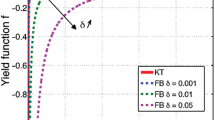
Abstract
In this paper we review our latest developments in the field of finite strain elastoplastic analysis using the method of mixed interpolation of tensorial components (MITC). In particular we review our 2D element, the QMITC-TLH, and our shell element, the MITC4-TLH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AhmadS.; IronsB. M.; ZienkiewiczO. C. 1970: Analysis of thick and thin shell structures by curved finite elements. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg., 2, 419–451
AnandL. 1979: On Hencky's approximate strain-energy function for moderate deformations. J. Appl. Mech., 46, 78–82
ArgyrisJ. H.; DoltsinisJ. St. 1979: On the large strain inelastic analysis in natural formulation. Part I. Quasistatic problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 20, 213–251
ArgyrisJ. H.; DoltsinisJ. St. 1980: On the large strain inelastic analysis in natural formulation. Part II. Dynamic problems. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 21, 91–126
AtluriS. N. 1984: Alternate stress and conjugate strain measures, and mixed variational formulations involving rigid rotations for computational analysis of finitely deformed solids, with applications to plates and shells. Part I. Comput. & Struct., 18, 93–116
AlturiS. N. 1985: An endochronic approach and other topics in small and finite deformation computational elasto-plasticity. In: Bergan et al (Eds.), Finite Element Methods for Nonlinear Problems, 143–162, Springer, Berlin
BatheK. J. 1982: Finite Element Procedures in Engineering Analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
BatheK. J.; DvorkinE. N. 1985: A four-node plate bending element based on Mindlin/Reissner plate theory and a mixed interpolation. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg., 21, 367–383
BatheK. J.; DvorkinE. N. 1986: A formulation of general shell elements — the use of mixed interpolation of tensorial components. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg., 22, 697–722
CrisfieldM. A. 1995: Incompatible modes, enhanced strain and substitute strains for continuum elements. In: N.-E.Wiberg (Ed.), Advances in Finite Element Technology, 47–61, CIMNE, Barcelona
DvorkinE. N. 1995: Nonlinear analysis of shells using the MITC formulation. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2, 1–50
DvorkinE. N.; AssanelliA. P. 1990: Elasto-plastic analysis using a quadrilateral 2D element based on mixed interpolation of tensorial components. In: OwenD. R. J. et al (Eds.), Proc. Second International Conference on Computational Plasticity, 263–283, Pineridge Press, Swansea
DvorkinE. N.; AssanelliA. P.; ToscanoR. G. 1996: Performance of the QMITC element in 2D elasto-plastic analysis, Comput. & Struct., 58, 1099–1129
DvorkinE. N.; BatheK. J. 1984: A continuum mechanics based four node shell element for general nonlinear analysis. Engrg. Comput., 1, 77–88
DvorkinE. N.; GoldschmitM. B.; PantusoD.; RepettoE. A. 1994: Comentarios sobre algunas herramientas utilizadas en la resolución de problemas no-lineales de mecánica del continuo. Rev. Int. de Met. Numéricos para Cálc. y Diseño en Ingeniería, 10, 47–65
DvorkinE. N.; PantusoD.; RepettoE. A. 1994: A finite element formulation for finite strain elasto-plastic analysis based on mixed interpolation of tensorial components. Comp. Meth. Appl. Mech. and Engrg., 114, 35–54
DvorkinE. N.; PantusoD.; RepettoE. A. 1995: A formulation of the MITC4 shell element for finite strain elasto-plastic analysis. Comput. Mech. Engrg., 125, 17–40
DvorkinE. N.; VassoloS. I. 1989: A quadrilateral 2D finite element based on mixed interpolation of tensorial components. Eng. Comput., 6, 217–224
EterovicA. L.; BatheK. J. 1990: A hyperelastic based large strain elasto-plastic constitutive formulation with combined isotropic/kinematic hardening using the logarithmic stress and strain measures. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg., 30, 1099–1114
HillR. 1978: Aspects of invariance in solid mechanics. Advances in Appl. Mechs., 18, 1–75
ImS.; AtluriS. N. 1987: A study of two finite strain plasticity models: an internal time theory using Mandel's director concept, and a general isotropic/kinematic-hardening theory. Int. J. of Plasticity, 3, 163–191
LeeE. H. 1969: Elastic plastic deformation at finite strain. J. Appl. Mech., 36, 1–6
LeeE. H.; LiuD. T. 1967: Finite strain elastic-plastic theory with application to plane-wave analysis. J. Appl. Phys., 38, 17–27
Mac NealR. H. 1987: A theorem regarding the locking of four-noded membrane elements. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg., 24, 1793–1799
MalvernL. E. 1969: Introduction to the Mechanics of a Continuous Medium, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
MarsdenJ. E.; HughesT. J. R. 1983: Mathematical Foundations of Elasticity, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
OrtizM.; SimoJ. C. 1986: An analysis of a new class of integration algorithms for elastoplastic constitutive relations. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg., 23, 353–366
SimoJ. C. 1988a: A Framework for finite strain elasto-plasticity based on maximun plastic dissipation and the multiplicative decomposition. Part I: Continuum formulation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 66, 199–219
SimoJ. C. 1988b: A Framework for finite strain elastoplasticity based on maximum plastic dissipation and the multiplicative decomposition. Part II: Computational aspects. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 68, 1–31
SimoJ. C.; MarsdenJ. E. 1984: On the rotated stress tensor and the material version of the Doyle Ericksen formula. Arch. Rat. Mechs. Anal., 86, 213–231
SimoJ. C.; OrtizM. 1985: A unified approach to finite deformation elastoplastic analysis based on the use of hyperelastic constitutive equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 49, 221–245
SimoJ. C.; TaylorR. L. 1985: Consistent tangent operators for rate-independent plasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg., 48, 101–118
SimoJ. C.; TaylorR. L. 1986: A return mapping algorithm for plane stress elasto-plasticity. Int. J. Num. Meth. Engrg., 22, 649–670
SussmanT.; BatheK. J. 1987: A finite element formulation for nonlinear incompressible elastic and inelastic analysis, Comput. & Struct., 26, 829–855
TruesdellC.; NollW. 1965: The nonlinear field theories of mechanics. In: Encyclopedia of Physics, Springer, Berlin
ZienkiewiczO. C.; and TaylorR. L. 1989: The Finite Element Method, 4th Edn., vol. 1, McGraw-Hill, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. N. Atluri, 26 March 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dvorkin, E.N. Finite strain elasto-plastic formulations using the method of mixed interpolation of tensorial components. Computational Mechanics 18, 290–301 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00364144
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00364144