-induced cleft palate in mice and H-2 haplotype: Maternal and embryonic effects. Immunogenetics 13: 443–450, 1981
Satterthwaite, F. W.: An approximate distribution of estimates of variance components. Biometrics Bull. 2: 110–114, 1946
Spudich, J. L. and Koshland, D. E.: Nongenetic individuality: Chance in the single cell. Nature 262: 467–471, 1976
Theiler, K.: The House Mouse, Springer Verlag, Berlin, 1972
Tyan, M. L. and Miller, K. K.: Genetic and environmental factors in cortisone-induced cleft palate. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 158: 618–621, 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melnick, M., Marazita, M. & Jaskoll, T. Corticosteroid-induced abnormality in fetal mice and H-2 haplotype: Evidence of a cytoplasmic effect. Immunogenetics 17, 141–146 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00364754
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00364754